Radiation from massive stars shapes planetary systems
2024-02-29
How do planetary systems such as the Solar System form? To find out, CNRS scientists taking part in an international research team1 studied a stellar nursery, the Orion Nebula, using the James Webb Space Telescope2. By observing a protoplanetary disc named d203-506, they have discovered the key role played by massive stars in the formation of such nascent planetary systems3.
These stars, which are around 10 times more massive, and more importantly 100,000 times more luminous than the Sun, expose any planets forming in such systems nearby to very intense ultraviolet radiation. Depending on the mass of the star at the centre of the planetary system, this radiation can either help planets to ...
Climate change disrupts seasonal flow of rivers
2024-02-29
Climate change is disrupting the seasonal flow of rivers in the far northern latitudes of America, Russia and Europe and is posing a threat to water security and ecosystems, according to research published today.
A team of scientists led by the University of Leeds analysed historical data from river gauging stations across the globe and found that 21% of them showed significant alterations in the seasonal rise and fall in water levels.
The study used data-based reconstructions and state-of-the-art simulations to show that river flow is now far less likely to vary with the seasons in latitudes ...
Researchers reveal mechanism of how the brain forms a map of the environment
2024-02-29
When you walk into your kitchen in the morning, you easily orient yourself. To make coffee, you approach a specific location. Maybe you step into the pantry to grab a quick breakfast and then head to your car to drive to your workplace.
How these apparently simple tasks happen is of major interest to neuroscientists at Baylor College of Medicine, Stanford University and collaborating institutions. Their work, published in the journal Science, has significantly improved our understanding of how this occurs by revealing a mechanism at the brain cell level that mediates how an animal moves about in the environment.
“It’s been known that animals and people can find their ...
Improving energy security with policies focused on demand-side solutions
2024-02-29
Governments typically rely on policies focused on energy supply to enhance energy security, ignoring demand-side options. Current indicators and indexes that measure energy security focus mostly on energy supply. This aligns with the International Energy Agency’s view, which defines energy security only in terms of security of supply. However, this approach does not fully capture the extent of vulnerability for states, businesses, and individuals during an energy crisis.
“Energy security assessments also need to reflect how vulnerable countries, firms, and households are to energy ...
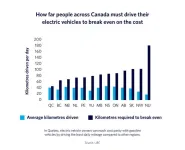
Driving an electric car is cheaper in some parts of Canada than others
2024-02-29
Electric vehicles are a critical part of Canada’s climate strategy, but a new University of British Columbia study highlights how it’s cheaper in some regions than others to drive electric—making it more challenging for certain households to make the switch.
Location, location, location
The researchers analyzed how far people need to drive their electric car to break even on the cost, factoring in the impacts of tax rebates and tax rates, charging costs, typical distance households travel in a region, and electricity ...
Emergency atmospheric geoengineering wouldn’t save the oceans
2024-02-29
WASHINGTON — Climate change is heating the oceans, altering currents and circulation patterns responsible for regulating climate on a global scale. If temperatures dropped, some of that damage could theoretically be undone. But employing “emergency” atmospheric geoengineering later this century in the face of continuous high carbon emissions would not be able to reverse changes to ocean currents, a new study finds. This would critically curtail the intervention’s potential effectiveness ...
New model of key brain tumor feature could help scientists understand how to develop new treatments
2024-02-29
ANN ARBOR, Michigan — Researchers at the University of Michigan Health Rogel Cancer Center are exploiting a unique biological feature of glioblastoma to gain a better understanding of how this puzzling brain cancer develops and how to target new treatments against it.
The team, led by senior author Pedro Lowenstein, M.D., Ph.D., Richard Schneider Collegiate Professor of Neurosurgery at Michigan Medicine, had previously identified oncostreams as a key feature in glioblastoma development and in more aggressive disease. These highly active, elongated, spindle-like cells ...
Study: Mutations in hereditary Alzheimer’s disease damage neurons without ‘usual suspect’ amyloid plaques
2024-02-29
LAWRENCE — A University of Kansas study of rare gene mutations that cause hereditary Alzheimer's disease shows these mutations disrupt production of a small sticky protein called amyloid.
Plaques composed of amyloid are notoriously found in the brain in Alzheimer’s disease and have long been considered responsible for the inexorable loss of neurons and cognitive decline. Using a model species of worm called C. elegans that’s often used in labs to study diseases at the molecular level, the research team came to the surprising conclusion that the stalled process of amyloid production — not the amyloid itself — can trigger loss of critical ...
