International team led by BSC develops artificial intelligence technology to improve treatment of rare diseases
2024-02-28
An international team of scientists led by ICREA researcher and Director of the Life Sciences Department at the Barcelona Supercomputing Centre - Centro Nacional de Supercomputación (BSC-CNS), Alfonso Valencia, has developed a technology based on artificial intelligence (AI) for the study of minority diseases and has successfully applied it to identify the possible causes of the appearance of what are known as myasthenic-congenital syndromes, a group of rare inherited disorders that limit the ability to move and cause varying degrees of muscle weakness in patients.
The lack of available data on minority, also known as rare, diseases makes research in this area extremely ...
Anti-cancer drug could improve symptoms after stroke
2024-02-28
A study by the Institut de Neurociències of the UAB (INc-UAB) demonstrates in animal models the benefits of vorinostat after having suffered a stroke. The drug, used in humans to treat cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, has been proved to mitigate brain injuries and help in restoring brain tissue.
Ischemic stroke is the second leading cause of death worldwide and occurs when blood flow cannot reach the brain due to an obstruction. For a more or less long period of time, the brain does not receive oxygen and this causes damage and functional impairment. Hypertension is the most frequent modifiable risk factor for stroke and is associated with worse recoveries.
Currently, ...
Consumers empowered with the facts on dairy’s nutritional benefits buy and consume more dairy foods
2024-02-28
Philadelphia, February 28, 2024 – Although most Americans consume dairy and many dairy foods are rising in popularity, fluid milk consumption has seen a significant decline among US consumers since the 1960s. To reverse this trend—and ensure consumers are getting adequate amounts of dairy in their diets—the dairy sector has developed educational materials to reach consumers through informational infographics and TV and print ads, and on social media. But do these kinds of educational ...
How air pollution can harm team performance
2024-02-28
High levels of air pollution can harm performance of teams, which are vital for solving complex problems such as developing clean energy technologies and vaccines, and this could harm economic development in highly polluted emerging economies, says a new study co-authored at Cambridge Judge Business School.
The study used data from 15,000 live escape-room games in London. It estimated based on the data and the study’s equations that for about 3,500 teams that participated for team-building exercises (usually from a corporate ...
Online toxicity can only be countered by humans and machines working together, according to Concordia researchers
2024-02-28
Wading through the staggering amount of social media content being produced every second to find the nastiest bits is no task for humans alone.
Even with the newest deep-learning tools at their disposal, the employees who identify and review problematic posts can be overwhelmed and often traumatized by what they encounter every day. Gig-working annotators, who analyze and label data to help improve machine learning, can be paid pennies per unit worked.
In a new Concordia-led paper published in IEEE Technology and Society Magazine, researchers argue that supporting ...
SwRI sponsors Future Leaders Program at 2024 ITS America Conference & Expo
2024-02-28
SAN ANTONIO– February 28, 2024 – Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) and ITS Arizona are inviting college students to participate in the Future Leaders Program at this year’s ITS America Conference & Expo, April 22-25, at the Phoenix Convention Center.
The Future Leaders Program allows the next generation of intelligent transportation systems (ITS) leaders to attend education sessions and meet with exhibitors, sponsors and technology providers, all while networking with ITS professionals who can offer career advice and mentorship.
“The ITS industry is continuously looking for smart and creative people to ...
New LOINC® semiannual release highlights health equity work with national and international partners
2024-02-28
LOINC® from Regenstrief Institute’s semiannual content update highlights the comprehensive nature of its work with international partners, including supporting interoperability for prescription drug records, reporting notifiable conditions and standardizing social risk screening tools to represent social determinants of health (SDOH) information in electronic health records (EHRs).
LOINC release 2.77 includes more than 800 new concepts and edits to more than 1,500 concepts. Work captured in the new release includes support for molecular genetic drug and toxicology ...
New study unveils scalable and efficient photoelectrode modules for green hydrogen production
2024-02-28
In a groundbreaking development towards practical photoelectrochemical water splitting, a research team in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST, led by Professors Jae Sung Lee, Ji-Wook Jang, and Sang Il Seok, in collaboration with Professor Hankwon Lim from the Graduate School of Carbon Neutrality at UNIST, has achieved a remarkable technological breakthrough in the production of green hydrogen. Through their innovative approach, the team has overcome the challenges of efficiency, stability, and scalability in photoelectrodes, paving the way for ...
Sedentary behavior increases mortality risk
2024-02-28
Based on decades-long observations of centenarians, author Dan Buettner (Blue Zones) conjectures that people live longer when they get up and move around after sitting for twenty minutes. Now, a rigorous new study published in the Journal of the American Heart Association (JAHA) has data showing that older women who sat for 11.7 hours or more per day increased their risk of death by 30 percent, regardless of whether they exercised vigorously.
