Revolutionary brain stimulation technique shows promise for treating brain disorders
2024-02-23
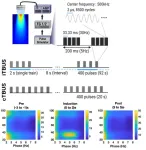
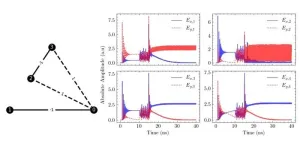
The human brain's adaptability to internal and external changes, known as neural plasticity, forms the foundation for understanding cognitive functions like memory and learning, as well as various neurological disorders. New research conducted by a team led by Dr. PARK Joo Min of the Center for Cognition and Sociality within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) unveils a novel technique that could transform the treatment landscape for brain disorders. The team developed a non-invasive brain stimulation method called Patterned Low-Intensity Low-Frequency Ultrasound (LILFUS), which holds tremendous potential for inducing long-lasting changes ...
Global warming increases the diversity of active soil bacteria
2024-02-23
Warmer soils harbour a greater diversity of active microbes, according to a new study from researchers at the Centre for Microbiology and Environmental Systems Science (CeMESS) at the University of Vienna. The study, published in Science Advances, represents a significant shift in our understanding of how microbial activity in the soil influences the global carbon cycle and possible feedback mechanisms on the climate. Until now, scientists have assumed that higher soil temperatures accelerate the growth of microbes, thus increasing the release of carbon into the atmosphere. However, this increased ...
Patient mindset training helps care teams
2024-02-23
A new study from Stanford University, published Jan. 19 in Patient Education and Counseling, evaluates the effectiveness of patient mindset training on provider learning and behavior.
Past research shows that what patients think, believe, or expect regarding medical care can influence care outcomes. Patients also have better outcomes when they have more adaptive mindsets about their treatments (e.g., “this treatment will be effective”), their bodies (e.g., “my body is capable”), their illnesses (e.g. “diabetes is manageable”), and their care team (e.g., “I am in good hands”). ...
Dual-energy harvesting device could power future wireless medical implants
2024-02-23
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Implantable biomedical devices — like pacemakers, insulin pumps and neurostimulators — are becoming smaller and utilizing wireless technology, but hurdles remain for powering the next-generation implants. A new wireless charging device developed by Penn State scientists could dramatically improve powering capability for implants while still being safe for our bodies, the researchers said.
The new device can harvest energy from magnetic field and ultrasound sources simultaneously, converting this energy to electricity to power implants, the scientists reported in the journal Energy & Environmental ...
Study: ‘Hexaplex’ vaccine aims to boost flu protection
2024-02-23
BUFFALO, N.Y. – Recombinant protein vaccines, like the Novavax vaccine used to fight COVID-19, offer several advantages over conventional vaccines.
They’re easy to precisely produce. They’re safe, and potentially more effective. And they could require smaller doses.
Because of these traits, there is much interest in developing recombinant influenza vaccines. To date, however, the Food and Drug Administration has approved only one such vaccine.
A University at Bufalo-led research team hopes to add to that number. It is developing a new recombinant flu vaccine – described ...
New structural insights could lead to mechanical enhancement in alloys
2024-02-23
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A new class of metallic materials with potential applications in airplane turbines, nuclear reactors and equipment for space exploration can withstand extreme temperatures and resist fractures, but scientists haven’t understood why until now. According to a new study co-led by Penn State researchers, the answer could relate to the material’s short-range order, or the local arrangement of atoms within a material. This knowledge could lead to further improvement in the mechanical performance and damage tolerance of these materials, the researchers said, leading in turn to advancements in the safety and reliability of next-generation ...
New research challenges conventional picture of Parkinson's disease
2024-02-23
Parkinson's disease, the second most common type of progressive dementia after Alzheimer's disease, affects nearly 1 million people in the U.S. and an estimated 10 million individuals worldwide. Each year, close to 90,000 new cases of Parkinson’s disease are diagnosed in the U.S.
In a new study, Jeffrey Kordower, director of the ASU-Banner Neurodegenerative Disease Research Center, and his colleagues unveil pivotal insights into the progression of Parkinson's disease, presenting new hope for patients battling the severely debilitating disorder.
The research highlights the role of a critical protein called tau in the early stages of the ...
Dairy cows fed botanicals-supplemented diets use energy more efficiently
2024-02-23
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Supplementing the feed of high-producing dairy cows with the botanical extract capsicum oleoresin, obtained from chili peppers, or a combination of that extract and clove oil resulted in the animals using feed energy more efficiently and emitting less methane from their largest stomach, according to a new study conducted by Penn State researchers.
