Reproducing the Moon's surface environment on Earth
2024-02-27
Continuous research is being conducted globally on using the Moon as an advanced base for deep space exploration, and Korea is no exception in these efforts. The Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim, Byung-suk) successfully implemented an electrostatic environment that simulates the Moon's surface conditions, not in space but on Earth. The researchers also assessed its performance and effectiveness.
Among the most serious threats in executing lunar missions is the Moon's surface environment, which is electrostatically charged. Due to its extremely thin atmosphere, the Moon is directly exposed to solar ultraviolet rays, X-rays, ...
Social media and adolescent mental health
2024-02-27
In an editorial, Sandro Galea and Gillian Buckley summarize the findings of a National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine consensus study report on social media and adolescent mental health. Social media has to some extent been treated as a monolith, but the report finds that different types of engagements with different digital platforms may have very different effects on mental health. In some situations, social media may benefit adolescent mental health, as when LGBTQ+ adolescents in isolating circumstances are able to form supportive ...
How decades of expertise with the fourth state of matter could bring satellites closer to Earth
2024-02-27
Thousands of satellites take pictures, gather information and relay internet traffic from high above the Earth. Now, the challenge is making satellites that operate closer to home, in what is called a very low earth orbit (VLEO), where there is ample space for additional satellites, and the pictures taken would be clearer.
Working at an altitude with air would mean more force would be needed to propel the satellite forward, but many scientists believe there is also an advantage: the air could be used as the propellant. They say charged particles of air-breathing plasma – the fourth state of matter – could be used to propel the thrusters, potentially ...
Living near pubs, bars and fast-food restaurants could be bad for heart health
2024-02-27
Research Highlights
Closer proximity to and a higher number of ready-to-eat food outlets — particularly pubs, bars and fast-food restaurants — may be associated with a greater risk of developing heart failure, according to a study of half a million adults in the UK Biobank.
The association between food environments and increased heart failure risk was stronger among people who did not have a college degree and those living in urban areas without access to facilities for physical activity such as gyms or fitness centers.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Tuesday, Feb. 27, 2024
DALLAS, Feb. 27, 2024 — Living close to pubs, bars and fast-food restaurats may ...
Research adds to knowledge about heart disease and stroke in women of all ages
2024-02-27
Research Highlights:
Women’s heart disease and stroke risks and outcomes differ throughout life in comparison to men.
A special Journal of the American Heart Association “spotlight” issue features a collection of the latest research about sex differences in cardiovascular disease and their implications for gender-specific care.
Among the topics in this issue: the impact of sedentary behavior on heart disease risk in older women; sex differences in the relationship between schizophrenia and the development ...
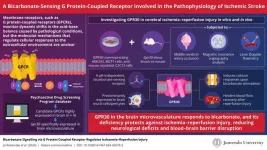
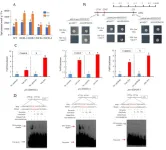
Innovative therapies for ischemic stroke: Novel bicarbonate-sensing G protein-coupled receptor shows promise
2024-02-27
Cells actively rely on maintaining an appropriate acid-base balance to support optimal function. Under normal physiological settings, the pH inside cells remains within a controlled range. However, disruptions in this equilibrium have been linked to a wide range of health conditions, both minor and catastrophic. Changes in the extracellular environment are monitored by “membrane receptors,” of which the G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are a large family of membrane proteins that mediate multiple cellular responses. However, the role of GPR30, also known as G protein-coupled estrogen ...
AI-driven lab speeds catalysis research
2024-02-27
Researchers have developed a “self-driving” lab that uses artificial intelligence (AI) and automated systems to provide in-depth analyses of catalytic reactions used in chemical research and manufacturing. The new tool, called Fast-Cat, can provide more information in five days than is possible in six months of conventional testing.
At issue are the yield and selectivity of chemical reactions in the presence of molecules called ligands.
Yield refers to how efficiently a chemical reaction produces a desired product from the chemicals you started with. Selectivity refers ...
Unveiling the sustainability landscape in cultural organizations: A global benchmark
2024-02-27
Are museums, theaters, and opera houses truly walking the talk when it comes to social and environmental sustainability? The University of Lausanne (UNIL) delved into this pressing question, conducting an international survey with over 200 major cultural organizations. The verdict? While there's significant room for improvement across the spectrum, Anglophone countries lead the charge.
Cultural organizations, with their wide-reaching influence and power to shape narratives and imaginations, are poised to ...
The mechanism of SlWRKY80 participating in salt alkali stress through its involvement in JA metabolic pathway
2024-02-27
Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) is the most widely cultivated and consumed horticultural crop. At present, saline–alkali is an important abiotic stress source that affects tomato production. Exogenous methyl jasmonate (MeJA) can enhance the resistance of tomatoes to various stress, but its exact mechanism is still unclear.
