Study: Dangerous surgical site infections can be reduced with simple prevention protocol
2024-03-28
Arlington, Va. — March 28, 2024 — A new study published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC) demonstrates the use of a simple pre-surgical infection prevention protocol to prevent dangerous post-surgical infections. Researchers performed this investigation at the Soroka University Medical Center in Israel.
Surgical site infections (SSIs) are a type of healthcare-associated infection with deadly consequences for some patients. According to the latest data from the Centers for ...
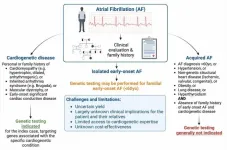
Genetic testing of patients with atrial fibrillation can alert clinicians to potential development of life-threatening conditions
2024-03-28
Philadelphia, March 28, 2024 – Although the vast majority of clinicians do not view atrial fibrillation (AF) as a genetic disorder, a White Paper in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology, published by Elsevier, analyzes the current understanding of genetics and the role of genetic testing in AF and concludes there is an increasing appreciation that genetic culprits for potentially life-threatening ventricular cardiomyopathies and channelopathies may initially present with AF.
AF is the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia and is associated with increased risks of heart failure, stroke, and death. It is ...
Artificial Intelligence tool successfully predicts fatal heart rhythm
2024-03-28
In a Leicester study that looked at whether artificial intelligence (AI) can be used to predict whether a person was at risk of a lethal heart rhythm, an AI tool correctly identified the condition 80 per cent of the time.
The findings of the study, led by Dr Joseph Barker working with Professor Andre Ng, Professor of Cardiac Electrophysiology and Head of Department of Cardiovascular Sciences at the University of Leicester and Consultant Cardiologist at the University Hospitals of Leicester NHS Trust, have been published in the European Heart Journal – Digital Health.
Ventricular arrhythmia (VA) is a heart rhythm disturbance originating from the bottom chambers (ventricles) where ...
What progress has China made in agriculture green development over the past five years?
2024-03-28
Reconciling the tasks of producing adequate amounts of nutritious food for the increasing global population while preserving the environment and natural ecosystems simultaneously is an enormous challenge. The concept of agriculture green development (AGD) was detailed in 2017 and the necessary governmental policies were developed to address the aforementioned challenge in China and to help achieve the related global sustainable development goals. AGD emphasizes the synergy between green and development; current agriculture has to transform from the intensive farming with high inputs, high environmental impacts ...
ALMA finds new molecular signposts in starburst galaxy
2024-03-28
The ALMA radio telescope has detected more than 100 molecular species, including many indicative of different star formation and evolution processes, in a galaxy where stars are forming much more actively than in the Milky Way. This is far more molecules than were found in previous studies. Now the team will try to apply this knowledge to other galaxies.
A team of researchers led by Sergio Martin of the European Southern Observatory/Joint ALMA Observatory, Nanase Harada of the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, and Jeff Mangum of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory ...
Open waste burning linked to air pollution in Northwestern Greenland
2024-03-28
A case study on the effects of open waste burning on air quality in Northwestern Greenland calls attention to the importance of no-one-left-behind sustainable air quality monitoring in the Arctic region.
To better understand the air quality risks faced by remote Arctic communities, an international team monitored aerial pollutants at a community in Northwestern Greenland. Their findings, published in Atmospheric Science Letters, reveal that open waste burning elevates the concern of health risks to the community.
The study focused on Qaanaaq, a small village in Northwestern Greenland with a population of approximately 600. During the summer of 2022, the team conducted the first-time measurement ...
Google Street View reveals how built environment correlates with risk of cardiovascular disease
2024-03-28
Researchers have used Google Street View to study hundreds of elements of the built environment, including buildings, green spaces, pavements and roads, and how these elements relate to each other and influence coronary artery disease in people living in these neighbourhoods.
Their findings, published in the European Heart Journal [1] today (Thursday), show that these factors can predict 63% of the variation in the risk of coronary heart disease from one area to another.
Coronary heart disease, where a build-up of fatty substances in the coronary arteries ...
Connecting the dots to shape growth forces
2024-03-28
Kyoto, Japan -- Branching patterns are prevalent in our natural environment and the human body, such as in the lungs and kidneys. For example, specific genes that express growth factor proteins are known to influence the development of the lungs' complex branches. Still, until now the mechanics behind this phenomenon have remained a mystery.
Kyoto University researchers have unveiled a regulatory system linking signal, force, and shape in mouse lung structure development. The team recognized that the signal protein ERK plays an active role in causing growing lung tissue to curve.
"ERK signals the cell tissue to stretch outward to smoothen its ...