Study co-author Steve Nguyen, Ph.D., M.P.H., a postdoctoral fellow at the University of California San Diego Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human Longevity Science, ...
New approach may prevent deadly intestinal disease in preemies
2024-02-28
Scientists from Stanley Manne Children’s Research Institute at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and colleagues found that an investigational protein replacement – recombinant human insulin-like growth factor 1 and its binding protein-3 (rhIGF-1/BP3) – protected neonatal mice from necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), a deadly intestinal disease that often strikes extremely premature infants. Results were published in the journal Pediatric Research.
“Our preclinical evidence is encouraging and paves the way to a clinical trial of rhIGF-1/BP3 for prevention of NEC,” said senior author Isabelle De Plaen, MD, a scientist ...
Endocrine Society supports federal legislation protecting IVF access
2024-02-28
WASHINGTON—The Endocrine Society is calling for members of Congress to support federal legislation protecting access to in vitro fertilization (IVF).
The Access to Family Building Act (S.3612/H.R.7056), proposed by Sens. Tammy Duckworth (D-IL), Patty Murray (D-WA), and Rep. Susan Wild (D-PA), would ensure people can access safe, effective IVF and other assisted reproductive technologies to start or grow their families.
Families’ access to IVF services is being threatened by an Alabama State Supreme Court ruling that frozen embryos ...
World’s first metamaterial developed to enable real-time shape and property control
2024-02-28
Inspired by the remarkable adaptability observed in biological organisms like the octopus, a breakthrough has been achieved soft machines. A research team, led by Professor Jiyun Kim in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at UNIST has successfully developed an encodable multifunctional material that can dynamically tune its shape and mechanical properties in real-time. This groundbreaking metamaterial surpasses the limitations of existing materials, opening up new possibilities for applications in robotics and other fields requiring adaptability.
Current soft machines lack the level of adaptability demonstrated by their ...
Pancreatic cancer lives on mucus
2024-02-28
Knowing exactly what’s inside a tumor can maximize our ability to fight cancer. But that knowledge doesn’t come easy. Tumors are clusters of constantly changing cancer cells. Some become common cancer variants. Others morph into deadlier, drug-resistant varieties. No one truly understands what governs this chaotic behavior.
Now, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor David Tuveson and his team have uncovered a mechanism involved in pancreatic cancer transformation—mucus. During the disease’s early stage, pancreatic cancer cells produce mucus. Additionally, these cells depend on the body’s regulators of mucus production. This new ...
Want fewer microplastics in your tap water? Try boiling it first
2024-02-28
Nano- and microplastics are seemingly everywhere — water, soil and the air. While many creative strategies have been attempted to get rid of these plastic bits, one unexpectedly effective solution for cleaning up drinking water, specifically, might be as simple as brewing a cup of tea or coffee. As reported in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology Letters, boiling and filtering calcium-containing tap water could help remove nearly 90% of the nano- and microplastics present.
Contamination of water supplies with nano- and microplastics (NMPs), which can be as small as one thousandth of a millimeter ...
AGA announces 12-point plan to improve the care of all patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
2024-02-28
Bethesda, MD (Feb. 28, 2024) — Today, the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) published a white paper on the future of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) care in the United States. AGA highlights the current barriers to care and calls for collaboration among our healthcare community, insurers, pharmaceutical companies and legislators to improve and optimize care for the more than three million Americans living with IBD.
IBD is a complex disease that requires a vigilant and coordinated multidisciplinary approach. ...
Shedding light on the intricacies of numerical simulations of soil behavior
2024-02-28
A solid understanding of soil mechanics and behavior is one of the fundamental pillars of geotechnical engineering. The stability and resilience of many modern geotechnical structures, including building foundations, dams, bridges, and embankments, rely on appropriate modelling based on accurate measurements of soil properties.
Over the past few decades, unprecedented growth in computing power has turned numerical simulations of soil behavior into an attractive tool in geotechnical engineering. By representing soil as a set of interacting particles, numerical simulations can help researchers understand complex soil behavior under various conditions. Moreover, numerical ...
Promising pathways to simplified Alzheimer's diagnosis unveiled in groundbreaking study
2024-02-28
Washington D.C., Feb. 28, 2024- The Global Alzheimer’s Platform Foundation®, (GAP) is releasing the first results from the Bio-Hermes-001 Study. This study in over 1000 community-based participants from throughout the US compared the results of blood and digital biomarkers with brain amyloid PET scans or cerebrospinal fluid assays. The study revealed a strong correlation between several blood tests, particularly p-tau 217, with the presence of amyloid plaques in the brain, a diagnostic hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). This relationship was demonstrated across the entire study ...