In January 2024, Horticulture Research published a research entitled by “SlWRKY80-mediated jasmonic acid pathway positively regulates tomato resistance to saline-alkali stress by enhancing spermidine content and stabilizing ...
Abdominal fat can impact brain health and cognition in high Alzheimer’s risk individuals
2024-02-27
The impact of abdominal fat on brain health and cognition is generally more pronounced in middle-aged men at high risk of Alzheimer’s disease as opposed to women, according to researchers at Rutgers Health.
In middle-aged individuals with a family history of Alzheimer’s disease, the amount of fat in their abdominal organs (pancreas, liver, and belly fat) is related to their brain volumes and cognitive function, according to the study published in the journal Obesity. The study was written by Sapir Golan Shekhtman, a Ph.D. student at the Joseph Sagol Neuroscience Center at the Sheba Medical Center in Israel and led by ...
New data analysis supports hedonic overdrive model in high-fat diet-induced mice
2024-02-27
ROCKVILLE, Md.— High-fat diets cause obesity in male mice. The underlying mechanism, however, remains controversial. After assessing three contrasting ideas, researchers have determined that the hedonic overdrive model provides the best fit, according to a new study published in the journal Obesity, The Obesity Society’s (TOS) flagship journal.
“Our work provides some direction as to why high-fat/high-carb macronutrient combinations stimulate overconsumption. The study is in mice so we ...
Pythagoras was wrong: there are no universal musical harmonies, new study finds
2024-02-27
The tone and tuning of musical instruments has the power to manipulate our appreciation of harmony, new research shows. The findings challenge centuries of Western music theory and encourage greater experimentation with instruments from different cultures.
According to the Ancient Greek philosopher Pythagoras, ‘consonance’ – a pleasant-sounding combination of notes – is produced by special relationships between simple numbers such as 3 and 4. More recently, scholars have tried to find psychological explanations, but these ‘integer ratios’ are still credited with making a chord sound beautiful, and deviation from them ...
Researchers uncover new clues about links between parent age and congenital disorders
2024-02-27
A new paper in Genome Biology and Evolution, published by Oxford University Press, finds that the link between paternal age and rare congenital disorders is more complex than scientists had previously thought. While researchers have long realized that older fathers are more likely to have children with bone and heart malformations, such as Achondroplasia, Apert, or Noonan syndrome or neurodevelopmental disorders, schizophrenia, and autism, new examination indicates that while the link between some pathogenic mutations increases with paternal age, others do not and may even occur in the father’s testis before sexual maturity.
Delayed fatherhood results in a higher ...
Study reveals parental smoking and childhood obesity link transcends socio-economic boundaries
2024-02-27
A study into parental smoking and childhood obesity has challenged previous notions by revealing that the links between the two are not confined to a specific socio-economic group.
The data shows a strong correlation between parents who smoke and their children’s consumption of high calorie unhealthy foods and drinks, across social classes.
Using longitudinal data on 5,000 Australian children collected over a 10-year period, the research found those living with parents who smoke, on average, eat less healthy, higher calorie food such as fruit juice, sausages, fries, snacks, full fat milk products, ...
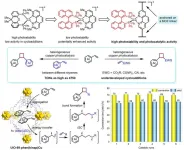
HKU chemists pave the way for sustainable organic synthesis with innovative heterogeneous copper photocatalysis, enabling efficient production of diverse bioactive compounds
2024-02-27
Professor Jian HE, from the Department of Chemistry at The University of Hong Kong (HKU), has spearheaded a research endeavour aimed at revolutionising organic synthesis. His research team has successfully developed a novel heterogeneous copper photocatalyst that enables the efficient formation of cyclobutane rings, a crucial structural element in a vast array of bioactive molecules. Cyclobutane rings are prominently featured in pharmaceuticals, natural products, and various biologically active compounds. By enabling researchers to construct these rings easily and selectively, ...
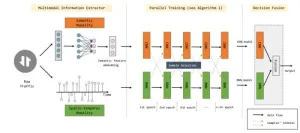
Using multimodal deep learning to detect malicious traffic with noisy labels
2024-02-27
The success of a deep learning-based network intrusion detection systems (NIDS) relies on large-scale, labeled, realistic traffic. However, automated labeling of realistic traffic, such as by sand-box and rule-based approaches, is prone to errors, which in turn affects deep learning-based NIDS.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Yuefei ZHU published their new research on 15 Feb 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
The team ...
Learning and memory problems in down syndrome linked to alterations in genome's ‘dark matter’
2024-02-27
Researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) reveal that the Snhg11 gene is critical for the function and formation of neurons in the hippocampus. Experiments with mice and human tissues revealed the gene is less active in brains with Down syndrome, potentially contributing to the memory deficits observed in people living with the condition. The findings are published today in the journal Molecular Psychiatry.
