Doctors received approximately $12.1 billion from drug and device makers between 2013-2022
2024-03-28
HERSHEY, Pa. — Despite evidence that financial conflicts of interest may influence medical practice and research and may erode patient trust in medical professionals, these relationships remain pervasive. According to a new analysis of the Open Payments platform, a database that tracks payments between physicians and industry, a team led by a Penn State researcher found that doctors received approximately $12.1 billion from drug and device makers between 2013 and 2022.
Their findings published today (March 28) in JAMA. It’s one of the first studies to look at industry payments longitudinally and by specialty.
“Overall, ...
Discovery suggests new strategy against follicular lymphoma
2024-03-28
A team led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine has identified important drivers of the transformation of a type of blood cancer called follicular lymphoma from a slow-growing form to the aggressive form it takes in some patients.
The study, published March 7 in Cancer Cell, showed that while mutations affecting a gene-regulating complex called BAF can put the cancer on a dangerous trajectory, they also make follicular lymphoma highly susceptible to experimental BAF-inhibitor drugs.
“These encouraging findings could address critical and urgent challenges with this disease and have prompted us to begin planning clinical trials ...
Making the future too bright: how wishful thinking can point us in the wrong direction
2024-03-28
Everyone indulges in wishful thinking now and again. But when is that most likely to happen and when could it actually be harmful? A new study, led by the University of Amsterdam (UvA), demonstrates unequivocally that the greater the insecurity and anxiety of a situation, the more likely people are to become overly optimistic – even to the point where it can prevent us from taking essential action. The study's results have now been published in the journal American Economic Review.
‘People aren't purely truth-seekers - many beliefs are influenced by ...
Ochsner Health named to Newsweek’s America’s Greatest Workplaces 2024 for Job Starters
2024-03-28
NEW ORLEANS, La – Newsweek and Plant-A Insights Group have named Ochsner Health one of America's Greatest Workplaces for Job Starters in 2024. In a survey that included more than 75,000 young professionals and more than 540,000 company reviews, Ochsner earned 5 out of 5 stars. As the leading not-for-profit healthcare provider in the Gulf South, Ochsner is committed to championing career development among new professionals.
"We at Ochsner are honored to receive recognition as a place of employment that offers ...
Three-year study of young stars with NASA’s Hubble enters new chapter
2024-03-28
In the largest and one of the most ambitious Hubble Space Telescope programs ever executed, a team of scientists and engineers collected information on almost 500 stars over a three-year period. This effort offers new insights into the stars' formation, evolution, and impact on their surroundings.
This comprehensive survey, called ULLYSES (Ultraviolet Legacy Library of Young Stars as Essential Standards), was completed in December 2023, and provides a rich spectroscopic dataset obtained in ultraviolet light that astronomers will be mining for decades to come. Because ultraviolet light can ...
North Carolina takes the lead in PFAs research with Collaboratory’s $3 million investment to expand the state’s research capacity
2024-03-28
WILMINGTON, N.C. (March 27, 2024) – The North Carolina Collaboratory – an organization dedicated to advancing scientific research for policymaking within North Carolina – today announced its partnership with Thermo Fisher Scientific to advance the State’s per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) research capabilities. Supported by critical appropriations from the North Carolina General Assembly (NCGA), the Collaboratory purchased five state-of-the-art mass spectrometers that continue to position North Carolina at the forefront of academic PFAS research nationally. This new partnership ...
Is it the school, or the students?
2024-03-28
Are schools that feature strong test scores highly effective, or do they mostly enroll students who are already well-prepared for success? A study co-authored by MIT scholars concludes that widely disseminated school quality ratings reflect the preparation and family background of their students as much or more than a school’s contribution to learning gains.
Indeed, the study finds that many schools that receive relatively low ratings perform better than these ratings would imply. Conventional ...
Exploring the relationship between HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis and the incidence of chlamydia, gonorrhea and syphilis – findings from Denmark
2024-03-28
In their research article published in Eurosurveillance, von Schreeb et al. challenge existing assumptions regarding the relationship between the use of HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and the incidence of bacterial sexually transmitted infections (STI). According to the concept of sexual risk compensation, the start of PrEP treatment – a drug regimen which effectively prevents acquiring HIV – is associated with rises in STI as people feel protected against HIV while using it. However, von Schreeb et al. argue that available ...
Music: Song lyrics have become simpler and more repetitive since 1980
2024-03-28
We have been alerted to a potential error in some of the coding used by the authors in their analyses and are looking into this as a matter of urgency. The authors are confident that the main findings of the paper will remain unaltered, however some aspects may be affected and we have removed two sentences from the press release to reflect this. We will provide an update if there are further developments. We apologise for any inconvenience caused.