Understanding genetic risk could save sight and predict multiple sclerosis earlier in young people
2024-02-28
Young people could be spared from going blind by a new genetic risk tool that could also help diagnose multiple sclerosis (MS) earlier, to start effective treatments.
Optic neuritis is a condition that affects people of all ages, but especially young adults, usually manifesting in blurred vision and sometimes pain when moving the eyes. Up to half of people affected in the UK eventually go on to develop MS – often many years later. Emerging evidence indicates that starting the very effective MS treatments earlier may improve long term health.
Optic neuritis occurs because of swelling in or around the optic nerve. For those with MS-related optic neuritis, the swelling subsides ...
Cannabis use linked to increase in heart attack and stroke risk
2024-02-28
Research Highlights:
An analysis of survey data for 430,000 adults in the U.S. found that using cannabis has a significant association with an increased risk of heart attack and stroke, independent of tobacco use, with higher odds among the adults with more frequent use (more days of use per month). The most common method of cannabis use was smoking, followed by eating or vaporizing it.
The increase in the combined risk of coronary heart disease, heart attack and stroke was similar to the risk among the subset of adults who had never used e-cigarettes but did use cannabis.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, February ...
Researchers model blood-brain barrier using “Tissue-in-a-CUBE" system
2024-02-28
A research team at the RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics Research (BDR) in Japan has succeeded in establishing a model of the blood-brain barrier using modularized tissue derived from human cells. The “Tissue-in-a-CUBE” is a small cubic structure that could provide a boost in the drug discovery field and be used as an alternative to animal models in pre-clinical studies. The study was published in Communications Biology on February 28.
The blood-brain barrier is a strict gatekeeper around the brain that prevents foreign substances in blood from entering the brain. Although protective, the barrier poses challenges when treatments ...
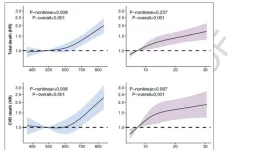
Study identifies blood biomarkers to predict risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
2024-02-28
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Rheumatoid arthritis is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease, but it can be challenging to predict which individuals are at highest risk.
Mass General Brigham experts in rheumatology and cardiovascular disease worked together to identify six biomarkers found in blood samples that can predict future risk of arterial inflammation among patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
The team is now working to test these biomarkers in a larger and more long-term cohort of patients with rheumatoid ...
Ai finds key signs that predict patient survival across dementia types
2024-02-28
New York, NY [February 28, 2024]—Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and others have harnessed the power of machine learning to identify key predictors of mortality in dementia patients.
The study, published in the February 28 online issue of Communications Medicine [10.1038/s43856-024-00437-7], addresses critical challenges in dementia care by pinpointing patients at high risk of near-term death and uncovers the factors that drive this risk. Unlike previous studies that focused on diagnosing dementia, this research delves into predicting patient prognosis, shedding light on mortality ...
Light stimulates a new twist for synthetic chemistry
2024-02-28
Molecules that are induced by light to rotate bulky groups around central bonds could be developed into photo-activated bioactive systems, molecular switches, and more.
Researchers at Hokkaido University, led by Assistant Professor Akira Katsuyama and Professor Satoshi Ichikawa at the Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, have extended the toolkit of synthetic chemistry by making a new category of molecules that can be induced to undergo an internal rotation on interaction with light. Similar processes are believed to be important in some natural biological systems. Synthetic versions might ...
More than just neurons: A new model for studying human brain inflammation
2024-02-28
LA JOLLA (February 28, 2024)—The brain is typically depicted as a complex web of neurons sending and receiving messages. But neurons only make up half of the human brain. The other half—roughly 85 billion cells—are non-neuronal cells called glia. The most common type of glial cells are astrocytes, which are important for supporting neuronal health and activity. Despite this, most existing laboratory models of the human brain fail to include astrocytes at sufficient levels or at all, which limits the models’ utility for studying ...
Urgent need to develop best practices to advance use of AI in cardiovascular care
2024-02-28
Statement Highlights:
The American Heart Association encourages research and development of artificial intelligence (AI) and other related tools and services that may support and enable more precise approaches to cardiovascular and stroke research, prevention and care.
Academia, industry and governments worldwide are pouring resources into developing AI-based tools to transform how and when health care is delivered.
While promising research is beginning to emerge in many areas of cardiovascular medicine, AI-based tools, algorithms and systems of care have not yet been proven to improve care enough to justify widespread use.
AI and machine learning digital tools currently exist that ...
[1] ... [1343]
[1344]
[1345]
[1346]
[1347]
[1348]
[1349]
[1350]
1351
[1352]
[1353]
[1354]
[1355]
[1356]
[1357]
[1358]
[1359]
... [8822]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.