Adding those substances, sometimes referred to as essential oils, to the cattle’s rations resulted in improved efficiency of energy utilization in peak-lactation dairy cows. According to Alex Hristov, distinguished professor of dairy nutrition, ...
Aston University receives nearly half a million pounds to create safer and greener batteries
2024-02-23
• Researchers to explore the use of gel electrolyte materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
• The batteries are the most commonly used in electric vehicles and electronics
• Will use non-harmful, non-flammable and renewably sourced materials for next generation battery technologies.
Aston University researchers are to explore the use of gel electrolyte materials to make lithium-ion batteries - the most commonly used for electric vehicles and electronics - safer and less environmentally damaging.
The University has received a grant of £443,058 from the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research ...
New study shows glycan sugar coating of IgG immunoglobulin can predict cardiovascular health
2024-02-23
When people hear about predicting heart disease, most will think of cholesterol levels. While cholesterol is a major contributor to heart disease, a recent study from Brigham and Women's Hospital, a founding member of Mass General Brigham, found that a glycan biomarker of IgG is also an important predictor for cardiovascular diseases (CVD). The researchers studied the sugar coatings on an antibody known as immunoglobulin G (IgG), which is implicated in the immune responses associated with chronic inflammation among participants in two case-control studies. The results of this investigation provide another biomarker for identifying risk of CVD, which could lead to earlier diagnosis ...
Sir Peter Rigby appointed as honorary chair of Aston University’s new Digital Futures Institute
2024-02-23
Sir Peter was knighted for his contribution to IT and businesses in the Midlands in 2002
He will provide guidance, support, advocacy and strong links to industry in his role
The Institute will drive digital innovation and ensure digital inclusion.
Aston University is delighted to announce that it has appointed one of the UK’s most respected and successful business leaders, Sir Peter Rigby, as honorary chair of its new Digital Futures Institute.
The announcement of Sir Peter’s appointment was made in front of guests at the inaugural lecture given by Professor Abdul Sadka, director of the Digital ...
Yale School of Medicine receives a $575,000 grant from PolyBio Research Foundation to fund long COVID research
2024-02-23
Yale School of Medicine and its Center for Infection & Immunity (CII) are receiving a $575,000 grant from PolyBio Research Foundation to fund Long COVID research. The grant—issued via PolyBio’s LongCovid Research Consortium (LCRC)— will support a collaboration to define mechanisms by which the SARS-CoV-2 virus can persist for long periods of time in tissue and blood.
There is growing evidence that SARS-CoV-2 may not fully clear from Long COVID patients after initial infection. Instead, reservoirs of the virus can persist in patient tissue for months or even years, with recent research finding the SARS-CoV-2 ...
Common plant could help reduce food insecurity, researchers find
2024-02-23
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — An often-overlooked water plant that can double its biomass in two days, capture nitrogen from the air — making it a valuable green fertilizer — and be fed to poultry and livestock could serve as life-saving food for humans in the event of a catastrophe or disaster, a new study led by Penn State researchers suggests.
Native to the eastern U.S., the plant, azolla caroliniana Willd — commonly known as Carolina azolla — also could ease food insecurity in the near future, according to findings ...
Innovative chemotherapy approach shows promise against lung cancer
2024-02-23
Lung cancer is not the most common form of cancer, but it is by far the deadliest.
Despite treatments such as surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy, only about a quarter of all people with the disease will live more than five years after diagnosis, and lung cancer kills more than 1.8 million people worldwide each year, according to the World Health Organization.
To improve the odds for patients with lung cancer, researchers from The University of Texas at Arlington and UT Southwestern Medical Center have pioneered a novel approach to deliver cancer-killing drugs directly into cancer cells.
“Our method ...
Encoding computers of the future
2024-02-23
In our data-driven era, solving complex problems efficiently is crucial. However, traditional computers often struggle with this task when dealing with a large number of interacting variables, leading to inefficiencies such as the von Neumann bottleneck. A new type of collective state computing has emerged to address this issue by mapping these optimization problems onto something called the Ising problem in magnetism.
Here's how it works: Imagine representing a problem as a graph, where nodes are connected by edges. Each node has two states, either +1 ...
Artifact could be linked to Spanish explorer Coronado's expedition across Texas Panhandle
2024-02-23
DALLAS (SMU) – It’s a small piece of obsidian, just over 5 centimeters long, likely found on a hard-scrabble piece of ranchland in the Texas panhandle. But when SMU anthropologist Matthew Boulanger looks at it, he gets a mental image of Spanish explorer Francisco Vasquez de Coronado making his way across the plains more than 470 years ago in search of a fabled city of gold.