Rice lab finds better way to handle hard-to-recycle material
2024-02-29
HOUSTON – (Feb. 29, 2024) – Glass fiber-reinforced plastic (GFRP), a strong and durable composite material, is widely used in everything from aircraft parts to windmill blades. Yet the very qualities that make it robust enough to be used in so many different applications make it difficult to dispose of ⎯ consequently, most GFRP waste is buried in a landfill once it reaches its end of life.
According to a study published in Nature Sustainability, Rice University researchers and collaborators have developed a new, energy-efficient upcycling method to transform glass fiber-reinforced plastic ...
Ice shell thickness reveals water temperature on ocean worlds
2024-02-29
ITHACA, N.Y. – Cornell University astrobiologists have devised a novel way to determine ocean temperatures of distant worlds based on the thickness of their ice shells, effectively conducting oceanography from space.
Available data showing ice thickness variation already allows a prediction for the upper ocean of Enceladus, a moon of Saturn, and a NASA mission’s planned orbital survey of Europa’s ice shell should do the same for the much larger Jovian moon, enhancing the mission’s findings about whether it could support ...
Garrett Isaac Neubauer Center for Cardiovascular Innovation launches at Columbia
2024-02-29
NEW YORK, NY (February 29, 2024)--Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons (VP&S) today announced the launch of a new center for pediatric cardiovascular innovation, made possible through a visionary gift by Lawrence Neubauer. The mission of the new center is to improve outcomes for patients through groundbreaking research and care and to define the next cures for and future practice in congenital heart disease (CHD)—here and across the world.
In recognition of the transformative generosity of Lawrence Neubauer, the center will be named the Garrett Isaac Neubauer Center for Cardiovascular ...
MSU co-authored study: 10 insights to reduce vaccine hesitancy on social media
2024-02-29
EAST LANSING, Mich. — Effective population level vaccination campaigns are fundamental to public health. Countercampaigns, which are as old as the first vaccines, can disrupt uptake and threaten public health globally.
Even before March 2020, vaccine hesitancy was directly linked to misinformation — false, inaccurate information promoted as factual — on social media. Once COVID-19 reached pandemic status, social media was acknowledged as the epicenter of information leading to vaccine hesitancy, which the World Health Organization, ...
New study: Deforestation exacerbates risk of malaria for most vulnerable children
2024-02-29
Malaria kills more than 600,000 people each year worldwide, and two thirds are children under age five in sub-Saharan Africa. Scientists have found a treatment that could prevent thousands of these deaths: trees. New research conducted at the University of Vermont (UVM) and published today in the journal GeoHealth suggests forests can provide natural protection against disease transmission, particularly for the most vulnerable children.
Malaria spreads through the bite of Anopheles mosquitoes. While malaria is a disease long associated with lower socioeconomic status, the UVM study links deforestation with higher risk of the disease, particularly for ...
DOE announces plans to host an informational meeting and requests expressions of interest for the Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility Management and Operating Contract Competition
2024-02-29
Washington, D.C. – The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced the schedule for upcoming events and submissions associated with the competition for the management and operating contract for the Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility (TJNAF).
TJNAF is a DOE national laboratory and DOE-sponsored Federally Funded Research and Development Center that has a mission focused on delivering breakthrough science and technology in nuclear physics.
DOE will host an informational meeting and site tour on March 27, 2024 at TJNAF to provide information regarding the site to interested parties. ...
Changes in flu circulation means US likely to see vaccines move from quadrivalent to trivalent
2024-02-29
U.S. flu vaccines are likely to move from quadrivalent to trivalent due to a change in circulating influenza viruses, says a University of Michigan researcher.
Currently, all influenza vaccines in the United States are quadrivalent, meaning that they protect against four different flu viruses.
In a new paper published in the New England Journal of Medicine, researchers detail the spread of influenza B/Yamagata virus, which has not been in circulation since early 2020; the regulatory discussions and recommendations on updating vaccines; and the manufacturing considerations ...
Accreditation with commendation awarded to the American College of Chest Physicians
2024-02-29
Glenview, IL– The American College of Chest Physicians® (CHEST) has received accreditation with commendation from the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME) and reaccreditation from the Society for Simulation in Healthcare (SSH).
This achievement grants CHEST reaccreditation through November 2029 and places the organization in the highest tier of all continuing medical education (CME) providers, including some of the nation’s most prestigious medical schools and professional medical societies.
“Receiving reaccreditation with commendation from the ACCME is a real testament to the education team at CHEST including both internal ...
Hahn awarded CZI grant to monitor, manipulate proteins important in nervous system function, neurological disease
2024-02-29
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – The Chan Zuckerberg Initiative (CZI) announced four multi-year Exploratory Cell Networks grants for researchers exploring the frontiers of genomics, cell biology, and synthetic biology by developing new measurement technologies. The projects will be bringing together regional labs in California, the Mid-Atlantic, and the Research Triangle.
