Florida Inventors Hall of Fame celebrates 2024 inductees: Ushering in a new era of innovation
2024-05-30
TAMPA, Fla (May 30, 2024) – The Florida Inventors Hall of Fame has announced its 2024 inductees: nine visionaries whose groundbreaking inventions have propelled technological advancement and reshaped the landscape of American innovation. These inventors exemplify Florida’s rich tradition of ingenuity.
Paul R. Sanberg, chair of the Florida Inventors Hall of Fame Advisory Board and president of the National Academy of Inventors, said of the new inductees: "The Class of 2024 represents the best of innovation in Florida, and their achievements underscore the critical role that innovation plays in driving progress and improving the quality of ...
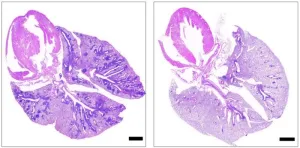
Inducing piezoelectricity in distorted rutile TiO2 for enhanced tetracycline hydrochloride degradation through photopiezocatalysis
2024-05-30
A team of material scientists led by Prof. Qi Li from Southwest Jiaotong University in Chengdu, China recently outlined the state of inducing piezoelectricity in distorted rutile TiO2 for enhanced tetracycline hydrochloride degradation through photopiezocatalysis. Various material design strategies have been developed to enhance photocatalytic performance of TiO2. However, no report is available on applications of the photopiezocatalysis strategy on TiO2 due to its lack of piezoelectricity. Here we developed a low-temperature molten salt etching process to create rutile TiO2 nanoparticles by etching [MgO6] ...
Physical and chemical properties of boiled oil: A traditional method of extracting oil from boiled olive fruits
2024-05-30
In certain towns in Northern Jordan, ranchers bubble some portion of their olive natural product gathered before oil extraction to expand the amount of oil, . They perceive it as a way to get a beneficial mixed bag, as they guarantee, and to get extra medical advantages. Local peoples call this oil Bubbled oil (BO), and its cost is around 20% higher than virgin olive oil (VOO) created by a similar rancher.
The speculation was thatpractice revolves around the belief that bubbling olive natural products might influence the nature of the created oil. Hence, ourResearchers from the Department of Nutrition and Food Technology, ...
Existing drug shows promise as treatment for rare genetic disorder
2024-05-30
WHAT:
A drug approved to treat certain autoimmune diseases and cancers successfully alleviated symptoms of a rare genetic syndrome called autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 (APS-1). Researchers identified the treatment based on their discovery that the syndrome is linked to elevated levels of interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), a protein involved in immune system responses, providing new insights into the role of IFN-gamma in autoimmunity. The study, led by researchers at the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute ...
Study examines prescribing patterns of drug associated with cognitive impairment
2024-05-30
INDIANAPOLIS -- Many adults with diabetes and the associated complication of peripheral neuropathy, which can be painful as well as harmful, are often prescribed drugs at doses and for durations that could impose an increased risk of cognitive impairment.
A new study, led by Regenstrief Institute and Purdue University College of Pharmacy Research Scientist Noll Campbell, PharmD, M.S., is one of the first explorations of prescribing patterns of tricyclic antidepressants for treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy at healthcare facilities predominantly serving diverse populations of low socioeconomic status.
With a study population of adults 18 years and older that ...
Cheap, dirty leftovers can produce pure oxygen
2024-05-30
New materials for producing oxygen may challenge traditional production methods. This is exciting news, because pure oxygen is in demand from many areas in industry and medicine.
“We have identified materials that can store and release pure oxygen much faster and at much lower temperatures than known materials currently used for this purpose,” says Professor Sverre Magnus Selbach at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU’s) Department of Materials Science and Engineering.
Oxygen is an element, so it ...
Violence, aggression against educators grew post-pandemic
2024-05-30
While threats and violence against pre-K to 12th-grade teachers and other school personnel in the United States declined during the pandemic, after the restrictions were lifted, incidents rebounded to levels equal to or exceeding those prior to the pandemic, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
As a result, the percentage of teachers expressing intentions to resign or transfer rose from 49% during the pandemic to 57% afterward, the researchers found.
“Aggression and violence against educators and school personnel are major concerns that affect the well-being of school personnel and the ...
Social media use and sleep duration connected to brain activity in teens
2024-05-30
DARIEN, IL – A new study to be presented at the SLEEP 2024 annual meeting found a distinct relationship between sleep duration, social media usage, and brain activation across brain regions that are key for executive control and reward processing.
Results show a correlation between shorter sleep duration and greater social media usage in teens. The analysis points to involvement of areas within the frontolimbic brain regions, such as the inferior and middle frontal gyri, in these relationships. ...
Study finds that better sleep is associated with lower loneliness
2024-05-30
DARIEN, IL – A new study to be presented at the SLEEP 2024 annual meeting found that better sleep health was associated with lower levels of loneliness, and this association was stronger among younger adults.
Results indicate that better sleep health was associated with significantly lower total loneliness, emotional loneliness and social loneliness. While better sleep health was associated with lower total and emotional loneliness across ages, this association was stronger for younger adults. However, age did not moderate the association ...
