Hostile environment policies linked to prolonged distress in people with Black Caribbean ancestry
2024-02-14
Psychological distress increased among people with Black Caribbean heritage in the UK, relative to the White population, following the 2014 Immigration Act and the Windrush scandal, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The researchers say their findings, published in The Lancet Psychiatry, suggest a causal link between government policies and a subsequent decline in mental health.
They were investigating the impact of the Immigration Act 2014, requiring landlords, employers, the NHS, banks and the police to check right-to-stay documentation. This was a key part of a set of measures known as the Home Office hostile environment policy, seeking ...
Clinical trial shows rheumatoid arthritis drug could prevent disease
2024-02-14
A drug used to treat rheumatoid arthritis could also prevent the disease in individuals deemed to be at risk.
Results from a Phase 2b clinical trial, published today in The Lancet by researchers led by King’s College London, provides hope for arthritis sufferers after it was shown that the biologic drug abatacept reduces progression to this agonising chronic inflammatory disease.
Rheumatoid arthritis affects half a million people in the UK and develops when the body’s immune system attacks itself, causing joint pain, swelling and significant disability. The disease most commonly begins in middle age, but much younger age groups can be afflicted, and until ...
Do apes have humor?
2024-02-14
Babies playfully tease others as young as eight months of age. Since language is not required for this behavior, similar kinds of playful teasing might be present in non-human animals. Now cognitive biologists and primatologists from the University of California Los Angeles (UCLA, US), the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior (MPI-AB, Germany), Indiana University (IU, US), and the University of California San Diego (UCSD, US) have documented playful teasing in four species of great apes. Like joking behavior in humans, ape teasing is provocative, persistent, and includes elements of surprise and play. Because all four great ape species used playful teasing, it is likely that the ...
New digital therapy reduces anxiety and depression in people living with long-term physical health conditions
2024-02-14
A therapist-guided digital cognitive behavioural therapy reduced distress in 89 per cent of participants living with long-term physical health conditions, a new King’s College London study finds.
Researchers at the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King’s College London found that people living with long-term conditions who received the therapist-guided digital programme called COMPASS showed a significant reduction in psychological distress (a combined score of anxiety and depression) 12-weeks after starting the study.
194 patients were recruited via long-term condition charities, including Crohn’s & ...
Researchers edge closer to delivering personalized medicine to cancer patients
2024-02-14
For the first time, Purdue researchers prove that measuring mechanical motions in living cancer tissues is a viable and promising approach for predicting chemoresistance
Chemotherapy can save lives, but often a cancer patient may be resistant to their prescribed chemotherapy, which costs the patient valuable time. Chemoresistance is a topic that researchers need to understand better so that they can match the right type of chemo to the right patient, which is called personalized medicine.
An unusual pairing of veterinary scientists and physicists believe ...
Trail cameras track ‘critically low’ New York bobcat population
2024-02-13
CORNELL UNIVERSITY MEDIA RELATIONS OFFICE
FOR RELEASE: Feb. 13, 2024
Kaitlyn Serrao
607-882-1140
kms465@cornell.edu
Trail cameras track ‘critically low’ New York bobcat population
ITHACA, N.Y. – With thousands of strategically placed cameras covering more than 27,000 square miles in central and western New York, biologists have evidence that bobcat populations remain critically low in central and western New York state.
Despite reports of recent recoveries elsewhere, bobcat populations in New York State displayed low occupancy, ...
Virginia Tech researchers discover that blocking an essential nutrient inhibits malaria parasite growth
2024-02-13
Living organisms often create what is needed for life from scratch.
For humans, this process means the creation of most essential compounds needed to survive. But not every living thing has this capability, such as the parasite that causes malaria, which affected an estimated 249 million people in 2022.
Virginia Tech researchers in the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences found that by preventing the malaria parasite from scavenging fatty acids, a type of required nutrient, it could no longer grow.
“The key to this breakthrough is that we were able to develop a screening method for the malaria ...
Children's Hospital Los Angeles researchers uncover social and economic factors that influence acute liver failure in children—and ways to overcome them
2024-02-13
Imagine your healthy child gets sick—so sick that you take them to the emergency department. You are shocked to find out that their liver is failing, and they will need a transplant to survive. Studies show that their chances of survival are higher the faster they can get to a hospital that performs liver transplants. But what factors affect how quickly that happens?
Pediatric acute liver failure, also called PALF, is a life-threatening condition that emerges with very little warning in previously healthy children. It is rare, affecting about 5,000 children in the United States a year, and can result from viral ...
Uncovering insights about prostate cancer risk and genetic ancestry
2024-02-13
This study included larger groups of people from African, Hispanic and Asian ancestries than many other previous studies.
A recent study involving scientists from the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory has uncovered insights into the prostate cancer risks of people from a variety of genetic ancestries. The project, which was led by the University of Southern California, included large increases in representation among men of African, Hispanic and Asian ancestries, that were contributed in part by an ongoing collaboration between the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) and DOE as ...
