Demystifying “black box” audio models
2024-02-26
AI decision-making is now common in self-driving cars, patient diagnosis and legal consultation, and it needs to be safe and trustworthy. Researchers have been trying to demystify complex AI models by developing interpretable and transparent models, collectively known as explainable AI methods or XAI methods. A research team offered their insight specifically into audio XAI models in a review article published Jan. 23 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
Although audio tasks are less researched than visual tasks, their expressive power is not less important. Audio signals are easy to understand and communicate, as they typically depend less on expert explanations ...
JMIR Neurotechnology invites submissions on brain-computer interfaces (BCIs)
2024-02-26
JMIR Publications is pleased to announce a new theme issue in JMIR Neurotechnology exploring brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) that represent the transformative convergence of neuroscience, engineering, and technology. The peer-reviewed journal aims to bridge the gap between clinical neuroscience and information technology by providing a platform for applied human research in the field of neurology.
JMIR Neurotechnology welcomes submissions from scientists, clinicians, and technologists. PhD students and early career researchers are ...
Obesity disrupts normal liver function in mice
2024-02-26
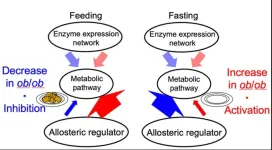
Your liver plays a vital role in your metabolism, the biological process which converts food into energy. We know that being overweight can negatively affect metabolic activity, but not exactly how. To better understand this, researchers compared the livers of mice which were a typical weight with mice which were obese. They were surprised to find that biological regulation of metabolic activity, after a period of feasting and fasting, was reversed between them. In typical mice, allosteric regulation (the process which controls metabolism) was inhibited during feeding and activated when fasting. However, ...
Watch these predatory fish use rapid color changes to coordinate attacks
2024-02-26
Striped marlin are some of the fastest animals on the planet and one of the ocean’s top predators. When hunting in groups, individual marlin will take turns attacking schools of prey fish one at a time. Now a new study reported in the journal Current Biology on February 5 helps to explain how they might coordinate this turn-taking style of attack on their prey to avoid injuring each other. The key, according to the new work, is rapid color changes.
“We documented for the first time rapid color change in a group-hunting predator, the striped marlin, as groups of marlin hunted schools of sardines,” says Alicia Burns of Humboldt University ...
Metal scar found on cannibal star
2024-02-26
When a star like our Sun reaches the end of its life, it can ingest the surrounding planets and asteroids that were born with it. Now, using the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope (ESO’s VLT) in Chile, researchers have found a unique signature of this process for the first time — a scar imprinted on the surface of a white dwarf star. The results are published today in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
“It is well known that some white dwarfs — slowly cooling embers of stars like our Sun — are ...
Treating adolescent opioid use disorder in primary care
2024-02-26
About The Study: This survey study found that primary care pediatricians felt less prepared to manage adolescents’ opioid use disorder (OUD) than alcohol, cannabis, or e-cigarette use and were more likely to refer them to offsite care. These results reveal an opportunity for greater workforce training in line with a 2019 survey showing fewer than 1 in 3 pediatric residency programs included education on prescribing OUD medications.
Authors: Scott E. Hadland, M.D., M.P.H., M.S., of Mass General for Children in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The ...
Use of tobacco products and suicide attempts among elementary school–aged children
2024-02-26
About The Study: The findings of this study of 8,988 preadolescent children suggest that the increased risk of suicide attempts, consistently reported for adolescents and adults who smoke cigarettes, extends to a range of emerging tobacco products and manifests among elementary school–aged children. Further investigations are imperative to clarify the underlying mechanisms and to implement effective preventive policies for children.
Authors: Phil H. Lee, Ph.D., of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Study of 1.2+M births in Sydney, Australia reveals associations between excess heat exposure and preterm births
2024-02-26
In the face of increasing temperatures globally, a new Monash-led study of 1.2 million births in Sydney over two decades has shown a strong association between the risk of pre-term birth and exposure to extreme hot temperatures in the third trimester of pregnancy. The data suggested that this association with extreme temperature might be reduced by the level of greenery in a pregnant person’s residential surrounds.
The findings suggest health services should consider preparing for an increase in preterm births as our climate warms.
The study, published in JAMA Pediatrics, looked at the relationship ...
Blindness from some inherited eye diseases may be caused by gut bacteria
2024-02-26
Sight loss in certain inherited eye diseases may be caused by gut bacteria, and is potentially treatable by antimicrobials, finds a new study in mice co-led by a UCL and Moorfields researcher.
The international study observed that in eyes with sight loss caused by a particular genetic mutation, known to cause eye diseases that lead to blindness, gut bacteria were found within the damaged areas of the eye.
