Early-life exposure to air pollution and childhood asthma cumulative incidence
2024-02-28
About The Study: In this study of 5,279 children, early life air pollution was associated with increased asthma incidence by early and middle childhood, with higher risk among minoritized families living in urban communities characterized by fewer opportunities and resources and multiple environmental co-exposures. Reducing asthma risk in the U.S. requires air pollution regulation and reduction combined with greater environmental, educational, and health equity at the community level.
Authors: Antonella Zanobetti, Ph.D., ...
Hourly heat exposure and acute ischemic stroke
2024-02-28
About The Study: The results of this study of 82,000 patients with acute ischemic stroke suggest that hourly heat exposure is associated with increased risk of acute ischemic stroke onset. This finding may benefit the formulation of public health strategies to reduce cerebrovascular risk associated with high ambient temperature under global warming.
Authors: Jing Zhao, Ph.D., and Haidong Kan, Ph.D., of Fudan University in Shanghai, China, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.0627)
Editor’s ...
CityUHK develops world-leading microwave photonics chip for high-speed signal processing
2024-02-28
A research team led by Professor Wang Cheng from the Department of Electrical Engineering (EE) at City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) has developed a world-leading microwave photonic chip that is capable of performing ultrafast analog electronic signal processing and computation using optics.
The chip, which is 1,000 times faster and consumes less energy than a traditional electronic processor, has a wide range of applications, covering 5/6G wireless communication systems, high-resolution radar systems, artificial intelligence, computer vision, and image/video processing.
The team's research findings were published in the prestigious scientific ...
The “switch” that keeps the immune system from attacking the body
2024-02-28
A microscopic battle rages in our bodies, as our cells constantly fend off invaders through our immune system, a complex system of cells and proteins designed to protect us from harmful pathogens. One of its central components is the enzyme cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS), which acts as a sentinel, detecting foreign DNA and initiating an immune response.
However, the immune system requires precise regulation to prevent cGAS from mistakenly attacking the body's own tissues, leading to autoimmune disorders, which now affect about 10% of the global population.
Previous studies have revealed a little of how this ...
Study unravels the earliest cellular genesis of lung adenocarcinoma
2024-02-28
HOUSTON ― Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center built a new atlas of lung cells, uncovering new cellular pathways and precursors in the development of lung adenocarcinoma, the most common type of lung cancer. These findings, published today in Nature, open the door for development of new strategies to detect or intercept the disease in its earliest stages.
Led by Humam Kadara, Ph.D., professor of Translational Molecular Pathology and Linghua Wang, M.D., Ph.D., associate professor of Genomic Medicine, the team generated an atlas of around 250,000 normal and cancerous ...
Change in gene code may explain how human ancestors lost tails
2024-02-28
A genetic change in our ancient ancestors may partly explain why humans don’t have tails like monkeys, finds a new study led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine.
Published online February 28 as the cover story of the journal Nature, the work compared the DNA of tail-less apes and humans to that of tailed monkeys, and found an insertion of DNA shared by apes and humans, but missing in monkeys. When the research team engineered a series of mice to examine whether the insertion, in a gene called TBXT, affected their tails, they found a variety of tail effects, including some mice born without tails. ...
Risk of hospital readmission after surgery is high for older Americans
2024-02-28
New Haven, Conn. — A new Yale study finds an increased risk of hospital readmission for older Americans within 180 days of undergoing major surgery — a risk that is particularly acute for individuals who are frail or have dementia.
The findings were published Feb. 28 in the journal JAMA Network Open.
Previous research by the same Yale team demonstrated that major surgery is a common event for older Americans and also demonstrated a heightened mortality risk within one year of major surgery for people who are age 65 and older. The new study is the first to describe both the short-term risk (within 30 days) and longer-term ...
How molecular “handedness” emerged in early biology
2024-02-28
LA JOLLA, CA—Molecules often have a structural asymmetry called chirality, which means they can appear in alternative, mirror-image versions, akin to the left and right versions of human hands. One of the great mysteries about the origins of life on Earth is that virtually all of the fundamental molecules of biology, such as the building blocks of proteins and DNA, appear in just one chiral form.
Scripps Research chemists, in two high-profile studies, have now proposed an elegant solution to this mystery, showing how this single-handedness or “homochirality” could have become established in biology.
The studies were published in the Proceedings ...
The James Webb Space Telescope reveals the central role of low-mass galaxies in the reionization process of the Universe
2024-02-28
PARIS, France and BEER-SHEVA, Israel, February 28, 2024 – The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST)[1], developed by NASA and ESA, has just obtained the first spectra of very low-mass galaxies less than a billion years after the Big Bang. A technological feat made possible by the unique combination of JWST sensitivity and the gravitational lensing effect of the Abell 2744 cluster: nearby galaxies act like cosmic magnifiers, distorting space and amplifying the light of background galaxies. By demonstrating that small galaxies are very likely at the origin of the reionization of the universe, this discovery represents a major breakthrough in our knowledge of the cosmos.
