Wild plants face viral surprise
2024-03-28
Just as many people battle seasonal colds and flu, native plants face their own viral threats. People have long known that plants can succumb to viruses just like humans. Now, a new study led by Michigan State University and the University of California, Riverside reveals a previously unknown threat: non-native crop viruses are infecting and jeopardizing the health of wild desert plants.
“For years, the ecological field assumed wild plants were immune to invasive viruses that damage crops,” said Carolyn ...
Storing electrons from hydrogen for clean chemical reactions
2024-03-28
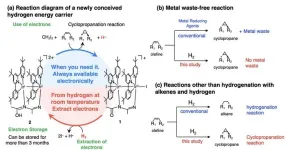
Fukuoka, Japan—Researchers from Kyushu University have developed a hydrogen energy carrier to address some of the biggest hurdles in the path towards a sustainable hydrogen economy. As explained in a paper published in JACS Au, this novel compound can efficiently “store electrons” from hydrogen in a solid state to use in chemical reactions later.
Hydrogen is a promising source of clean energy with a lot of untapped potential applications in industry and everyday life. Unlike conventional fuels, hydrogen can be used to generate electricity without producing greenhouse ...
Unlocking how to use mRNA to target Alzheimer’s disease
2024-03-28
Scientists at The Florey have developed an mRNA technology approach to target the toxic protein tau, which builds up in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias.
To date, mRNA has been predominantly used for vaccines, including those used to fight COVID-19.
New research published today in Brain Communications establishes The Florey as a key player in the mRNA field, with Dr Rebecca Nisbet taking the technology in a new direction.
“This is the first time mRNA has been explored for use in Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr Nisbet said. “Our work in cell models demonstrates that this technology ...
Kessler Foundation secures $770,000 in grants to advance leading-edge spinal cord research
2024-03-28
East Hanover, NJ – March 28, 2024 – Kessler Foundation received two grants from The New Jersey Commission on Spinal Cord Research that will fuel innovative research in the field of spinal cord injury (SCI). These grants will fund efforts aimed at improving the cognitive assessment of individuals with traumatic SCI and pilot-testing the first-of-its-kind Spinal Cord Injury Personal Assistance Services Survey (SCI-PASS).
Traumatic spinal cord injury (tSCI) often leads to cognitive impairment, affecting up to 60 percent of individuals living with this condition. “The challenge lies in assessing cognitive functions in people with tSCI, as many existing tests rely on upper limb ...
Going ‘back to the future’ to forecast the fate of a dead Florida coral reef
2024-03-28
Rising temperatures and disease outbreaks are decimating coral reefs throughout the tropics. Evidence suggests that higher latitude marine environments may provide crucial refuges for many at-risk, temperature-sensitive coral species. However, how coral populations expand into new areas and sustain themselves over time is constrained by the limited scope of modern observations.
What can thousands of years of history tell us about what lies ahead for coral reef communities? A lot. In a new study, Florida Atlantic University researchers and collaborators provide geological insights into coral range expansions by reconstructing the composition of a Late Holocene-aged subfossil coral ...
How extratropical ocean-atmosphere interactions can contribute to the variability of jet streams in the Northern Hemisphere
2024-03-28
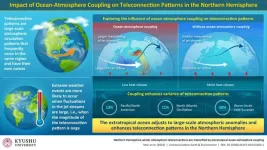
Fukuoka, Japan—The interaction between the oceans and the atmosphere plays a vital role in shaping the Earth’s climate. Changing sea surface temperatures can heat or cool the atmosphere, and changes in the atmosphere can do the same to the ocean surface. This exchange in energy is known as “ocean-atmosphere coupling.”
Now, researchers from Kyushu University have revealed that this ocean-atmosphere coupling enhances teleconnection patterns—when climate conditions change across vast regions of the globe—in the Northern Hemisphere. In their recent ...
MSK Research Highlights, March 28, 2024
2024-03-28
Low recurrence seen with cryoablation for large breast tumors
Cryoablation, a minimally invasive technique used to freeze and destroy small tumors, is effective for breast cancer patients with larger tumors, according to research presented by MSK interventional radiologist Yolanda Bryce, MD, at the 2024 Society of Interventional Radiology Annual Scientific Meeting.
The retrospective study assessed outcomes for 60 patients who underwent cryoablation because they were not candidates for surgery or declined surgery due to other health concerns. The average size of their tumors was 2.5 centimeters. In a follow-up after 16 months, only 10% of patients experienced a recurrence ...