Parental avoidance of toxic exposures could help prevent autism, ADHD in children, new study shows
2024-03-28
SAN ANTONIO, March 27, 2024 – Autism and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) may be preventable if parents avoid toxic exposures and adopt interventions such as environmental house calls, according to a published study led by researchers from The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio).
Using a validated, self-administered questionnaire now used worldwide to identify individuals with chemical intolerance – the Quick Environmental ...
Trends in the incidence of renal replacement therapy due to rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis in Japan, 2006–2021
2024-03-28
Niigata, Japan - A new Japanese nationwide study revealed that from 2006 to 2021, the number of patients with incident renal RRT due to RPGN increased, with an increase in the age-specific incidence of RRT due to RPGN in the older age groups (≥70 years old). Given the increasing trend in the incidence of RRT in older age groups and the ongoing population aging in Japan, the number of patients with incident RRT due to RPGN is likely to continue to increase in the future.
"RPGN is clinical syndrome that causes a rapid loss of kidney function, usually within a few days to a ...
Olympics not likely to swallow up skateboarding’s subversive nature into its corporate spectacle, study says
2024-03-28
The subversive nature of skateboarding is not likely to be affected by its continuing place in the corporate world of the Olympics, experts have predicted.
The inclusion of the street sport – which happened for the first time in Tokyo 2020 – could help to promote pacifism and egalitarianism and help to combat sexism, homophobia and racism, research suggests.
Some had suggested the subversive sport and its links to rebellion, pools, ramps, and skateparks, as well as less typical type of competition, would not fit easily into a world ...
Looking after the NHS workforce must be a top priority, say experts
2024-03-28
Looking after the NHS workforce is not only an ethical imperative but also a sound investment and must be a top priority, say experts in the third report of The BMJ Commission on the Future of the NHS.
From improving basic working conditions to planning for the impact of AI, the authors set out a bold vision to enhance the stewardship of the NHS workforce.
In the most recent (2023) NHS Staff Survey only a quarter (26.4%) of respondents said there were enough staff at their organisation for them to do their job properly, just over a quarter (25.6%) are satisfied with their pay, and only 42% say they are satisfied with the extent to which their organisations ...
Prolonged use of certain hormone drugs linked to increased brain tumor risk
2024-03-28
Prolonged use of certain progestogen hormone drugs is associated with an increased risk of developing a type of brain tumour known as an intracranial meningioma, finds a study from France published by The BMJ today.
The researchers say this study is the first to assess the risk associated with progestogens used by millions of women worldwide, and further studies are urgently needed to gain a better understanding of this risk.
Progestogens are similar to the natural hormone progesterone, which are widely used for gynaecological conditions such ...
Delirium a ‘strong risk factor’ for dementia among older people
2024-03-28
Delirium is a strong risk factor for dementia and death among older people, finds the largest study of its kind published by The BMJ today.
The findings show that, among hospital patients with at least one episode of delirium, the risk of receiving a new dementia diagnosis was three times higher than for patients without delirium and each additional episode of delirium increased that risk by 20%.
The researchers say their findings support the theory that delirium has a strong independent effect on dementia risk in this clinical population.
Delirium is a sudden change in a person’s usual mental state. Symptoms include agitation, confusion or being unable to stay ...
People experiencing homelessness more likely to develop dementia at younger ages, study finds
2024-03-28
London, ON, March 27, 2024 – Dementia in unhoused people was 1.9 times greater than the general population, with a higher prevalence for age groups younger than 85 years, according to new research from Lawson Health Research Institute and ICES.
In one of the first population-based studies of its kind and published in The Lancet Public Health, researchers compared dementia prevalence in people experiencing homeless with the general population and people living in low-income neighbourhoods in Ontario, Canada.
“Not only did we find that dementia was more common among unhoused individuals, but the difference was greatest between the ages of 55 to ...
Can metalens be commercialized at a fraction of the cost?
2024-03-28
Metalenses, nano-artificial structures capable of manipulating light, offer a technology that can significantly reduce the size and thickness of traditional optical components. Particularly effective in the near-infrared region, this technology holds great promise for various applications such as LiDAR which is called the ‘eyes of the self-driving car’, miniature drones, and blood vessel detectors. Despite its potential, the current technology requires tens of millions of won even for fabricating a ...
Reclaim ‘wellness’ from the rich and famous, and restore its political radicalism, new book argues
2024-03-28
A new cultural history of the 1970s wellness industry offers urgent lessons for today. It reveals that in the seventies, wellness was neither narcissistic nor self-indulgent, and nor did its practice involve buying expensive, on-trend luxury products. Instead, wellness emphasised social well-being just as much as it focused on the needs of the individual. Wellness practitioners thought of self-care as a way of empowering people to prioritise their health so that they could also enhance the well-being of those around them.