The lyrics of English-language songs have become simpler and more repetitive over the past 40 years, according to a study published in Scientific Reports.
Eva Zangerle and ...
Environment: More than half of Colorado River’s water used to irrigate crops
2024-03-28
Irrigation for agriculture uses more than half of the Colorado River’s total annual water flow, reports a paper published in Communications Earth & Environment. This finding is part of a new comprehensive assessment of how the Colorado River’s water is consumed — including both human usage and natural losses — and provides a more complete understanding of how the river’s water is used along its over 2,300 km (almost 1,500-mile) length.
The Colorado River flows through the southwestern United States (including the Grand Canyon) and northwestern Mexico whilst supplying water to more than 40 million people and more than 2 million ...
When inequality is more than “skin-deep”: Social status leaves traces in the epigenome of spotted hyenas in Tanzania
2024-03-28
A research consortium led by scientists from the Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (Leibniz-IZW) provide evidence that social behaviour and social status are reflected at the molecular level of gene activation (epigenome) in juvenile and adult free-ranging spotted hyenas. They analysed non-invasively collected gut epithelium samples from both high-ranking and low-ranking female hyenas and showed that rank differences were associated with epigenetic signatures of social inequality, i.e., the pattern of activation or switching off of genes that regulate important physiological processes such as energy conversion and immune response ...
Study explores the future of at-home cancer treatment
2024-03-28
LOS ANGELES — A clinical trial from Keck Medicine of USC will test the feasibility of treating non-small cell lung cancer with immunotherapy provided at home.
Immunotherapy, medicines that use the body’s immune system to eliminate or control cancer cells, are effective for many cancer patients, but are currently only administered intravenously (into the vein) in a doctor’s office or hospital.
The study will examine if a new formulation of atezolizumab, an immunotherapy approved for treating certain types of non-small cell lung cancer, can instead be safely and effectively ...
First performance standards published to measure the effectiveness of lifestyle medicine treatments
2024-03-28
An expert panel has published the first performance measures to identify remission and evaluate the effectiveness of lifestyle medicine treatments, which will allow more objective comparisons between lifestyle behavior interventions and other non-lifestyle treatments.
The performance measures are significant because, as interest in the field of lifestyle medicine has grown, it became clear that the lack of standards to document remission or long-term progress following lifestyle medicine treatment was a barrier to the widespread integration of the ...
To keep volunteers, connect them
2024-03-28
At a time when America needs volunteers more than ever, to tackle social problems from homelessness to disaster recovery, fewer people have been volunteering.
The number of volunteers for nonprofit and community-based organizations declined recently for the first time in decades, from 30% of the population in 2019 to 23% in 2021. That’s according to AmeriCorps and the U.S Census Bureau, which have tracked rates of volunteerism since 2002.
New research from Yifan Yu, assistant professor of ...
Suppressing boredom at work hurts future productivity, study shows
2024-03-28
Boredom is more common at work than in any other setting, studies show, and employees are bored at work for more than 10 hours per week on average.
Even astronauts and police officers get bored on the job. No occupation is immune.
Boredom serves an important purpose — it signals the need to stop an action and find an alternative project. But boredom becomes problematic when it’s ignored.
New research from the University of Notre Dame shows that trying to stifle boredom prolongs its effects and that alternating boring and meaningful tasks helps to prevent the effects of one boring task from ...
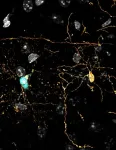
Older brain cells linger unexpectedly before their death
2024-03-28
For oligodendrocytes—the central nervous system cells critical for brain function—age may not bring wisdom, but it does come with the power to cling to life for much, much longer than scientists knew. That's according to a new study featured on the March 27 cover of the Journal of Neuroscience.
Mature oligodendrocytes took a shocking 45 days to die following a fatal trauma that killed younger cells within the expected 24 hours, Dartmouth researchers report. The findings suggest there's a new pathway for efforts to reverse or prevent the damage that aging and diseases such as multiple sclerosis cause to these important cells.
In the brain, ...
Clear shift in arterial diseases in diabetes
2024-03-28
There has been a redistribution in the risk of arterial disease in type 1 and 2 diabetes. The risks of heart attack and stroke have decreased significantly, while complications in more peripheral vessels have increased in relative importance, according to studies at the University of Gothenburg.
It is well known that type 1 and 2 diabetes increase the risk of heart attack and stroke. Previous research has also identified the clearest cardiometabolic risk factors in this context, such as obesity, lipid disorders, and high blood pressure.
How diabetes and cardiometabolic risk factors affect blood ...