Traditionally, much of the focus in genomics has been on protein-coding genes, which in humans constitutes around just 2% of the entire genome. The rest is "dark ...
Race, racism, and covid-19 in the US: lessons not learn
2024-02-27
In The BMJ today, Keisha Bentley-Edwards at Duke University, North Carolina, and colleagues argue that systemic racism and economic inequality are at the root of disparity in covid-19 outcomes and suggest how to distribute resources more equitably.
The article is part of a series that highlights the lessons that can be learned from the US’s covid-19 experience and the actions that are needed to prevent the loss of another million citizens in the next pandemic and improve and protect population health.
"Rather than waiting for the next pandemic to address systemic failures, the ...
Low-Temperature Plasma used to remove E. coli from hydroponically grown crops
2024-02-27
A group led by researchers at Nagoya University and Meijo University in Japan has developed a disinfection technology that uses low-temperature plasma generated by electricity to cultivate environmentally friendly hydroponically grown crops. This innovative technology sterilizes the crops, promoting plant growth without the use of chemical fertilizers. Their findings appeared in Environmental Technology & Innovations.
In hydroponic agriculture, farmers cultivate plants by providing their roots with a nutrient solution. However, the nutrient solution can become infected with pathogenic E. coli strains, contaminating the crop and leading to foodborne illnesses.
To avoid ...
UK cancer treatment falls behind other countries
2024-02-27
Two major studies part-funded by Cancer Research UK reveal that the use of chemotherapy and radiotherapy in the UK has lagged behind comparable countries in the past decade
Patients faced longer waits to begin key cancer treatment, which could be impacting people’s chances of survival in the UK
With an upcoming UK general election, Cancer Research UK is calling on political leaders to step up and ensure patients get the level of care that they deserve
People in the UK were treated with chemotherapy ...
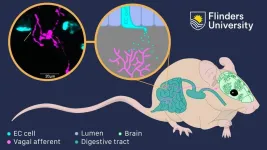
Gut-brain communication turned on its axis
2024-02-27
The mechanisms by which antidepressants and other emotion-focused medications work could be reconsidered due to an important new breakthrough in the understanding of how the gut communicates with the brain.
New research led by Flinders University has uncovered major developments in understanding how the gut communicates with the brain, which could have a profound impact on the make-up and use of medications such as antidepressants.
“The gut-brain axis consists of complex bidirectional neural communication pathway between the brain and the gut, which links emotional and cognitive ...
NSF and DOE establish a Research Coordination Network dedicated to enhancing privacy research
2024-02-27
In response to the rapidly evolving landscape of data collection and analysis driven by advances in artificial intelligence, the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) and the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) have established a Research Coordination Network (RCN) dedicated to advancing privacy research and the development, deployment and scaling of privacy enhancing technologies (PETs). Fulfilling a mandate from the "Executive Order on the Safe, Secure, and Trustworthy Development and Use of Artificial Intelligence," the initiative advances the recommendations in the National Strategy to Advance ...
Want to encourage allyship? Highlight its appreciation, research shows
2024-02-27
Allyship — the practice of relatively advantaged group members acting with the intention to support, advocate and improve circumstances for relatively disadvantaged groups — is critical to promoting more inclusive and equitable organizations.
Not only are advantaged group members typically received more favorably within an organization than disadvantaged group members would be when they speak out against injustice, their allyship can improve disadvantaged group members’ psychological experience in the organization. For instance, men are more likely to believe other men, compared with women, when they confront sexism. And Black Americans report higher levels of self-esteem ...
UM School of Medicine awarded $3.5 million in federal funding to expand medical countermeasures program
2024-02-26
University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) Dean Mark T. Gladwin, MD, announced today that UMSOM faculty scientists have been selected as key contractors by the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA), for the federal agency’s Radiation Nuclear Animal Model Development program. The $3.5 million award that Erika Davies, PhD, Assistant Professor of Radiation Oncology, received to develop Acute Radiation Syndrome Animal Models, has a $16 million potential total. The Division of Translational Radiation Sciences (DTRS), within the Department of Radiation Oncology, will support this project.
Dr. Davies and her colleagues ...
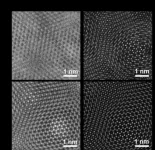
Reimagining electron microscopy: Bringing high-end resolution to lower-cost microscopes
2024-02-26
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have shown for the first time that expensive aberration-corrected microscopes are no longer required to achieve record-breaking microscopic resolution.
The field of microscopy is in the middle of a great revolution. Since the 1800s and the invention of the compound light microscope, there have only been a few major jumps in resolution to see different length scales: from bacteria and cells, to viruses and proteins, and even down to single atoms. Generally, ...
[1] ... [1348]
[1349]
[1350]
[1351]
[1352]
[1353]
[1354]
[1355]
1356
[1357]
[1358]
[1359]
[1360]
[1361]
[1362]
[1363]
[1364]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.