Today’s wellness industry generates trillions of dollars in revenue, ...
Curtin research unlocks supernova stardust secrets
2024-03-28
Curtin University-led research has discovered a rare dust particle trapped in an ancient extra-terrestrial meteorite that was formed by a star other than our sun.
The discovery was made by lead author Dr Nicole Nevill and colleagues during her PhD studies at Curtin, now working at the Lunar and Planetary Science Institute in collaboration with NASA’s Johnson Space Centre.
Meteorites are mostly made up of material that formed in our solar system and can also contain tiny particles which originate from stars born long before our sun.
Clues that these particles, known as presolar grains, are relics from other stars ...
New documents reveal patient safety concerns over strike day cover
2024-03-28
An investigation published by The BMJ today reveals new details of requests to recall striking junior doctors from picket lines for patient safety reasons.
Documents show that while most trusts in England did not make such requests, those that did were rejected by the BMA in most cases. Some of these trusts warned of potential harm to patients from cancelling operations at the last minute and short staffing, reports assistant news editor Gareth Iacobucci.
However, the BMA said it takes ...
UTA hosts Solar-bration watch party for April 8 eclipse
2024-03-28
The University of Texas at Arlington is hosting an April 8 watch party that is open to the public so the community can join Maverick students, faculty and staff in viewing the first total solar eclipse visible in North Texas since 1878.
The party will offer food trucks, an audio program featuring eclipse experts from UTA’s faculty, and more. Visit UTA’s Solar-bration website for details, including parking information. The event is sponsored in part by Whataburger.
For visitors, UTA is offering a limited number of free eclipse glasses available for pickup at viewing locations across campus. If you wish to guarantee that you will have glasses, or you need more ...
Researchers discover molecule that promotes production of cancer cells in triple-negative breast cancer
2024-03-28
A team of researchers from Hiroshima University has discovered a molecule that promotes the production of cancer cells. This molecule may prove to be a potential therapeutic target in the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer, an aggressive form of breast cancer.
Their work was published in the journal Molecular Cancer Research on January 18, 2024.
Breast cancer is the most common type of cancer, ranking fifth among all cancers in cancer-related deaths. In 2020, there were 2.3 million new cases of breast cancers reported around the globe. In that year, breast cancer caused ...
New tool provides researchers with improved understanding of stem cell aging in the brain
2024-03-27
MADISON — Researchers can use the light naturally thrown off by biological specimens to better study the different states of stem cells in the nervous system, thanks to a tool developed at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, brightening their chances for studying the way stem cells age.
The UW–Madison team combined autofluorescence — that natural light emission — and sequencing genetic material in single cells to study the behavior of neural stem cells. Autofluorescence is often considered a hindrance, as it can obscure the glowing labels researchers use to track specific signals within a cell. In their new technique, however, the ...
Around half of people living with HIV in developed countries are now aged 50 years and over and at higher risk of becoming frail and having multiple comorbidities
2024-03-27
*Please mention the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2024, Barcelona, 27-30 April) if using this material*
A new research review to be presented at a pre-congress day for this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2024) will focus on the growing prevalence of HIV in older adults, with, using England as an example, half of adults accessing care aged now 50 years and older, and around 1 in 11 aged 65 years and older. Similar trends exist in Italy and other ...
You are never too old for an STI – more older adults being diagnosed with STIs such as gonorrhea and syphilis
2024-03-27
Infectious disease expert addresses how to manage the rise in sexually transmitted infections in older adults.
STIs in Americans aged 55 to 64 years have more than doubled over the past decade; in England the number of over 45s diagnosed with gonorrhoea and syphilis doubled between 2015 and 2019.
Availability of sildenafil (Viagra) in late 1990s had an impact on STIs in older men.
Sexual health campaigns overlook the needs and experiences of the baby boom generation.
Health professionals must be proactive in discussing sexual concerns and making sexual health a routine part of general health care for older adults.
**Note: ...
University of Minnesota researchers introduce enhanced brain signal analysis technique
2024-03-27
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (3/27/2024) — University of Minnesota Medical School researchers have introduced a new, refined method for analyzing brain signals, enhancing our understanding of brain functionality. This research has the potential to improve treatments for neurological conditions such as Parkinson's disease, pain, epilepsy and depression. The findings were recently published in NeuroImage.
"This breakthrough provides a more detailed understanding of the brain's complex activity, akin to upgrading from a basic telescope to a sophisticated space observatory,” said David Darrow, MD, MPH, an assistant ...
[1] ... [1243]
[1244]
[1245]
[1246]
[1247]
[1248]
[1249]
[1250]
1251
[1252]
[1253]
[1254]
[1255]
[1256]
[1257]
[1258]
[1259]
... [8791]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.