Celebrating half a century of pioneering excellence: EBMT marks its 50th anniversary
2024-03-28
Barcelona, 27 March 2024 – The EBMT proudly commemorates its 50th anniversary, marking five decades of transformative advancements in the field of hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) and cellular therapy. More than 5,000 healthcare professionals will gather from the 14th to the 17th of April, 2024, at the Scottish Event Campus in Glasgow for this special edition and they will immerse themselves in cutting-edge scientific content, network with their peers from across the globe, and be part of a community that is driving innovation and change.
In 1974, a small group ...
Ancient DNA reveals the appearance of a 6th century Chinese emperor
2024-03-28
What did an ancient Chinese emperor from 1,500 years ago look like? A team of researchers reconstructed the face of Chinese Emperor Wu of Northern Zhou using DNA extracted from his remains. The study, published March 28 in the journal Current Biology, suggests the emperor’s death at the age of 36 might be linked to a stroke. It also sheds light on the origin and migration patterns of a nomadic empire that once ruled parts of northeastern Asia.
Emperor Wu was a ruler of the Northern Zhou dynasty in ancient China. Under his reign from AD 560 to AD 578, Emperor Wu built a strong military and unified the northern part ...
DNA study IDs descendants of George Washington from unmarked remains, findings to aid service member IDs going back to World War II
2024-03-28
New DNA sequencing technologies have identified the historical remains of George Washington’s grandnephews, Samuel Walter Washington and George Steptoe Washington Jr., and their mother, Lucy Payne Washington, from unmarked, fragmentary bones left at the Harewood family cemetery in Charles Town, West Virginia, in the mid-1800s.
In addition to enabling the remains in question to be reunited and reburied if desired, the researchers plan to apply the validated DNA analysis techniques to their ongoing efforts to identify the remains of service members lost around the world in past conflicts going back to World War II. The findings appear March 28 in the journal iScience.
“The ...
Familial Alzheimer’s disease transferred via bone marrow transplant in mice
2024-03-28
Familial Alzheimer’s disease can be transferred via bone marrow transplant, researchers show March 28 in the journal Stem Cell Reports. When the team transplanted bone marrow stem cells from mice carrying a hereditary version of Alzheimer’s disease into normal lab mice, the recipients developed Alzheimer’s disease—and at an accelerated rate.
The study highlights the role of amyloid that originates outside of the brain in the development of Alzheimer’s disease, which changes the paradigm of Alzheimer’s from being a disease ...
Perspectives of oncologists on the ethical implications of using AI for cancer care
2024-03-28
About The Study: In this survey study of 204 oncologists, few reported that patients needed to understand artificial intelligence (AI) models, but most agreed that patients should consent to their use, and many tasked patients with choosing between physician- and AI-recommended treatment regimens. These findings suggest that the implementation of AI in oncology must include rigorous assessments of its effect on care decisions as well as decisional responsibility when problems related to AI use arise.
Authors: Gregory A. Abel, M.D., M.P.H., of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Industry payments to US physicians by specialty and product type
2024-03-28
About The Study: From 2013 to 2022, U.S. physicians received $12.1 billion from industry. More than half of physicians received at least one payment. Payments varied widely between specialties and between physicians within the same specialty. A small number of physicians received the largest amounts, often exceeding $1 million, while the median physician received much less, typically less than a hundred dollars.
Authors: Andrew J. Foy, M.D., of the Penn State Milton S. Hershey ...
Andrew E. Place, MD, PhD appointed as Dana-Farber/Boston Children’s Cancer and Blood Disorders Center Vice President, Pediatric Chief Medical Officer
2024-03-28
BOSTON -- Andrew E. Place, MD, PhD, has been named as Vice President, Pediatric Chief Medical Officer (CMO) at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (within the Department of Pediatric Oncology) and Boston Children’s Hospital (within the Division of Hematology/Oncology) for the Dana-Farber/Boston Children’s Cancer and Blood Disorders Center.
In this role, Place will work closely with institutional and departmental leaders at Boston Children’s Hospital (BCH) and Dana-Farber to help define and implement clinical strategies and operational approaches that enhance smooth and efficient running of clinical care ...
COVID-19 antibody discovery could explain long COVID
2024-03-28
UVA Health researchers have discovered a potential explanation for some of the most perplexing mysteries of COVID-19 and long COVID. The surprising findings could lead to new treatments for the difficult acute effects of COVID-19, long COVID and possibly other viruses.
Researchers led by UVA’s Steven L. Zeichner, MD, PhD, found that COVID-19 may prompt some people’s bodies to make antibodies that act like enzymes that the body naturally uses to regulate important functions – blood pressure, for example. Related enzymes also regulate ...
[1] ... [1241]
[1242]
[1243]
[1244]
[1245]
[1246]
[1247]
[1248]
1249
[1250]
[1251]
[1252]
[1253]
[1254]
[1255]
[1256]
[1257]
... [8791]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.