Pioneering research reveals empathetic communication can help overcome vaccine hesitancy
2024-03-04
An international study has shown for the first time how empathetic correction of misinformation among vaccine-hesitant patients can significantly improve attitudes towards vaccination – and potentially boost vaccine uptake.
The research, led by the University of Bristol, also found this new style of communication could help build and maintain a positive relationship with health professionals, increasing trust and public confidence. With the UK currently facing a growing measles outbreak, fuelled by declining rates of the Measles, ...
Rare astrolabe discovery reveals Islamic – Jewish scientific exchange
2024-03-04
The identification of an eleventh century Islamic astrolabe bearing both Arabic and Hebrew inscriptions makes it one of the oldest examples ever discovered and one of only a handful known in the world. The astronomical instrument was adapted, translated and corrected for centuries by Muslim, Jewish and Christian users in Spain, North Africa and Italy.
Dr Federica Gigante, from Cambridge University’s History Faculty, made the discoveries in a museum in Verona, Italy, and published them today in the journal Nuncius.
Dr Gigante first came across a newly-uploaded ...
Sleep apnea symptoms linked to memory and thinking problems
2024-03-03
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, SUNDAY, MARCH 3, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – People who experience sleep apnea may be more likely to also have memory or thinking problems, according to a preliminary study released today, March 3, 2024, that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology’s 76th Annual Meeting taking place April 13–18, 2024, in person in Denver and online. The study shows a positive association but did not determine whether sleep apnea causes cognitive decline.
Sleep ...
Nanoscale topcoat can turbocharge supported gold nanoparticle catalysts
2024-03-02
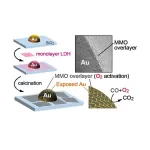
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a way to add single nanosheets of mixed metal oxide to gold nanoparticles supported on silica to enhance their catalytic activity. Converting carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide, they found that the temperature required for the reaction was greatly reduced, with significant improvements over existing methods for coating gold/silica structures. The method paves the way for the development of a wide range of new high-performance catalysts.
Gold nanoparticles, particles less than five nanometers in diameter, are known to be excellent catalysts ...
Beyond the ink: Painting with physics
2024-03-02
Falling from the tip of a brush suspended in mid-air, an ink droplet touches a painted surface and blossoms into a masterpiece of ever-changing beauty. It weaves a tapestry of intricate, evolving patterns. Some of them resemble branching snowflakes, thunderbolts or neurons, whispering the unique expression of the artist's vision.
Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) researchers set out to analyse the physical principles of this fascinating technique, known as dendritic painting. They took inspiration from the artwork ...
Only 9 percent of older Americans were vaccinated against RSV before the disease hit this fall and winter
2024-03-02
A new study from the Texas A&M University School of Public Health found that only 9 percent of older Americans had been vaccinated against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) prior to this fall and winter, despite the threat of increased rates of hospitalization and deaths nationwide from the virus.
“RSV—along with COVID-19 and influenza—form the current ‘tripledemic’ found across the United States this fall and winter,” said Simon Haeder, PhD, the study’s author. “While the elderly, as well as the very young and those with chronic health conditions, typically are affected ...
Evolution-capable AI promotes green hydrogen production using more abundant chemical elements
2024-03-02
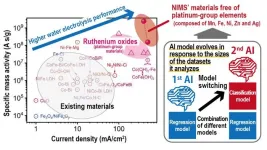
1. A NIMS research team has developed an AI technique capable of expediting the identification of materials with desirable characteristics. Using this technique, the team was able to discover high-performance water electrolyzer electrode materials free of platinum-group elements—substances previously thought to be indispensable in water electrolysis. These materials may be used to reduce the cost of large-scale production of green hydrogen—a next-generation energy source.
2. Large-scale production of green ...
In wake of powerful cyclone, remarkable recovery of Pacific island’s forests
2024-03-01
After one of the most intense cyclones in world history tore through the Pacific island of Tanna in Vanuatu, new research led by the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa showed the resilience of the island’s forests.
In the Pacific islands, climate change is expected to increase the intensity and frequency of cyclones, causing huge potential risks to forests and the people who depend on them. In March 2015, Cyclone Pam touched down on the island of Tanna as the strongest Pacific island cyclone in history ...
PSU study sheds light on 2020 extreme weather event that brought fires and snow to western US
2024-03-01
The same weather system that led to the spread of the devastating Labor Day wildfires in 2020 brought record-breaking cold and early-season snowfall to parts of the Rocky Mountains. Now, new research from Portland State is shedding light on the meteorology behind what happened and the impacts of such an extreme weather event.
