From opioid overdose to treatment initiation: outcomes associated with peer support in emergency departments
2024-04-16
People with a nonfatal opioid overdose who have access to a peer support program while in the emergency department are more likely to initiate treatment and less likely to have repeated overdoses, according to a Rutgers Health study.
The study is the largest study on outcomes associated with emergency department-based peer support for opioid use disorders and was published in JAMA Network Open online ahead of print in the April 2024 issue.
According to the Centers for Disease ...
NIH awards $3.4 million to Wayne State University to investigate biomarkers for better reproductive success
2024-04-16
DETROIT - The diagnosis of male fertility has not changed in decades and primarily relies on conventional semen parameter analyses such as sperm count, motility and morphology, which are poor predictors of couples’ reproductive success.
A new $3.4 million award to the Wayne State University School of Medicine from the National Institutes of Health aims to overcome the limitations of conventional semen analyses by examining mitochondrial DNA levels in sperm as a novel biomarker of sperm fitness.
The project will be led by School of Medicine Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology J. Richard Pilsner, Ph.D., M.P.H. ...
New study shows corporate misconduct at home hurts sales overseas
2024-04-16
New research in the Global Strategy Journal has bad news for companies struggling with corruption, discrimination, or sweatshops in their supply chain: corporate misconduct demonstrably hurts international sales. Consumers and investors increasingly read about unethical business practices globally and demonstrate their displeasure locally.
“Socially irresponsible acts transcend geographic boundaries and negatively affect foreign subsidiary performance,” said Nuruzzaman Nuruzzaman of the University of Manchester, one of the study’s ...
Take it from the rats: A junk food diet can cause long-term damage to adolescent brains
2024-04-16
A new USC-led study on rats that feasted on a high-fat, sugary diet raises the possibility that a junk food-filled diet in teens may disrupt their brains’ memory ability for a long time.
“What we see not just in this paper, but in some of our other recent work, is that if these rats grew up on this junk food diet, then they have these memory impairments that don’t go away,” said Scott Kanoski, a professor of biological sciences at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences. “If you just simply put them on a healthy diet, these effects unfortunately last well into adulthood.”
The study appears in the May issue of the journal ...
Fralin Biomedical Research Institute team unpacking genetic mysteries of childhood epilepsies
2024-04-15
Epilepsy is a brain disorder that causes recurring seizures.
It is one of the most common neurological diseases, and it affects approximately 50 million people worldwide, according to the World Health Organization. In 2023, nearly 450,000 children in the United States were diagnosed with the disease.
Virginia Tech researchers at the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC are exploring how gene variants identified in children with severe epilepsy can have an impact on neurons, leading to abnormal ...
UNC-Chapel Hill researchers discover new clues to how tardigrades can survive intense radiation
2024-04-15
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill researchers have discovered that tardigrades – microscopic animals famed for surviving harsh extremes – have an unusual response to radiation.
Led by UNC-Chapel Hill researcher Bob Goldstein’s lab, the new research paper published on April 12 in Current Biology reveals new details on tardigrades’ responses to radiation. Radiation has long been known to damage DNA, and in humans, DNA damage from excessive radiation exposure can lead to diseases. But the tardigrades have an unexpected way to correct the damage.
“What we saw surprised us,” said Goldstein. “The ...
UT Arlington prioritizes entrepreneurship efforts
2024-04-15
Universities are engines for economic growth that today are supporting technology development, innovation and economic advancement as never before.
With the launch of its Center for Entrepreneurship and Technology Development (CETD), The University of Texas at Arlington is beginning a new era of support for student and faculty entrepreneurship. The center, whose mandate also includes supporting the region’s vibrant innovation economy, will expand UTA’s engagement with public and private partners everywhere.
“CETD fosters a vibrant and supportive atmosphere ...
Ochsner Health receives 2024 Top Workplaces Culture Excellence Awards
2024-04-15
NEW ORLEANS, La – Ochsner Health is the recipient of the 2024 Top Workplaces Culture Excellence awards in four distinguished categories: Innovation, Work-Life Flexibility, Leadership and Purposes & Values. These accolades are administered by Energage, a purpose-driven organization that develops solutions to build and brand Top Workplaces.
The Top Workplaces program has a 17-year history of surveying and celebrating people-first organizations nationally and across 60 regional markets. Top Workplaces awards are based on feedback from a research-backed employee engagement survey.
“It is an honor to receive ...
Are these newly found rare cells a missing link in color perception?
