New study finds that pregnancy complications can also affect child’s health later in life
2024-02-12
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) and gestational diabetes (GDM) are two of the most common pregnancy complications and put pregnant people at increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease later in life.
Now, in a new study to be presented today at the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine’s (SMFM) annual meeting, The Pregnancy Meeting™, researchers will unveil findings that suggest these pregnancy complications may also result in worse cardiovascular health for the child.
In a secondary analysis of 3,317 maternal-child pairings from the prospective Hyperglycemia ...
Scientists discover biological mechanism of hearing loss caused by loud noise – and find a way to prevent it
2024-02-12
Anyone who has ever been to a loud concert knows the feeling of ringing ears. Some people experience temporary or even permanent hearing loss or drastic changes in their perception of sound after the loud noises stop. Thanos Tzounopoulos, Ph.D., director of the Pittsburgh Hearing Research Center at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine has focused his scientific career on investigating how hearing works and developing ways to treat tinnitus and hearing loss.
In a paper published today in ...
Widespread machine learning methods behind ‘link prediction’ are performing very poorly
2024-02-12
As you scroll through any social media feed, you are likely to be prompted to follow or friend another person, expanding your personal network and contributing to the growth of the app itself. The person suggested to you is a result of link prediction: a widespread machine learning (ML) task that evaluates the links in a network — your friends and everyone else’s — and tries to predict what the next links will be.
Beyond being the engine that drives social media expansion, link prediction is also used in a wide range of scientific research, such as predicting the interaction between genes and proteins, and is used by researchers as a benchmark for ...
The hidden rule for flight feathers—and how it could reveal which dinosaurs could fly
2024-02-12
Birds can fly— at least, most of them can. Flightless birds like penguins and ostriches have evolved lifestyles that don’t require flight. However, there’s a lot that scientists don’t know about how the wings and feathers of flightless birds differ from their airborne cousins. In a new study in the journal PNAS, scientists examined hundreds of birds in museum collections and discovered a suite of feather characteristics that all flying birds have in common. These “rules” provide clues as to how the dinosaur ancestors of modern birds first evolved the ability to fly, ...
Machine learning promises to accelerate metabolism research
2024-02-12
A new study shows that it is possible to use machine learning and statistics to address a problem that has long hindered the field of metabolomics: large variations in the data collected at different sites.
“We don’t always know the source of the variation,” said Daniel Raftery, professor of anesthesiology and pain medicine at the University of Washington School of Medicine in Seattle. “It could be because the subjects are different with different genetics, diets and environmental exposures. Or it could be the way samples were collected and ...
Researchers uncover a key link in legume plant-bacteria symbiosis
2024-02-12
Legume plants have the unique ability to interact with nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the soil, known as rhizobia. Legumes and rhizobia engage in symbiotic relations upon nitrogen starvation, allowing the plant to thrive without the need for externally supplied nitrogen. Symbiotic nodules are formed on the root of the plant, which are readily colonized by nitrogen-fixing bacteria. The cell-surface receptor SYMRK (symbiosis receptor-like kinase) is responsible for mediating the symbiotic signal from rhizobia perception to formation of the nodule. ...
Genetic analysis and archaeological insight combine to reveal the ancient origins of the fallow deer
2024-02-12
Modern populations of fallow deer possess hidden cultural histories dating back to the Roman Empire which ought to be factored into decisions around their management and conservation.
New research, bringing together DNA analysis with archaeological insights, has revealed how fallow deer have been repeatedly moved to new territories by humans, often as a symbol of colonial power or because of ancient cultures and religions.
The results show that the animal was first introduced into Britain by the Romans ...
Researchers studying ocean transform faults, describe a previously unknown part of the geological carbon cycle
2024-02-12
Woods Hole, Mass. (February 12, 2024) – Studying a rock is like reading a book. The rock has a story to tell, says Frieder Klein, an associate scientist in the Marine Chemistry & Geochemistry Department at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI).
The rocks that Klein and his colleagues analyzed from the submerged flanks of the St. Peter and St. Paul Archipelago in the St. Paul’s oceanic transform fault, about 500 km off the coast of Brazil, tells a fascinating and previously unknown story about parts of the geological ...
Salt substitutes help to maintain healthy blood pressure in older adults
2024-02-12
The replacement of regular salt with a salt substitute can reduce incidences of hypertension, or high blood pressure, in older adults without increasing their risk of low blood pressure episodes, according to a recent study in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology. People who used a salt substitute had a 40% lower incidence and likelihood of experiencing hypertension compared to those who used regular salt.