“It’s really interesting to see such an amplified pattern result in opposing extremes in the Pacific Northwest and the Rocky Mountains,” said Emma Russell, a master’s student in geography ...
Rice physicist earns NSF CAREER Award to revolutionize quantum technology
2024-03-01
HOUSTON – (March 1, 2024) – Yonglong Xie, assistant professor of physics at Rice University, has been awarded a Faculty Early Career Development (CAREER) Award from the National Science Foundation (NSF). The $888,555 grant over five years will support Xie’s research into harnessing magnons, quantum mechanical wavelike objects in magnetic materials, to create synthetic matter and develop next-generation quantum devices and sensors.
The CAREER program offers NSF’s most prestigious awards in support of early career faculty who have the potential to serve as academic role models in research and education. Xie’s project focuses ...
Mining the treasures locked away in produced water
2024-03-01
In an ironic twist, a treasure trove of critical minerals is dumped out with water considered too polluted and expensive to clean.
Texas A&M University researcher Dr. Hamidreza Samouei is investigating the components of produced water and says this waste byproduct of oil and gas operations contains nearly every element in the periodic table, including those of significant interest to national economies.
His goal is to treat the water using unwanted carbon dioxide (CO2) in stages to recover these valuable elements and ultimately produce fresh water for agricultural use once the processes are complete.
“Recognizing the latent value ...
Minoritized groups face high anxiety when taking part in research experiments
2024-03-01
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- When participating in research studies, moderately anxious or highly anxious children from minoritized groups are likely to be hypervigilant to threat, further compounding the effects of their general state of anxiety, a research study led by a University of California, Riverside, psychologist reports.
The study, which involved the participation of 46 Inland Southern California preadolescent Latina girls (8–13 years), has implications also for children from families with low socioeconomic status.
“Psychological research is often conducted in white, educated, and affluent communities,” said Kalina Michalska, ...
Orcas demonstrating they no longer need to hunt in packs to take down the great white shark
2024-03-01
An orca (killer whale) has been observed, for the first-ever time, individually consuming a great white shark – and within just two minutes.
“The astonishing predation, off the coast of Mossel Bay, South Africa, represents unprecedented behavior underscoring the exceptional proficiency of the killer whale”, remarks Dr. Alison Towner from Rhodes University, who led an international research team into the discovery.
Their findings are published today in the peer-reviewed African Journal of Marine Science.
The groundbreaking insight is the latest from Dr. Towner and the team, who, in 2022 in the same journal, ...
Scientists discover a novel vehicle for antibiotic resistance
2024-03-01
By David L. Chandler
WOODS HOLE, Mass. -- Antibiotic resistance is a significant and growing medical problem worldwide. Researchers at the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) and collaborators have found a novel genetic arrangement that may help a common bacterium in the human gut, Bacteroides fragilis, protect itself from tetracycline, a widely used antibiotic.
While these findings will not lead directly to new ways of combating tetracycline-resistant bacteria, the researchers have discovered previously unseen genetic arrangements that confer antibiotic resistance. Such understanding might help in developing new ways to limit the spread of antibiotic resistance genes, through genetic ...
Large-scale study explores link between smoking and DNA changes across six racial and ethnic groups
2024-03-01
Smoking changes the way genes are expressed, which later contributes to the development of lung cancer and other smoking-related illnesses. But the link between epigenetics (the study of mechanisms that impact gene expression) and smoking is not fully understood, especially in terms of differences across racial and ethnic groups.
“We know that smoking affects people differently based on their race and ethnicity, but identifying epigenetic signatures of smoking would help us better predict risk for smoking-related diseases,” said Brian Huang, PhD, an assistant professor in the department of population ...
EU funding for outstanding early-career researcher Pieter Gunnink
2024-03-01
Dr. Pieter Gunnink from the Institute of Physics at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) has been awarded a EUR 190,000 Marie Skłodowska-Curie Postdoctoral Fellowship by the European Commission. The grant is an individual award for Gunnink's outstanding achievements in the field of spintronics and provides financial support for his research over a period of 24 months.
Modern information processing relies heavily on the use of electrical current, the transport of which requires large amounts of energy. The field of ...
Associate Professor Ron Korstanje, Ph.D., of The Jackson Laboratory named Evnin Family Chair
2024-03-01
Associate Professor Ron Korstanje, Ph.D., has been named the Evnin Family Chair at The Jackson Laboratory. An expert in the genetics of kidney function and disease, Korstanje’s appointment marks a new chapter in his 20 years of service to JAX’s mission.