2024-04-15
Scientists have long wondered how the eye’s three cone photoreceptor types work together to allow humans to perceive color. In a new study in the Journal of Neuroscience, researchers at the University of Rochester used adaptive optics to identify rare retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) that could help fill in the gaps in existing theories of color perception.
The retina has three types of cones to detect color that are sensitive to either short, medium, or long wavelengths of light. Retinal ganglion cells transmit input from these cones to the central nervous system.
In the 1980s, David Williams, the William G. Allyn Professor of Medical Optics, ...
Annals supplement highlights important new evidence readers ‘may have missed’ in 2023
2024-04-15
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 15 April 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf ...
NIH awards $2.3 million grant to University of Oklahoma for gene therapy research
2024-04-15
NORMAN, OKLA. – University of Oklahoma engineering researcher Sangpil Yoon, Ph.D., has been awarded a $2.3 million grant from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health, for his project titled “Development of protein-based nanostructures activated by ultrasound.”
The five-year grant is part of the NIH’s Research Project Grant (R01) program, which supports cutting-edge health-related research and development initiatives. Yoon’s funding, totaling $363,919 for ...
Hidden threat: Global underground infrastructure vulnerable to sea-level rise
2024-04-15
As sea levels rise, coastal groundwater is lifted closer to the ground surface while also becoming saltier and more corrosive. A recent study by earth scientists at the University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa compiled research from experts worldwide showing that in cities where there are complex networks of buried and partially buried infrastructure, interaction with this shallower and saltier groundwater exacerbates corrosion and failure of critical systems such as sewer lines, roadways, and building foundations.
“While it has been recognized that shallowing groundwater will eventually result in chronic flooding as it surfaces, ...
Study reveals AI enhances physician-patient communication
2024-04-15
As one of the first health systems in the country to pilot the use of generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) to draft replies to patient messages inside the Epic Systems electronic health record, UC San Diego Health is a pioneer in shaping the future of digital health.
The results of a new University of California San Diego School of Medicine study indicate that, although AI-generated replies did not reduce physician response time, they have contributed to relieving cognitive burden by starting an empathetic draft, which physicians can edit rather than starting from scratch.
The study, published in the April 15, 2024 online edition of the Journal of ...
Mitchell A. Lazar honored with prestigious George M. Kober Medal for pioneering contributions to diabetes and metabolic research
2024-04-15
PHILADELPHIA— Mitchell A. Lazar, M.D., Ph.D., the Rhoda and Willard Ware Professor in Diabetes and Metabolic Disease, and Director of the Institute for Diabetes, Obesity, and Metabolism in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, is the 2025 recipient of the George M. Kober Medal from the Association of American Physicians (AAP). Lazar will receive the honor in Chicago at the AAP’s annual meeting which takes place April 25-27, 2025.
The AAP, an elected society of the nation’s most distinguished physician scientists, was founded in 1885 by seven physicians, including Sir William ...
SMU prof to use NSF grant to develop game-based semiconductor curriculum for high school students
2024-04-15
DALLAS (SMU) – The challenge is to connect the dots for high school students between the technology in their cell phones and the career options manufacturing the devices. To that end, the National Science Foundation (NSF) has awarded an Innovative Technology Experiences for Students and Teachers (ITEST) grant to SMU professor Lin Lipsmeyer and colleagues toward developing one of the first game-based semiconductor curricula for high school students.
The online game-based semiconductor curriculum will be made available to a wide range of students through a collaboration with Dallas-based gaming company Stimuli. Additional ...
Advance in light-based computing shows capabilities for future smart cameras
2024-04-15
Researchers developing the next generation of computing technology aim to bring some light to the field — literally.
Optical computing, which relies on particles of light called photons, is expected to provide alternatives to traditional electronic approaches. Such systems — or light-based components of hybrid systems that also retain electronic parts — could be faster, consume less energy and compute visual information more efficiently through simultaneous, parallel processing.
To date, ...
Q&A: How claims of anti-Christian bias can serve as racial dog whistles
2024-04-15
In a speech to a group of religious broadcasters in February, Donald Trump promised to create a task force to counter “anti-Christian bias,” which he said would investigate the “discrimination, harassment and persecution against Christians in America.”
It’s not the first time Trump has claimed that Christians are being persecuted, and he’s not alone. As more politicians repeat these statements, researchers from the University of Washington investigated whether anti-Christian bias claims can also be ...