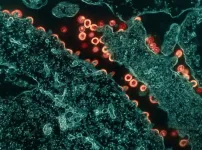
Novel vaccine concept generates immune responses that could produce multiple types of HIV broadly neutralizing antibodies
2024-05-30
WHAT:
Using a combination of cutting-edge immunologic technologies, researchers have successfully stimulated animals’ immune systems to induce rare precursor B cells of a class of HIV broadly neutralizing antibodies (bNAbs). The findings, published today in Nature Immunology, are an encouraging, incremental step in developing a preventive HIV vaccine.
HIV is genetically diverse making the virus difficult to target with a vaccine, but bNAbs may overcome that hurdle because they bind to parts of the virus that remain constant even when it mutates. ...
Study links sleep apnea treatment and happier, healthier relationships
2024-05-30
DARIEN, IL – A new study to be presented at the SLEEP 2024 annual meeting demonstrates that when individuals with obstructive sleep apnea use their positive airway pressure machine more regularly, it benefits their relationship with their partner.
Results show that greater adherence to PAP therapy was associated with higher levels of relationship satisfaction and lower levels of relationship conflict. Higher sleep efficiency among patients also was associated with higher levels of relationship satisfaction as reported by both the patient and their partner.
“Recognizing that sleep ...
Too much or too little: The impact of protein dosage on development
2024-05-30
New research from the University of Lausanne reveals that both the excess and the deficiency of a single protein can lead to severe intellectual deficiencies. The discovery offers critical insights for early diagnosis of a rare developmental disorder.
A team of scientists led by Alexandre Reymond, an expert in human genetics at the Center for Integrative Genomics (CIG) and professor at the Faculty of Biology and Medicine (FBM) of the University of Lausanne (UNIL), presents a major step forward in the detection of a rare genetic disease. For ...
Dana-Farber researchers uncover disparities in lived experiences for patients and physicians
2024-05-30
Boston – Four teams of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute investigators have found that people experience discrimination and bias in different ways and in more realms of cancer care than previously understood. The findings, in different studies, suggest that oncology professionals and the systems they work in have more work to do to adapt to the realities of increasing diversity and inclusion, not only in the patient population but also in the oncology workforce. The research teams will present their findings at the 2024 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) in Chicago. ASCO is the world’s largest clinical cancer ...
Mayo scientists developing at-home swab tests for endometrial, ovarian cancer
2024-05-30
ROCHESTER, Minnesota — Early detection improves treatment outcomes for endometrial and ovarian cancers, yet far too often women are diagnosed in advanced stages of these diseases. Unlike many other cancers, there are no standard screenings for early detection of endometrial and ovarian cancers. The incidence rate for endometrial cancer is expected to rise, driven by environmental factors, obesity and diabetes.
Marina Walther-Antonio, Ph.D., and colleagues at Mayo Clinic's Center for Individualized Medicine are on a mission to catch these cancers early.
Their research dives deep into the microbiome, a community of ...
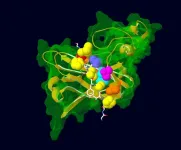
UAB researchers uncover protein SRSF1’s uncommon ability to bind and unfold RNA G-quadruplexes
2024-05-30
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – RNA transcription is the genomic process in which a cell produces a duplicate of a gene’s DNA sequence.
In a study published in Nucleic Acids Research, University of Alabama at Birmingham Department of Chemistry Professor Jun Zhang, Ph.D., and his team reveal how the protein SRSF1 possesses the novel function of binding and unfolding complex RNA Guanine-quadruplexes.
Present in both DNA and RNA sequences, a G-quadruplex (GQ) is a structure of four guanine bases attached in a planar array. ...
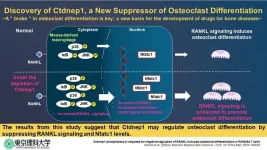
New study reveals key protein that could help prevent excessive bone loss in osteoporosis
2024-05-30
Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by porous and fragile bones, poses a significant threat to skeletal health. As the very framework of the human body, bones provide crucial structural support. When bone mass diminishes, it not only compromises this support but also impairs overall function, leading to a diminished quality of life. With the aging population experiencing a surge in osteoporosis cases, the strain on healthcare resources for long-term care is evident. Hence, there is a need to understand the mechanisms that contribute to osteoporosis and develop effective targeted therapies ...
Testosterone therapy: A safe and effective gender-affirming hormone therapy for trans men
2024-05-30
Transgender individuals often face unique challenges in aligning their physical bodies with their true gender identity. Among the various methods employed, gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT) stands as a vital means for transgender men to achieve physical changes in consonance with their gender identity. Navigating the complexities that come with gender transition, transgender individuals seek medical interventions to alleviate gender dysphoria and align their bodies with their gender identity.
For transgender men, testosterone therapy holds promise in inducing masculinizing effects such as increased muscle mass, cessation of ...
Statisticians call for rigour and transparency in the evaluation of diagnostic tests
2024-05-30
Recommendations designed to reframe the evaluation of in vitro diagnostic tests have been published today by the Royal Statistical Society in its Series A journal.