USDA, Nueta Hidatsa Sahnish College collaborate to support Indigenous Seed Sovereignty
2024-03-28
MANDAN, N.D., March 28, 2024—The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) Agricultural Research Service (ARS) announces a cooperative agreement with the Nueta Hidatsa Sahnish (NHS) College to conduct research supporting Indigenous Seed Sovereignty. This collaborative effort will increase the number of traditional varieties of seeds of the Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara (MHA) Nation crops within NHS College's traditional seed cache.
This agreement builds upon USDA’s strengthened partnerships with ...
For younger women, mental health now may predict heart health later
2024-03-28
Younger women are generally thought to have a low risk of heart disease, but new research urges clinicians to revisit that assumption, especially for women who suffer from certain mental health conditions. A new study being presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session found that having anxiety or depression could accelerate the development of cardiovascular risk factors among young and middle-aged women.
The study draws new attention to the importance of cardiovascular screening and preventive care as rates of cardiovascular risk factors rise and heart attacks become more common in younger people. Anxiety and depression ...
Missed opportunity: AEDs near cardiac arrests rarely used by bystanders
2024-03-28
Automated external defibrillators (AEDs) are a common resource in public buildings, yet a new analysis reveals that they are rarely used to help resuscitate people suffering cardiac arrest. Research, which will be presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session, found that AEDs were only used in 13 of nearly 1,800 cases of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, even though many of the incidents occurred near a public AED.
Cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating. It is different from a heart attack, which is when a blockage prevents blood ...
Eggs may not be bad for your heart after all
2024-03-28
Whether you like your eggs sunny-side up, hard boiled or scrambled, many hesitate to eat them amid concerns that eggs may raise cholesterol levels and be bad for heart health. However, results from a prospective, controlled trial presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session show that over a four-month period cholesterol levels were similar among people who ate fortified eggs most days of the week compared with those who didn’t eat eggs.
A total of 140 patients with or at high risk for cardiovascular disease were enrolled in ...
Alcohol raises heart disease risk, particularly among women
2024-03-28
Young to middle-aged women who reported drinking eight or more alcoholic beverages per week—more than one per day, on average—were significantly more likely to develop coronary heart disease compared with those who drank less, finds a study presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session. The risk was highest among both men and women who reported heavy episodic drinking, or “binge” drinking, and the link between alcohol and heart disease appears to be especially strong among women, according to the findings.
The study focused on 18- to 65-year-old ...
TTUHSC announces new center for nursing research
2024-03-28
The Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center (TTUHSC) School of Nursing announced March 27 the establishment of the TTUHSC Center for Nursing Research, Collaboration and Innovation.
“Interprofessional collaboration is essential for advancing research in health care,” TTUHSC School of Nursing Dean and Professor Holly Wei, Ph.D., said. “By bringing together professionals from various disciplines, we can harness a wide range of perspectives and skills to develop innovative solutions that significantly impact patient care and outcomes.”
For years, the TTUHSC School of Nursing has been recognized for its ability to educate ...
Adding just enough fuel to the fire
2024-03-28
How much fuel can we add to the fire while still maintaining control?
Metaphorically speaking, that’s the question one team at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) has been asking themselves lately.
Now, they believe they have the answer for one particular scenario. It’s all a part of the Lab’s work to bring energy from fusion to the power grid.
Building upon recent findings showing the promise of coating the inner surface of the vessel containing a fusion plasma in liquid lithium, the researchers have determined the maximum density of uncharged, or neutral, particles at the edge of a plasma before the edge ...
Impact of synbiotic supplements on the gut microbiome and overall health of penguins
2024-03-28
A healthy gut plays an indispensable role in the absorption and metabolism of nutrients, maintaining immune function, and promoting general well-being. The profound impact of a healthy microbiome is not just limited to the gut, but there is mounting evidence that it influences almost every function of the body. Thus, the composition of the gut microbiome becomes an important indicator of health status of the body.
Probiotics are a type of supplements containing live strains of bacteria that improve and diversify the gut microbiome population. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum, a type of microorganism ...
Promising advances in organosilica membranes for separating organic liquid mixtures
2024-03-28
In many chemical-related industries, such as pharmaceuticals, oil refineries, and food and beverage factories, separating organic liquid mixtures is an essential step. A staple method to achieve this is distillation, which involves heating a mixture to a specific temperature so that only one of its components vaporizes. Though widely used, distillation fails to separate organic liquid mixtures in which both components have the same boiling point. Moreover, it’s an energy- and resource-intensive process, ...
Cell phone video technology unveils new method for analyzing walking and gait
2024-03-28
BALTIMORE, March 27, 2024— Researchers at Kennedy Krieger Institute and Johns Hopkins Medicine have developed a new, accessible approach to analyze a patient’s walking ability and stances more effectively. Following numerous tests, they determined that a simple video recorded on a personal pocket device, such as a smartphone or tablet, can be used to measure gait at a clinical, high-quality level.