Three advances in pavement technology — for safer, more sustainable roadways
2024-04-15
While April showers bring May flowers, these months also kick off road construction season — when cracks and potholes that developed over the winter get fixed. But recent advances could make future roadways safer and repairs more sustainable, thanks to smart pothole monitoring, snail shells and graphene. The new approaches can be found in three papers recently published in ACS journals. Reporters can request free access to these papers by emailing newsroom@acs.org.
A smart pothole monitoring system for cars. By harnessing the vibrations that shake a vehicle as it drives over uneven pavement, researchers have created a system that ...
Civil engineer looks to remedy inequities in traffic safety
2024-04-15
Alyssa Ryan, an assistant professor of civil and architectural engineering and mechanics, in the University of Arizona College of Engineering, is leading a national study to identify disparities in traffic safety for all transportation users, including drivers, bicyclists and walkers.
"Transportation engineering is very focused on people and impacting society and how people interact with the world," said Ryan. "If you don't have transportation, you can't do anything."
With a $467,000 ...
New research highlights effects of gentrification on urban wildlife populations across U.S. cities
2024-04-15
Chicago (April 15, 2024) – New research published on Monday, April 15 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) identifies how gentrified parts of a city have notably more urban wildlife than ungentrified parts of the same city, further limiting marginalized communities’ opportunity to connect with nature. The study, led by Lincoln Park Zoo’s Urban Wildlife Institute, analyzed data from 23 cities across the continental U.S., collected by partners of the Urban Wildlife Information Network ...
Vaccine breakthrough means no more chasing strains
2024-04-15
Scientists at UC Riverside have demonstrated a new, RNA-based vaccine strategy that is effective against any strain of a virus and can be used safely even by babies or the immunocompromised.
Every year, researchers try to predict the four influenza strains that are most likely to be prevalent during the upcoming flu season. And every year, people line up to get their updated vaccine, hoping the researchers formulated the shot correctly.
The same is true of COVID vaccines, which have been reformulated to target sub-variants of the most prevalent strains ...
Epilepsy drug prevents brain tumors in mice with NF1
2024-04-15
A drug used to treat children with epilepsy prevents brain tumor formation and growth in two mouse models of neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), according to a study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. NF1 is a genetic condition that causes tumors to grow on nerves throughout the body, including the optic nerves, which connect the eyes to the brain.
The findings lay the groundwork for a clinical trial to assess whether the drug, lamotrigine, can prevent or delay brain tumors in children with NF1. The study is online in the journal Neuro-Oncology.
“Based on these data, the Neurofibromatosis Clinical Trials Consortium is considering launching a first-of-its-kind ...
Study uses thermodynamics to describe expansion of the Universe
2024-04-15
The idea that the Universe is expanding dates from almost a century ago. It was first put forward by Belgian cosmologist Georges Lemaître (1894-1966) in 1927 and confirmed observationally by American astronomer Edwin Hubble (1889-1953) two years later. Hubble observed that the redshift in the electromagnetic spectrum of the light received from celestial objects was directly proportional to their distance from Earth, which meant that bodies farther away from Earth were moving away faster and the universe must be expanding.
A surprising new ingredient was added to the model in 1998 when observations of ...
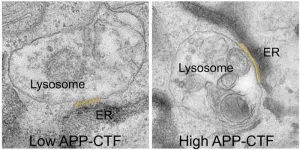
New mechanism uncovered in early stages of Alzheimer's disease
2024-04-15
Leuven (Belgium), 16 April 2024 – Alzheimer's disease (AD) remains one of the most challenging and prevalent neurodegenerative disorders, affecting millions of individuals worldwide. In a new study published in Developmental Cell, researchers from the lab of Wim Annaert (VIB-KU Leuven) have identified a novel mechanism potentially connected to the early stages of AD. They demonstrated that a fragment of the amyloid precursor protein (APP), called APP-CTF, disrupts communication between cellular compartments crucial for calcium storage and waste disposal, which ...
Elite coaches leaving home as Western countries seek sport success
2024-04-15
Nations battling for Olympic success in a global sporting ‘arms race’ has led to elite coaches migrating to Western countries as they bid to escape antiquated and restrictive coaching regimes in their home countries, reveals a new study funded by the International Olympic Committee’s Olympic Studies Centre.
National teams pursuing Olympic gold medals are increasingly recruiting foreign elite coaches from the leading countries, as they try to close the gap between themselves and the top medal-winners in particular ...
[1] ... [1240]
[1241]
[1242]
[1243]
[1244]
[1245]
[1246]
[1247]
1248
[1249]
[1250]
[1251]
[1252]
[1253]
[1254]
[1255]
[1256]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.