According to the World Health Organization, hypertension is the leading risk factor for cardiovascular disease and mortality. It affects over 1.4 billion adults and results in 10.8 million deaths per year worldwide. One of the ...
Heart disease risk factors in women highlight need for increased awareness, prevention
2024-02-12
Statement Highlights:
The new scientific statement highlights heart disease as the leading cause of death for women and emerging evidence that has identified several gender-specific risk factors for heart disease in women, including complications during pregnancy and premature menopause.
Compared to men, women also have different symptoms of heart disease, are less likely to receive evidence-based therapies and are more likely to have adverse cardiovascular outcomes after a cardiac event.
Targeted public health interventions ...
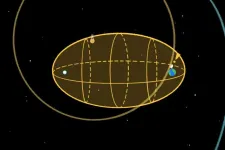
SETI institute employs SETI ellipsoid technique for searching for signals from distant civilizations
2024-02-12
February 12, 2024, Mountain View, CA -- In a paper published in the Astronomical Journal, a team of researchers from the SETI Institute, Berkeley SETI Research Center and the University of Washington reported an exciting development for the field of astrophysics and the search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI), using observations from the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) mission to monitor the SETI Ellipsoid, a method for identifying potential signals from advanced civilizations in the ...
Sugar-reduced chocolate with oat flour just as tasty as original, study finds
2024-02-12
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — The secret to making delicious chocolate with less added sugar is oat flour, according to a new study by Penn State researchers. In a blind taste test, recently published in the Journal of Food Science, 25% reduced-sugar chocolates made with oat flour were rated equally, and in some cases preferred, to regular chocolate. The findings provide a new option for decreasing chocolate’s sugar content while maintaining its texture and flavor.
“We were able to show that there is a range in which you can ...
AI-supported image analysis: metrics determine quality
2024-02-12
How well do the algorithms used in the AI-supported analysis of medical images perform their respective tasks? This depends to a large extent on the metrics used to evaluate their performance. An international consortium led by scientists from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) and the National Center for Tumor Diseases (NCT) in Heidelberg has compiled the knowledge available worldwide on the specific strengths, weaknesses and limitations of the various validation metrics. With "Metrics Reloaded", the researchers are ...
Innovative decarbonization: UH researcher offers carbon-driven framework to accelerate shift toward net-zero electric power sector
2024-02-12
Houston, Texas, the epicenter of the global energy market, and the University of Houston – the Energy University – are leading the transition towards a cleaner, more sustainable future with innovative solutions.
With three-quarters of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions stemming from burning fossil fuels for energy, it's clear that the key to curbing emissions lies in reimagining how energy is produced and consumed. In Texas, the shift is already well on its way. Technologies like giant batteries, ...
White people more likely to confront authors of racist online posts to set discussion rules
2024-02-12
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — White people surveyed in a recent study indicated they would be more likely to confront those who post racist content on social media if their objective were to defend the norms for political discussions rather than to change the person’s prejudiced beliefs.
Communication professors Stewart M. Coles of the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and Daniel S. Lane of the University of California, Santa Barbara surveyed people during the 2020 U.S. presidential election cycle to explore the conditions under ...
University of Rhode Island Nutrition study to help inform official USDA dietary guidelines
2024-02-12
Ultra-processed foods make up more than half the food average Americans eat. Including frozen and prepared meals, most packaged snacks, desserts and carbonated soft drinks—but also including more innocuous foods—they are often considered the bane of healthy eating, containing little to no nutrition to fuel healthy bodies.
However, “not all processed foods are created equal,” according to University of Rhode Island Nutrition Professor Kathleen Melanson. Evidence to support the assumption that ultra-processed foods are all bad for one’s health is limited, and the nutritional ...
Number of at-risk youth with intellectual disability and autism in the U.S. foster care system is growing
2024-02-12
Youth with foster care involvement have an increased risk for mental health diagnoses, trauma and worse outcomes in adulthood than their peers. Research about how youth with disabilities, including autism and intellectual disability, interact with this system is lacking. Evidence for how youth with autism or intellectual disability in the foster care system access and use services is needed to advance ways to improve their outcomes.
Recently published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) Pediatrics, researchers at Drexel University’s A.J. Drexel Autism Institute, in collaboration with George Mason University’s ...