Experts say current state-of-the-art approaches to gait analysis are often expensive and inaccessible due ...
Ancient isolation’s impact on modern ecology
2024-03-28
A new study led by Michigan State University researcher Peter Williams sheds light on the profound influence of deep geographic isolation on the evolution of mammals. Published in Nature Communications on March 28, the research reveals how long-lasting separation between continents has shaped distinct mammal communities around the globe.
“Today’s ecology was not inevitable. If there were different isolating factors long ago, we might have vastly different ecosystems today,” said Peter Williams, the lead author of the study. Williams is a research ...
Synaptic protein change during development offers clues on evolution and disease
2024-03-28
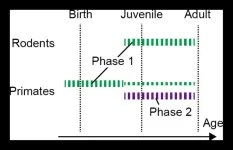
The first analysis of how synaptic proteins change during early development reveals differences between mice and marmosets but also what's different in individuals with autism spectrum disorders. The Kobe University findings offer first insights into the mechanism behind synaptic development and open up routes for research on possible treatments.
Given that synapses are the connections between our brain cells, one might think that having as many of these as possible is a good thing. However, primate brains do something unexpected: After early childhood, ...
How commercial rooftop solar power could bring affordable clean energy to low-income homes
2024-03-28
Lower-income communities across the United States have long been much slower to adopt solar power than their affluent neighbors, even when local and federal agencies offer tax breaks and other financial incentives.
But, commercial and industrial rooftops, such as those atop retail buildings and factories, offer a big opportunity to reduce what researchers call the “solar equity gap,” according to a new study, published in Nature Energy and led by researchers at Stanford University.
“The ...
Taking a closer look at pulmonary fibrosis genetics
2024-03-28
PHOENIX, Ariz. — March 28, 2024 — Regulators of gene expression are thought to play an outsized role in disorders from cancers to heart disease. But how exactly do variations in gene regulation translate into a disease’s biology?
A team of scientists led by researchers from the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen), part of the City of Hope, together with investigators at St. Vincent’s Institute of Medical Research and Vanderbilt University Medical Center, now have a better answer for this question when it comes to pulmonary fibrosis (PF), an incurable respiratory disease.
Their study, published today in Nature Genetics, is the first to look at these ...
Cats with MDR1 mutation at risk of severe reactions to popular medication
2024-03-28
PULLMAN, WA -- More than half a million cats in the United States could be at risk of a severe or even fatal neurological reaction to the active ingredient in some top-selling parasite preventatives for felines.
While the ingredient, eprinomectin, which is found in products like NexGard COMBO and Centragard, appears safe and effective for the significant majority of cats when used at label doses, a study conducted by Washington State University’s Program for Individualized Medicine identified a risk of severe adverse effects in cats with the ...
IOP Publishing and IPEM mandate reporting of sex and gender in research
2024-03-28
IOP Publishing (IOPP) and the Institute of Physics and Engineering (IPEM) have introduced checks for sex and gender equality for all manuscripts submitted to their jointly published journal Physiological Measurement.
In line with the Sex and Gender Equity in Research (SAGER) guidelines, which were introduced to ensure that sex and gender considerations are appropriately reported in scholarly literature, all research published in Physiological Measurement must declare the sex and gender balance of subject groups. Authors are ...
Dogs trained to detect trauma stress by smelling humans’ breath
2024-03-28
Dogs’ sensitive noses can detect the early warning signs of many potentially dangerous medical situations, like an impending seizure or sudden hypoglycemia. Now, scientists have found evidence that assistance dogs might even be able to sniff out an oncoming PTSD flashback, by teaching two dogs to alert to the breath of people who have been reminded of traumas.
“PTSD service dogs are already trained to assist people during episodes of distress,” said Laura Kiiroja of Dalhousie University, first author of the paper ...
Electronic device thermal management made simpler and slightly better!
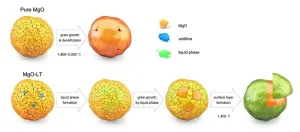
2024-03-28
Dr. Cheol-Woo Ahn, leading a research team at the Department of Functional Ceramics within the Ceramic Materials Division at the Korea Institute of Materials Science(KIMS), has developed the world's first heat dissipation material. This material reduces hydrophilicity through a chemical reaction that forms a nanocrystalline composite layer and increases thermal conductivity by controlling point defects. This process occurs during a simple sintering process that does not require surface treatment. KIMS is a government-funded research institute under the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Conventional ...
[1] ... [1242]
[1243]
[1244]
[1245]
[1246]
[1247]
[1248]
[1249]
1250
[1251]
[1252]
[1253]
[1254]
[1255]
[1256]
[1257]
[1258]
... [8791]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.