The authors of the new paper, published in Cell and jointly led by researchers in China, say their findings suggest that the genetic mutation may relax the body’s defences, thus allowing harmful bacteria to reach the eye and cause blindness.
The gut contains trillions ...
Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis articles provide novel insights into previously unknown disease mechanisms
2024-02-26
DCM is the leading cause of heart failure in patients with chronic diabetes. However, the underlying mechanisms of DCM are poorly understood, and treatment options are limited. Another mystery is the regulation of cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYPs) in the central nervous system. Moreover, the link between the gut microbiome, microbiota-derived metabolites, and the progression of AD remains unknown. In the December issue of JPA, three articles provide insights into the pathologies of DCM, hippocampal neurotoxicity, and AD, providing a comprehensive ...
Enhancing electrogenerated chemiluminescence of an iridium complex
2024-02-26
Electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) cells, characterized by their self-emissive nature, have gathered significant interest for prospective display applications due to their uncomplicated structure and straightforward fabrication process. These cells are created by sandwiching a solution-based emitting layer between two transparent electrodes. Nevertheless, when compared to other self-emissive devices like light-emitting diodes (LED) and organic LEDs, the luminescent performance of ECL cells ...
The structure of HSV-1 gB bound to a potent neutralizing antibody reveals a conservative antigenic domain across herpesviruses
2024-02-26
Human herpesviruses comprise the alpha, beta, and gamma subfamilies and are a widely prevalent group of DNA-enveloped viruses, capable of establishing lifelong latent infections in humans and causing various diseases. Among them, herpes simplex virus (HSV) belongs to the alpha herpesvirus group and infects a wide population, causing symptoms like oral or genital herpes. As an enveloped virus, HSV possesses a series of glycoproteins involved in virus recognition, adhesion, and infection processes. Among these, gB serves as the viral fusion protein, mediating the fusion between the virus and host cell membranes, and ...
Fighting the flu: The surprising power of a century-old vaccine for tuberculosis
2024-02-26
As Canada’s flu season collides with record strep A cases and ongoing COVID-19 concerns, a new study is shedding light on our understanding of respiratory immune responses. Scholars from the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre (RI-MUHC) have discovered a surprising facet about a century-old vaccine for tuberculosis, Bacillus Calmette Guérin (BCG). The study, published in the journal Nature Immunology, uncovered a previously unknown mechanism that extends the vaccine’s shield to combat influenza A virus—the most prevalent flu strain.
“The immune interactions ...
The effects of primer pairs, PCR conditions, and peptide nucleic acid clamps on plant root fungal diversity assessment
2024-02-26
Fungi are frequently found both around and within plant tissues (especially in roots) and are involved in both plant nutrient acquisition and resistance to pathogens. Thus, characterizing the diversity and composition of plant-associated fungal communities has been a growing interest in recent years.
High-throughput sequencing (HTS), also called metabarcoding, has become a prominent tool to assess complex microbial communities from environmental samples. However, HTS applied to plant-associated ...
Can hunger be eradicated by 2030?
2024-02-26
World hunger is growing at an alarming rate, with prolonged conflicts, climate change, and COVID-19 exacerbating the problem. In 2022, the World Food Programme helped a record 158 million people. On this trajectory, the United Nations’ goal to eradicate hunger by 2030 appears increasingly unattainable. New research at McGill University shines the spotlight on a significant piece of the puzzle: international food assistance.
With no global treaty in place, food aid is guided by a patchwork of international agreements and institutions. Using the concept of a “regime ...
A novel method for easy and quick fabrication of biomimetic robots with life-like movement
2024-02-26
Ultraviolet-laser processing is a promising technique for developing intricate microstructures, enabling complex alignment of muscle cells, required for building life-like biohybrid actuators, as shown by Tokyo Tech researchers. Compared to traditional complex methods, this innovative technique enables easy and quick fabrication of microstructures with intricate patterns for achieving different muscle cell arrangements, paving the way for biohybrid actuators capable of complex, flexible movements.
Biomimetic robots, which mimic the movements and biological functions of living organisms, are a fascinating area of research that ...
Austria isolates and genotypes Leptospira bacteria for the first time
2024-02-26
[Vienna, Feb 26 2024] — Leptospirosis is a globally distributed infectious disease that affects both animals and humans. While the infection is endemic in tropical regions, its incidence seems to increase in temperate regions. The serological diagnostic test used in routine to detect antibodies against the bacteria responsible for the disease performs better when local variants are used. In Austria, however, no locally circulating strain has been available to date. A new study, published in the latest issue of Scientific Reports, has now been able to close this research gap.
"In our study, ...