A century of reforestation helped keep the eastern US cool
2024-02-13
American Geophysical Union
13 February 2024
AGU Release No. 24-5
For Immediate Release
This press release and accompanying multimedia are available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/a-century-of-reforestation-helped-keep-the-eastern-us-cool/
A century of reforestation helped keep the eastern US cool
Much of the U.S. warmed during the 20th century, but the eastern part of the country remained mysteriously cool. The recovery of forests could explain why
AGU press contact:
Liza Lester, +1 (202) 777-7494, news@agu.org (UTC-5 hours)
Contact information for the researchers:
Kim ...
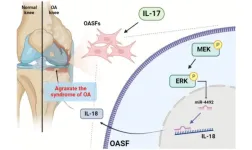
IL-17 promotes IL-18 production in osteoarthritis synovial fibroblasts via…
2024-02-13
“This study provides novel insights into the pathogenesis of OA and suggests a potential therapeutic target in OA treatment.”
BUFFALO, NY- February 13, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 2, entitled, “IL-17 promotes IL-18 production via the MEK/ERK/miR-4492 axis in osteoarthritis synovial fibroblasts.”
The concept of osteoarthritis (OA) as a low-grade inflammatory ...
New data speed record on optical fiber
2024-02-13
As data traffic continues to increase, there is a critical need for miniaturized optical transmitters and receivers that operate with high-order multi-level modulation formats and faster data transmission rates. In an important step toward fulfilling this requirement, researchers developed a new compact indium phosphide (InP)-based coherent driver modulator (CDM) and showed that it can achieve a record high baud rate and transmission capacity per wavelength compared to other CDMs. CDMs are optical transmitters used in optical communication systems that can put information on light by modulating the amplitude and phase before it is transmitted through optical fiber.
“Services that require ...
UBCO researchers get to the bottom of non-invasive gut tests
2024-02-13
New research from UBC Okanagan could make monitoring gut health easier and less painful by tapping into a common—yet often overlooked—source of information: the mucus in our digestive system that eventually becomes part of fecal matter.
Correct, what’s in our poop.
Researcher Dr. Kirk Bergstrom and post-graduate student Noah Fancy of UBCO's Biology department discovered a non-invasive technique to study MUC2, a critical gut protein, from what we leave behind in the bathroom.
“MUC2 is like the silent star in our guts. It’s constantly working ...
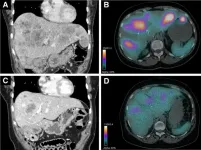
Radiopharmaceutical therapy controls symptoms and reduces medications in insulinoma patients
2024-02-13
Reston, VA—Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) is effective for clinical control of symptomatic metastatic insulinomas, according to new research published in the February issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. In the largest study to date of metastatic insulinoma patients treated with PRRT, more than 80 percent of patients had long-lasting symptom control, and nearly 60 percent were able to reduce the use of other drugs to treat the disease.
Metastatic insulinoma is a rare malignant neuroendocrine tumor characterized ...
First-of-its-kind ACC registry tracks cardiac procedures performed in ambulatory surgical settings
2024-02-13
The American College of Cardiology’s newest registry offers data-driven insights on cardiac procedures performed in the ambulatory surgery setting through its first-of-its-kind dashboard. The number of cardiac procedures being performed in ambulatory surgery centers has grown significantly in the last decade, leading ACC’s NCDR to create the CV ASC Registry Suite to fit into the established workflow and allow these facilities to measure and compare their patient care and outcomes to similar procedures performed in the hospital outpatient setting.
Ambulatory surgery centers (ASCs) are health care facilities that provide same-day surgical care, ...
Business operations affect fishermen's resilience to climate change, new study finds
2024-02-13
Timothy Frawley has spent the better of the past two decades working in and around commercial fisheries. Born and raised in Casco Bay, Maine, he grew up packing lobsters and pitching bait on Portland’s working waterfront. He has worked in commercial fisheries in California, Alaska and the Mexican state of Baja California Sur.
Throughout his years spent on working waterfronts, Frawley, a postdoctoral researcher affiliated with the University of Maine’s Darling Marine Center, closely observed the ways in which fishermen conducted their business, making decisions about what and how they fished, and how it affected their operations and profit.
“While ...
Not too late to repair: gene therapy improves advanced heart failure in animal model
2024-02-13
Heart failure remains the leading cause of mortality in the U.S. During a heart attack blood stops flowing into the heart. Without oxygen, part of the heart muscle dies. The heart muscle does not regenerate, instead it replaces dead tissue with a scar made of cells called fibroblasts that do not help the heart pump. If there is too much scarring, the heart progressively enlarges, or dilates, weakens and eventually stops working.
“The current thought is that advanced or chronic heart failure, a stage in which the cardiac muscle has become too weak, is a point of no return. The present ...