The report, which will be submitted to the UK Covid-19 Inquiry, is intended to help prevent future scenarios in which IVDs are marketed widely, but later attract serious concerns about the standards applied to their evaluation.
The research was prompted by concerns about the standards applied to the evaluation of diagnostic tests during the Covid-19 pandemic – particularly lateral flow tests – however the recommendations cover all new tests, especially those ...
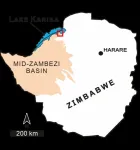
Musankwa sanyatiensis, a new dinosaur from Zimbabwe
2024-05-30
Fossils found on the shoreline of Lake Kariba in Zimbabwe represent a completely new dinosaur species. This remarkable find, named Musankwa sanyatiensis, marks only the fourth dinosaur species named from Zimbabwe. The research detailing this significant discovery is set to be published in the prestigious journal Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. The study was conducted by an international team of scientists from the University of the Witwatersrand (Wits) in South Africa, the Natural History Museum of Zimbabwe, Stony Brook University in New York and was led by Prof Paul Barrett from the Natural History Museum ...
Statin therapy may prevent cancer by blocking inflammatory protein
2024-05-30
BOSTON – A new study led by investigators from Mass General Cancer Center, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, reveals that statins—commonly used cholesterol-lowering drugs—may block a particular pathway involved in the development of cancer that results from chronic inflammation. The findings are published in Nature Communications.
“Chronic inflammation is a major cause of cancer worldwide,” said senior author Shawn Demehri, MD, PhD, a principal investigator at the Center for Cancer Immunology and Cutaneous Biology Research Center of Massachusetts General Hospital and an associate professor of Dermatology at ...
A novel ‘senolytic’ strategy for treating aging-related diseases
2024-05-30
The process of aging is accompanied by a decline in physiological functions, which can lead to cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, and metabolic diseases. Aging of cells, also known as ‘cellular senescence’— is a process in which a cell ages and permanently stops dividing but does not die. The accumulation of such ‘senescent’ cells in tissues is then known to contribute to age-associated diseases. Elimination of senescent cells or ‘senolysis’ can, therefore, serve as an effective therapeutic strategy for the improvement of physiological function and prevention ...
Risk of death from COVID-19 lessens, but infection still can cause issues 3 years later
2024-05-30
New findings on long COVID — long-term effects on health experienced by many who have had COVID-19 — present a good-news, bad-news situation, according to a study at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and the Veterans Affairs St. Louis Health Care system.
The bad news: COVID-19 patients who were hospitalized within the first 30 days after infection face a 29% higher risk of death in the third year compared with people who have not had the virus. However, the three-year death risk still marks a significant decline compared with such risk at the one- and two-year marks post-infection. The findings also show that even people with mild COVID-19 were still ...
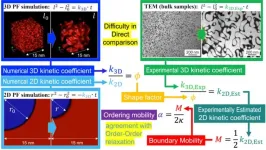
Combining simulations and experiments to get the best out of Fe3Al
2024-05-30
Osaka, Japan – The compound of iron and aluminum with the chemical formula Fe3Al has some very useful mechanical properties. A team from Osaka University has combined simulations with experimental techniques to better understand the kinetics of the formation of microstructures to enhance and utilize these properties and how to harness them for specific applications.
In a study recently published in Acta Materialia, the researchers took an in-depth look at the way the microstructure of Fe3Al develops because the ordered domains that form contribute to one of its key properties: superelasticity.
When high loads are applied to superelastic materials they ...
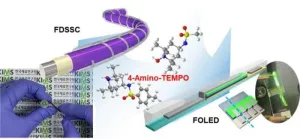
Both high performance and stability were achieved with multifunctional materials!
2024-05-30
Through joint research with Professor Chul-jin Ahn’s team at Changwon National University, the research team of Dr. Jae-Ho Kim and Dr. Myung-kwan Song from the Department of Energy & Electronic Materials in the Surface & Nano Materials Division has developed a 4-Amino-TEMPO derivative with photocatalytic properties and successfully used it to produce high-performance and stable fiber-shaped dye-sensitized solar cells (FDSSCs) and fiber-shaped organic light-emitting diodes (FOLEDs). The developed 4-Amino-TEMPO derivative has the characteristic of simultaneously improving the performance of both fiber-shaped dye-sensitized solar cells (FDSSCs) and fiber-shaped ...
Structural inequities amplify homelessness challenges for pregnant people in Washington DC
2024-05-30
WASHINGTON -- New research conducted with Washington, DC, residents who experienced homelessness during pregnancy sheds light on the intersection of homelessness, pregnancy, and racial inequities. The findings underscore the urgent need for policy and practice changes to support vulnerable populations.
The study, published May 30, 2024 in the journal Health Equity (DOI: 10.1089/heq.2023.0235), is grounded in a reproductive justice framework and delves into the lived experiences of 20 DC residents who faced homelessness while pregnant.
Homelessness ...
[1] ... [1144]
[1145]
[1146]
[1147]
[1148]
[1149]
[1150]
[1151]
1152
[1153]
[1154]
[1155]
[1156]
[1157]
[1158]
[1159]
[1160]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.