Major new funding supports early career investigators working on cures for pancreatic cancer
2024-02-26
Bethesda, MD (Feb. 26, 2024) — The AGA Research Foundation has announced a $1.4 million endowment grant from The Bern Schwartz Family Foundation. The AGA Institute will provide matching support, resulting in a $2.8 million endowment dedicated to advancing basic research in pancreatic cancer, the third leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S.
The endowment will fund a second AGA-Bern Schwartz Family Fund Research Scholar Award in Pancreatic Cancer. The first award, created in 2013, will also continue. Both awards provide selected early career-investigators with $100,000 per year for three years ...
Poison center calls for ‘magic mushrooms’ spiked after decriminalization, study finds
2024-02-26
Calls to U.S. poison centers involving psilocybin, or “magic mushrooms,” among adolescents and young adults rose sharply after several U.S. cities and states began decriminalizing the hallucinogen, University of Virginia School of Medicine researchers have found.
Psilocybin-related calls more than tripled among teens ages 13-19 from 152 to 464 and more than doubled among adults ages 20-25 from 125 to 294 between 2018 and 2022, according to anonymized data gathered from the National Poison Data System. Local and state efforts to decriminalize the possession, use and cultivation of psilocybin began in May 2019. Oregon and Colorado have decriminalized psilocybin, as ...
Researchers overestimate their own honesty
2024-02-26
The average researcher thinks they are better than their colleagues at following good research practice. They also think that their own research field is better than other research fields at following good research practice. This is shown in a new study by researchers at Linköping University, Sweden. The results point to a risk of becoming blind to one’s own shortcomings, according to the Linköping researchers.
“The starting point for the project is that there’s a bit of a crisis in the research world. Research misconduct or difficulties to replicate research results have been discovered in many studies. Credibility has been called into question,” ...
Tattoo inks don’t match the ingredients listed on the bottle
2024-02-26
When you get a tattoo, do you know what you’re putting under your skin? According to new Binghamton University research, the ingredient labels on tattoo ink don’t match the actual substances in the bottle.
Produced by the lab of Binghamton Univerity Assistant Professor of Chemistry John Swierk, “What’s in my ink: An analysis of commercial tattoo ink on the U.S. market” was recently published in the journal Analytical Chemistry.
Swierk’s lab explores the potential impact of light on tattoos and their chemical breakdown. Early on, doctoral student Kelli Moseman ...
May I have a quick word? Study shows talking faster is linked to better brain health as we age
2024-02-26
As we get older, we may start to notice it takes us longer to find the right words. This can lead to concerns about cognitive decline and dementia.
However, a new study by Baycrest and the University of Toronto suggests that talking speed is a more important indicator of brain health than difficulty finding words, which appears to be a normal part of aging. This is one of the first studies to look at both differences in natural speech and brain health among healthy adults.
“Our results indicate that changes in general talking speed may reflect changes in the brain,” says Dr. Jed Meltzer, ...
Vanishing forests and suffering children: The hidden toll of deforestation in Cambodia
2024-02-26
Deforestation, a critical consequence of human activity, has garnered significant attention due to its impact on environmental sustainability, biodiversity and climate change. However, an equally pressing yet less explored aspect is the relationship between deforestation and human health, especially in impoverished regions. Scientists have increasingly recognized the detrimental effects of deforestation on various aspects of human health, particularly among children. Studies reveal that children residing in areas with high deforestation rates are at an elevated risk of malaria, ...
Birth outcomes improve in states that extend driver’s licenses to undocumented immigrants, research finds
2024-02-26
In 2023, Rhode Island, Massachusetts and Minnesota joined a growing list of states that allow undocumented immigrants to obtain driver’s licenses if an applicant can provide certain documentation, such as a foreign birth certificate or passport and evidence of current residency in the state. Altogether, 19 states and the District of Columbia have similar legislation in place. And lawmakers in other states, such as Michigan and Oklahoma, have introduced similar legislation.
In many cases, these laws were passed ...
First-in-humans discovery reveals brain chemicals at work influencing social behavior
2024-02-26
In a study in today’s (Monday Feb. 26) Nature Human Behavior, scientists delve into the world of chemical neuromodulators in the human brain, specifically dopamine and serotonin, to reveal their role in social behavior.
The research, conducted in Parkinson's disease patients undergoing brain surgery while awake, homed in on the brain’s substantia nigra, a crucial area associated with motor control and reward processing.
Led by Virginia Tech computational neuroscientist Read Montague, the international team revealed ...
[1] ... [1363]
[1364]
[1365]
[1366]
[1367]
[1368]
[1369]
[1370]
1371
[1372]
[1373]
[1374]
[1375]
[1376]
[1377]
[1378]
[1379]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.