The international research ...
Immunotherapy combination may benefit patients with transplanted kidneys and advanced skin cancers
2024-02-28
People who have had a kidney transplant are at high risk for developing skin cancers. New research directed by investigators from the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center is exploring the best combination of treatments to target skin cancers while preserving the transplanted organs.
Now, they report results from a clinical trial testing a novel drug combination designed to stimulate the immune system to fight advanced, potentially lethal skin cancers while not permanently damaging patients’ transplanted kidneys. The treatment included two immune-suppressing drugs ...
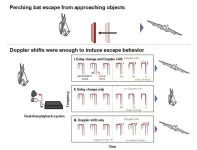
Nature’s sonar: Scientists reveal how Japanese horseshoe bats perceive moving objects
2024-02-28
Unlike most animals that rely on visual senses, bats navigate and locate prey or obstacles through echolocation. By emitting sounds and comparing them to the reflected echoes, bats can “visualize” movement in the environment. When sound waves encounter a moving object, they can undergo changes such as a Doppler shift in frequency or experience a delay, which the bat can sense. However, it is unclear which acoustic characteristics bats rely on to detect moving objects.
Japanese horseshoe bats (Rhinolophus ferrumequinum nippon) emit ultrasound pulses that are characterized ...
Dimensions Research GPT – evidence-based research insights for ChatGPT platform users
2024-02-28
Digital Science is pleased to announce the launch of two new products – Dimensions Research GPT and Dimensions Research GPT Enterprise – bringing the unmatched, trusted research coverage of Dimensions to the ChatGPT platform.
Users can get AI-generated answers to research-related questions on the GPT platform informed by Dimensions’ huge database, making ChatGPT more research-specific for topic exploration.
Available to users of both the free and paid Dimensions Analytics web application, Dimensions Research GPT and Dimensions Research GPT Enterprise help overcome ...
Calcium crystal deposits in the knee contribute to joint damage
2024-02-28
(Boston)— Knee osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis, affecting approximately 600 million people worldwide and 34 million people in the U.S. There are no treatments available that prevent its progression to date. Recommended pharmacological treatments for symptoms have either small-to moderate effects or short-term effects, often with side effects, and lifestyle behaviors such as exercise and weight loss are under-utilized.
Historically, intra-articular mineralization (IAM) or calcium crystal deposits in the joint, were thought to be of no clinical consequence, and perhaps just something that happens with older ...
International team led by BSC develops artificial intelligence technology to improve treatment of rare diseases
2024-02-28
An international team of scientists led by ICREA researcher and Director of the Life Sciences Department at the Barcelona Supercomputing Centre - Centro Nacional de Supercomputación (BSC-CNS), Alfonso Valencia, has developed a technology based on artificial intelligence (AI) for the study of minority diseases and has successfully applied it to identify the possible causes of the appearance of what are known as myasthenic-congenital syndromes, a group of rare inherited disorders that limit the ability to move and cause varying degrees of muscle weakness in patients.
The lack of available data on minority, also known as rare, diseases makes research in this area extremely ...
Anti-cancer drug could improve symptoms after stroke
2024-02-28
A study by the Institut de Neurociències of the UAB (INc-UAB) demonstrates in animal models the benefits of vorinostat after having suffered a stroke. The drug, used in humans to treat cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, has been proved to mitigate brain injuries and help in restoring brain tissue.
Ischemic stroke is the second leading cause of death worldwide and occurs when blood flow cannot reach the brain due to an obstruction. For a more or less long period of time, the brain does not receive oxygen and this causes damage and functional impairment. Hypertension is the most frequent modifiable risk factor for stroke and is associated with worse recoveries.
Currently, ...
Consumers empowered with the facts on dairy’s nutritional benefits buy and consume more dairy foods
2024-02-28
Philadelphia, February 28, 2024 – Although most Americans consume dairy and many dairy foods are rising in popularity, fluid milk consumption has seen a significant decline among US consumers since the 1960s. To reverse this trend—and ensure consumers are getting adequate amounts of dairy in their diets—the dairy sector has developed educational materials to reach consumers through informational infographics and TV and print ads, and on social media. But do these kinds of educational ...
How air pollution can harm team performance
2024-02-28
High levels of air pollution can harm performance of teams, which are vital for solving complex problems such as developing clean energy technologies and vaccines, and this could harm economic development in highly polluted emerging economies, says a new study co-authored at Cambridge Judge Business School.
The study used data from 15,000 live escape-room games in London. It estimated based on the data and the study’s equations that for about 3,500 teams that participated for team-building exercises (usually from a corporate ...