Boulanger believes that the flaked-stone tool with its sharp edge was likely dropped by a member of Coronado’s ...
Do’s and don'ts with direct oral anticoagulants
2024-02-23
Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) are a common treatment for patients with a wide variety of cardiovascular conditions. DOACs are the preferred treatment over vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) for many patients with atrial fibrillation or venous thromboembolism, since the latter would have a higher risk of intracranial bleeding and more complex dosing routine. However, new research suggests that DOACs should not be the first line of treatment for every patient who need to treat or prevent blood clots. A systematic overview from researchers at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of Mass General Brigham, discusses the efficacy ...
Super strong magnetic fields leave imprint on nuclear matter
2024-02-23
UPTON, NY—A new analysis by the STAR collaboration at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC), a particle collider at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory, provides the first direct evidence of the imprint left by what may be the universe’s most powerful magnetic fields on “deconfined” nuclear matter. The evidence comes from measuring the way differently charged particles separate when emerging from collisions of atomic nuclei at this DOE Office of Science user ...
TMEM208 variants cause a new developmental disorder
2024-02-23
A recent study conducted in the lab of Dr. Hugo J. Bellen, distinguished service professor at Baylor College of Medicine and principal investigator at the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute at Texas Children’s Hospital, has discovered a biological role of a specific transmembrane protein called TMEM208.
The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, showed that a majority of fruit flies lacking this gene do not survive, and the few that do survive have many developmental defects. Similarly, a child with variants ...
Researchers explore whether gut microbes cause some COVID-19 patients to have higher blood clot risk
2024-02-23
A gut microbial metabolite called 2-methylbutyrylcarnitine (2MBC) plays a role in exacerbating thrombosis -- the formation of blood clots – researchers report February 23rd in the journal Cell Metabolism. The results also revealed that 2MBC is accumulated in individuals with COVID-19, potentially explaining why these patients are at increased risk of thrombosis.
“Our study provides mechanistic insight by implicating 2MBC as a metabolite that links gut microbiota dysbiosis to elevated thrombotic ...
Childhood factors associated with unnatural death through midadulthood
2024-02-23
About The Study: In this urban population-based cohort study of 2,180 participants, no modifiable risk factors of mortality at the level of the individual (e.g., depression or anxiety and substance use) or the family (e.g., household education level) were identified. However, the degree of neighborhood poverty in early childhood was significantly associated with death by unnatural causes (death due to unintentional injury, suicide, and homicide) in early adulthood, suggesting that economic policies are needed to advance health equity in relation to premature mortality.
Authors: Holly C. Wilcox, Ph.D., of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg ...
Severe COVID-19 in vaccinated adults with hematologic cancers in the Veterans Health Administration
2024-02-23
About The Study: In this case-control study including 6,122 patients with hematologic cancers and SARS-CoV-2 infection, odds of severe COVID-19 remained high through mid-2022 despite vaccination, especially in patients requiring treatment.
Authors: Paul A. Monach, M.D., Ph.D., of the VA Boston Cooperative Studies Program in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.0288)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
Recreational marijuana legalization and workplace injuries among younger workers
2024-02-23
About The Study: In this study, recreational marijuana laws that allow recreational marijuana sales were associated with a 10% increase in workplace injuries among individuals ages 20 to 34. The findings are consistent with the hypothesis that recreational marijuana impedes cognitive function and care among younger workers.
Authors: Joseph J. Sabia, Ph.D., of San Diego State University, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
New study identifies 13 strategies for advancing racial and ethnic equity in the academic health sciences
2024-02-23
BOSTON - Amid continued debate over how to advance diversity and equity in higher education following the Supreme Court’s decision striking down affirmative action, researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital and Northeastern University today issued a “roadmap” of strategies to help academic health institutions maintain their commitments to racial and ethnic diversity among their students, staff, and faculty in academic health sciences.
Their recommendations, published in JAMA Health Forum, outline 13 evidence-based strategies for increasing racial and ethnic equity in graduate-level health programs.
“This ...
School focus on grades, test scores linked to violence against teachers
2024-02-23
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Violence against teachers is likely to be higher in schools that focus on grades and test scores than in schools that emphasize student learning, a new study has found.
Researchers surveyed over 9,000 U.S. teachers shortly before and during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic about their perception of the instructional emphasis in their schools. Participants also reported whether they had been subjected to physical, verbal or property violence – by students, parents, colleagues and/or administrators.
Results ...
[1] ... [1365]
[1366]
[1367]
[1368]
[1369]
[1370]
[1371]
[1372]
1373
[1374]
[1375]
[1376]
[1377]
[1378]
[1379]
[1380]
[1381]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.