Klaus Hahn, PhD, the Ronald G. Thurman Distinguished Professor of Pharmacology and member of the UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center, will be co-leading a ...
All-light communication network bridges space, air and sea for seamless connectivity
2024-02-29
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed an all-light communication network that enables seamless connectivity across space, air and underwater environments. The new network design combines different types of light sources to ensure connectivity no matter the environment.
“In today’s world, data transmission is critical for communication, navigation, emergency response, research and commercial activities,” said research team leader Yongjin Wang from Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications and ...
Parents, wealth, race drive girls’ chances to play sports
2024-02-29
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The likelihood that a girl will participate in high school sports in the United States is driven not so much by individual choice, new research suggests. Instead, decisions made by parents, the wealth of one’s family and community, and racial dynamics matter.
By combining interviews with elite college athletes and analysis of data on over 4,000 high school girls, researchers found that socioeconomic status – of families and the school districts in which they live ...
Study sheds light on how neurotransmitter receptors transport calcium, a process linked with origins of neurological disease
2024-02-29
A new study from a team of McGill University and Vanderbilt University researchers is shedding light on our understanding of the molecular origins of some forms of autism and intellectual disability.
For the first time, researchers were able to successfully capture atomic resolution images of the fast-moving ionotropic glutamate receptor (iGluR) as it transports calcium. iGluRs and their ability to transport calcium are vitally important for many brain functions such as vision or other information coming from sensory organs. Calcium also brings about changes in the signalling capacity of iGluRs ...
Artificial intelligence reveals prostate cancer is not just one disease
2024-02-29
Artificial Intelligence has helped scientists reveal a new form of aggressive prostate cancer which could revolutionise how the disease is diagnosed and treated in the future.
A Cancer Research UK-funded study published today, 29 February 2024, reveals that prostate cancer, which affects one in eight men in their lifetime, includes two different subtypes termed evotypes.
The discovery was made by an international team led by the University of Oxford, and the University of Manchester, who applied AI (artificial intelligence) on data from DNA to identify two different subtypes affecting the prostate.
The team hope their findings could save thousands ...
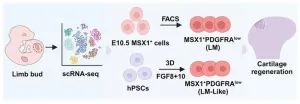
New type of stem cells contains potential for knee cartilage regeneration in arthritic mice
2024-02-29
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a debilitating joint disease which affects over 500 million people worldwide, with trends increasing as populations age. OA is caused by progressive, irreversible degeneration of joint cartilage, leading to pain, swelling and immobility in the affected joint. Current therapies focus on symptom relief but cannot restore degenerated cartilage.
A potentially alternative treatment is the regeneration of cartilage from stem cells. Importantly, not all types of stem cells can make cartilage and earlier clinical trials with mesenchymal stem or stromal cells (MSCs) obtained did not convincingly show that MSCs make new cartilage when given to OA patients. In search for the ...
Becoming human: An ancient genome perspective
2024-02-29
Writing a commentary in the 50th anniversary issue of Cell, FU Qiaomei and E. Andrew Bennett, both of the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, explored the contribution of paleogenomics to our understanding of the evolution of modern humans.
Given her numerous contributions to the field of human evolution through the analysis of both archaic and early modern human genomes, Prof. FU was invited by the journal Cell to write a commentary reviewing what we have learned about the evolution ...
Extreme weather events tied to increased mortality and emergency department activity
2024-02-29
Climate change is increasing the frequency and intensity of severe weather events, which may particularly endanger vulnerable populations such as the elderly. Researchers from Mass General Brigham and colleagues examined how weather disasters between 2011 and 2016 influenced healthcare delivery and mortality among Medicare beneficiaries in affected counties, finding that one week after major weather events, emergency department (ED) use and mortality remained elevated by 1.22% and 1.4%, respectively, from pre-disaster ...
Bottlenecks and beehives: how an invasive bee colony defied genetic expectations
2024-02-29
For more than a decade, invasive Asian honeybees have defied evolutionary expectations and established a thriving population in North Queensland, much to the annoyance of the honey industry and biosecurity officials.
Research published today in Current Biology has shown the species, Apis cerana, has overcome what is known as a genetic bottleneck to grow from a single swarm into a population of more than 10,000 colonies over a 10,000 square kilometre area – which is about the size of Greater Sydney.
Co-lead author Dr Rosalyn Gloag from the University of Sydney School of Life and Environmental Sciences said: “Our study of this bee population shows that some species can ...
[1] ... [1351]
[1352]
[1353]
[1354]
[1355]
[1356]
[1357]
[1358]
1359
[1360]
[1361]
[1362]
[1363]
[1364]
[1365]
[1366]
[1367]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.