Online toxicity can only be countered by humans and machines working together, according to Concordia researchers
2024-02-28
Wading through the staggering amount of social media content being produced every second to find the nastiest bits is no task for humans alone.
Even with the newest deep-learning tools at their disposal, the employees who identify and review problematic posts can be overwhelmed and often traumatized by what they encounter every day. Gig-working annotators, who analyze and label data to help improve machine learning, can be paid pennies per unit worked.
In a new Concordia-led paper published in IEEE Technology and Society Magazine, researchers argue that supporting ...
SwRI sponsors Future Leaders Program at 2024 ITS America Conference & Expo
2024-02-28
SAN ANTONIO– February 28, 2024 – Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) and ITS Arizona are inviting college students to participate in the Future Leaders Program at this year’s ITS America Conference & Expo, April 22-25, at the Phoenix Convention Center.
The Future Leaders Program allows the next generation of intelligent transportation systems (ITS) leaders to attend education sessions and meet with exhibitors, sponsors and technology providers, all while networking with ITS professionals who can offer career advice and mentorship.
“The ITS industry is continuously looking for smart and creative people to ...
New LOINC® semiannual release highlights health equity work with national and international partners
2024-02-28
LOINC® from Regenstrief Institute’s semiannual content update highlights the comprehensive nature of its work with international partners, including supporting interoperability for prescription drug records, reporting notifiable conditions and standardizing social risk screening tools to represent social determinants of health (SDOH) information in electronic health records (EHRs).
LOINC release 2.77 includes more than 800 new concepts and edits to more than 1,500 concepts. Work captured in the new release includes support for molecular genetic drug and toxicology ...
New study unveils scalable and efficient photoelectrode modules for green hydrogen production
2024-02-28
In a groundbreaking development towards practical photoelectrochemical water splitting, a research team in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST, led by Professors Jae Sung Lee, Ji-Wook Jang, and Sang Il Seok, in collaboration with Professor Hankwon Lim from the Graduate School of Carbon Neutrality at UNIST, has achieved a remarkable technological breakthrough in the production of green hydrogen. Through their innovative approach, the team has overcome the challenges of efficiency, stability, and scalability in photoelectrodes, paving the way for ...
Sedentary behavior increases mortality risk
2024-02-28
Based on decades-long observations of centenarians, author Dan Buettner (Blue Zones) conjectures that people live longer when they get up and move around after sitting for twenty minutes. Now, a rigorous new study published in the Journal of the American Heart Association (JAHA) has data showing that older women who sat for 11.7 hours or more per day increased their risk of death by 30 percent, regardless of whether they exercised vigorously.
Study co-author Steve Nguyen, Ph.D., M.P.H., a postdoctoral fellow at the University of California San Diego Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human Longevity Science, ...
New approach may prevent deadly intestinal disease in preemies
2024-02-28
Scientists from Stanley Manne Children’s Research Institute at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and colleagues found that an investigational protein replacement – recombinant human insulin-like growth factor 1 and its binding protein-3 (rhIGF-1/BP3) – protected neonatal mice from necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), a deadly intestinal disease that often strikes extremely premature infants. Results were published in the journal Pediatric Research.
“Our preclinical evidence is encouraging and paves the way to a clinical trial of rhIGF-1/BP3 for prevention of NEC,” said senior author Isabelle De Plaen, MD, a scientist ...
Endocrine Society supports federal legislation protecting IVF access
2024-02-28
WASHINGTON—The Endocrine Society is calling for members of Congress to support federal legislation protecting access to in vitro fertilization (IVF).
The Access to Family Building Act (S.3612/H.R.7056), proposed by Sens. Tammy Duckworth (D-IL), Patty Murray (D-WA), and Rep. Susan Wild (D-PA), would ensure people can access safe, effective IVF and other assisted reproductive technologies to start or grow their families.
Families’ access to IVF services is being threatened by an Alabama State Supreme Court ruling that frozen embryos ...
World’s first metamaterial developed to enable real-time shape and property control
2024-02-28
Inspired by the remarkable adaptability observed in biological organisms like the octopus, a breakthrough has been achieved soft machines. A research team, led by Professor Jiyun Kim in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at UNIST has successfully developed an encodable multifunctional material that can dynamically tune its shape and mechanical properties in real-time. This groundbreaking metamaterial surpasses the limitations of existing materials, opening up new possibilities for applications in robotics and other fields requiring adaptability.
Current soft machines lack the level of adaptability demonstrated by their ...
[1] ... [1356]
[1357]
[1358]
[1359]
[1360]
[1361]
[1362]
[1363]
1364
[1365]
[1366]
[1367]
[1368]
[1369]
[1370]
[1371]
[1372]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.