Multiple city hubs, dispersed parks keep metro areas cooler
2024-02-12
ITHACA, N.Y. – Metropolitan areas with multiple city centers and dispersed green spaces mitigate extreme heat more effectively than those with one dominant city, an analysis by Cornell University city planning scholars finds.
Compared to “monocentric” development, “polycentric” spatial patterns better distribute the density of urban cores and curb the sprawl of impervious, heat-absorbing surfaces, according to the analysis of 50 city regions in Germany. Particularly in larger urban areas, polycentric development can moderate the urban heat island effect, ...
Innovation to overcome deficiencies in 3D printing
2024-02-12
The University of Houston is collaborating with Texas A&M University to tackle the challenge hindering the use of Additive Manufacturing (AM), commonly known as 3D printing, for a variety of commercial applications – the need for real-time monitoring and analysis to ensure consistent quality and reproducibility throughout the production process.
At present, quality control and qualification of metal AM parts is mostly carried out through offline inspection and characterization, but ideally, a broad range of sub-surface and bulk microstructural ...
Novel bispecific design improves CAR T–cell immunotherapy for childhood leukemia
2024-02-12
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – February 12, 2024) St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital scientists improved chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T–cell immunotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia (AML), demonstrating better efficacy in the lab. To overcome common problems with CAR T cells, the researchers created an additional means for the therapy to find and eliminate cancer cells, using a small peptide. The study also showed how a computational approach incorporating AlphaFold predicted protein models could help ...
Including socioeconomic status of patients in calculation of Medicare readmission penalties would reduce stress on safety-net hospitals
2024-02-12
INDIANAPOLIS -- The Affordable Care Act requires Medicare to issue penalties that reduce payment to hospitals if post-operative readmission rates within 30 days exceed the national average. A new study led by Regenstrief Institute Research Scientist Andrew Gonzalez, M.D., J.D., MPH, reports that including socioeconomic status in the penalty calculation would reduce the amount of readmission penalties for safety-net hospitals, which typically care for the sickest patients. Other factors, including age and sex are ...
Are ammonia engines the way of the future? (video)
2024-02-12
WASHINGTON, Feb. 12, 2024 — Could ammonia engines power the cars of the future? Carmakers like Toyota are working to make this a reality. Ammonia is combustible and holds promise as a relatively low-effort way to decarbonize the internal combustion engine — but the devil’s in the details. Join George as he discovers at least one of those details by burning stuff in his basement. https://youtu.be/KZ_NlnmPQYk?si=BleQF9-aReuttCU4
Reactions is a video series produced by the American Chemical Society and PBS Digital Studios. Subscribe to Reactions at http://bit.ly/ACSReactions ...
Prevalence of young children fed only breast milk in low- and middle-income countries
2024-02-12
About The Study: In this study of 276,000 children ages 6 to 23 months in 92 low- and middle-income countries, 10.4% were zero-food children (i.e., children who did not consume any animal milk, formula, or solid or semisolid food during the last 24 hours). The prevalence of zero-food children underscores the need for targeted interventions to improve infant and young child feeding practices and ensure optimal nutrition during this critical period of development. The issue is particularly urgent in West and Central ...
Emergency department use disparities among transgender and cisgender Medicare beneficiaries
2024-02-12
About The Study: The results of this study suggested that transgender and gender-diverse Medicare beneficiaries use significantly more emergency department services than cisgender beneficiaries, particularly for psychological care, and these visits were more likely to be followed by an admission. This study quantifies this excess use of emergent services and highlights upstream implications of delays in seeking timely health care.
Authors: Gray Babbs, M.P.H., of the Brown University School of Public Health in Providence, Rhode Island, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our ...
Foster care involvement among youth with intellectual and developmental disabilities
2024-02-12
About The Study: This study found that among youth with intellectual and developmental disabilities, Black youth and females faced higher risk for foster care involvement, and the likelihood of foster care involvement increased with age. There is an urgent need for research that focuses on addressing system-level factors that drive increased risk. Understanding the specific health needs of Black and female youth with intellectual and developmental disabilities is critical to ensure the formation, ...
[1] ... [1376]
[1377]
[1378]
[1379]
[1380]
[1381]
[1382]
[1383]
1384
[1385]
[1386]
[1387]
[1388]
[1389]
[1390]
[1391]
[1392]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.