Seeking a middle ground for reducing greenhouse emissions
2024-02-13
As the world gradually transitions to making meaningful reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, one of the most crucial questions that needs to be answered is how much that change is going to cost.
The United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has put out reports on this potential cost that showed global greenhouse gas emissions can be reduced by at least half in 2030 at a cost of less than $100 per ton of CO2 equivalent. A new study from the University of Delaware, Yale University and Columbia University, however, points out that these estimates do not consider some hidden, underlying frictions ...
New study finds no significant association between preterm delivery and autism
2024-02-13
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL: Feb. 13, 2024, 3:00 PM EST
Media Contacts: Karen Addis, APR, karen@addispr.com, +1 (301) 787-2394; Kerri Wade, MPA, kwade@smfm.org, +1 (202) 236-1780
National Harbor, Md. -- Autism, also known as Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), is one of the most common developmental disorders and is increasingly diagnosed worldwide. According to the World Health Organization, an estimated one in 100 children has autism. In the U.S., those numbers are much higher, with an estimated one in 36 children being diagnosed with autism, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Research into the causes of autism, specifically whether there is ...
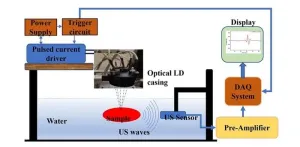
Advancing biomedical diagnostics: Compact photoacoustic sensing instrument for breast tissue characterization
2024-02-13
In the realm of biomedical sciences, the quest for accurate and efficient diagnostic tools is ever-evolving. One such promising innovation making waves is the photoacoustic (PA) technique. In the past decade, PA imaging has emerged as a viable imaging modality demonstrated in many clinical applications with promising outcomes. Unlike traditional methods, PA offers a noninvasive approach to probing biological tissues, yet the technique has still been limited in wide clinical applications, partially due to bulky and expensive laser sources.
In a recent study published in the Journal of Biomedical Optics, researchers from the Indian Institute of Technology Indore ...
Updating allocation algorithms could help donor hearts reach the transplant patients who need them most
2024-02-13
Receiving a heart transplant is a matter of life and death for many patients. Every time a heart becomes available, a “match run” is created to generate a list of transplant candidates ranked by an algorithm based on medical urgency, geography and pediatric status. Unfortunately, deceased donor organs are very scarce in the United States – so much so that some patients aren’t even placed on waitlists because it’s too unlikely that a heart will become available to them.
A research team led by experts at the University of Chicago Medicine developed a new risk score designed to predict the likelihood that ...
New study reveals dynamic impact of nicotine on brain regions responsible for reward and aversion
2024-02-13
HUNTINGTON, W.Va. – A new study led by researchers at the Marshall University Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine sheds light on the intricate interplay of brain regions involved in nicotine's effects on the human brain.
The research, published in eNeuro, an open-access, peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Society for Neuroscience, explores how nicotine influences key areas associated with reward and aversion, showcasing a nuanced relationship that varies based on dosage, sex and distinct brain regions. The medial ...
New assay identifies clinically relevant gene fusions in pediatric tumors more accurately and efficiently
2024-02-13
Philadelphia, February 13, 2024 – Identification of specific gene fusions is critical for the successful targeted treatment of pediatric cancer patients. Researchers at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles have developed a novel assay that automatically integrates the data from multiple fusion identification tools (callers) and efficiently and accurately identifies clinically relevant gene fusions in pediatric tumors. Their results are reported in The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, published by ...
Pediatric sickle cell disease team uses pain screening to improve care
2024-02-13
CLEVELAND -- A recent study from researchers at University Hospitals (UH) Connor Whole Health and UH Rainbow Babies & Children’s Hospital describes a quality improvement project where pain screening procedures were embedded within an outpatient pediatric sickle cell disease (SCD) clinic. The study examined (1) the feasibility of routine pain screening, (2) the prevalence of various clinical pain presentations, and (3) what integrative health and medicine modalities were preferred by youth aged 8 to 18 with SCD.
The study, entitled “Pain Screening in Youth with Sickle Cell Disease: A Quality Improvement ...
Grantees selected for The Mark Foundation for Cancer Research and the Samuel Waxman Cancer Research Foundation Aging and Cancer Initiative
2024-02-13
New York, NY – February 13, 2024 – The Mark Foundation for Cancer Research and the Samuel Waxman Cancer Research Foundation (SWCRF) have selected six investigators to receive three grants for their collaborative, two-year program aimed at improving our understanding of the links between aging and cancer. With additional support from the Melanoma Research Alliance (MRA), $1.5 million will fund three innovative projects, each pairing one lab focused on aging with another working on cancer research.
Aging is a major risk factor for developing and dying of cancer. In fact, 90 percent of cancer diagnoses and deaths occur in people ...
[1] ... [1373]
[1374]
[1375]
[1376]
[1377]
[1378]
[1379]
[1380]
1381
[1382]
[1383]
[1384]
[1385]
[1386]
[1387]
[1388]
[1389]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.