“Ron’s exceptional contributions to JAX have advanced research discoveries and nurtured generations of future scientists,” said President and CEO Lon Cardon, Ph.D., FMedSci. “His appointment as the Evnin Family ...
Researchers create coating solution for safer food storage
2024-03-01
In a collaborative effort to improve the food industry, Dr. Mustafa Akbulut, professor of chemical engineering, and Dr. Luis Cisneros-Zevallos, professor of horticultural science, have developed a two-step coating solution for galvanized steel that is more hygienic and reduces the risk of corrosion.
Galvanized steel containers and surfaces are used for harvested produce because of their durability, strength and lower cost compared to stainless steel. However, bacteria residing in storage containers can cause corrosion.
The ...
An overgrowth of nerve cells appears to cause lingering symptoms after recurrent UTIs
2024-03-01
DURHAM, N.C. – A perplexing problem for people with recurring urinary tract infections (UTIs) is persistent pain, even after antibiotics have successfully cleared the bacteria.
Now Duke Health researchers have identified the likely cause - an overgrowth of nerve cells in the bladder.
The finding, appearing March 1 in the journal Science Immunology, provides a potential new approach to managing symptoms of recurring UTIs that would more effectively target the problem and reduce unnecessary antibiotic usage.
“Urinary tract infections account for almost 25% of infections in women,” said senior author Soman Abraham, Ph.D., professor in the departments ...
New findings on the immune system
2024-03-01
T follicular helper cells (Tfh) are essential for strong antibody-mediated reactions of our immune system during infections and vaccinations. However, if they get out of control, this can cause diseases such as autoimmunity, allergies or cancer. Researchers from the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and the Cluster of Excellence ImmunoSensation2 at the University of Bonn investigated the underlying mechanisms of Tfh cell development in a mouse model and thus decoded their internal networking. They hope that this will lead to new strategies for the development of highly effective vaccines and new therapies to combat various diseases. The results have ...
Most smokers in England wrongly believe vaping is at least as harmful as smoking
2024-03-01
More than half of smokers in England wrongly believe that vaping is more harmful or as harmful as smoking, according to a new study led by UCL (University College London) researchers.
The study, published in the journal JAMA Network Open and funded by Cancer Research UK, looked at survey responses from 28,393 smokers in England between 2014 and 2023.
The research team found that public perceptions of e-cigarettes had worsened considerably over the past decade, with an overall increase in the perceived harm of e-cigarettes since 2021, coinciding with a sharp rise in vaping among young ...
New antibodies target “dark side” of influenza virus protein
2024-03-01
WHAT:
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health have identified antibodies targeting a hard-to-spot region of the influenza virus, shedding light on the relatively unexplored “dark side” of the neuraminidase (NA) protein head. The antibodies target a region of the NA protein that is common among many influenza viruses, including H3N2 subtype viruses, and could be a new target for countermeasures. The research, led by scientists at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases’ Vaccine Research Center, part of NIH, was published today in Immunity.
Influenza, or flu, sickens millions ...
Fred Hutch announces 2024 Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award recipients
2024-03-01
Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center announced 12 recipients of the 2024 Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award, which recognizes exceptional achievement in graduate studies in the biological sciences.
This year’s recipients come from U.S. and international research institutions with thesis topics that include brain signals related to learning and emotion, bacterial pathogens and health, AI algorithms in rare disease diagnosis and treatment, and immune cells involved in brain tumors.
“Weintraub awardees showcase how scientists are using advancements in technology to explore questions that have been out of reach,” said Jihong Bai, ...
New academic journal on artificial intelligence launched
2024-03-01
STARKVILLE, Miss. -- Mississippi State University's Department of Computer Science and Engineering has launched a new open-access academic journal focused on advancements in artificial intelligence.
The journal AI Letters aims to fill a gap in peer-reviewed publications covering AI research. Department Head Shahram Rahimi and Assistant Research Professor Noorbakhsh Amiri Golilarz, editors-in-chief of the journal, saw the need for a publication that could quickly share new ideas and insights in AI, a hot topic ...
UMaine researchers use GPS-tracked icebergs in novel study to improve climate models
2024-03-01
Over the last four decades, warming climate and ocean temperatures have rapidly altered the Greenland Ice Sheet, creating concern for marine ecosystems and weather patterns worldwide. The environment has challenged scientists in their attempts to measure how water moves around and melts the ice sheet because equipment can be destroyed by icebergs floating near the glaciers.
Collected using a novel approach, research from the University of Maine has unearthed new information to help scientists better understand circulation patterns of ocean water around glaciers. A group of pioneers in glacial research attached GPS devices to icebergs and used their mobility to understand fjord circulation, ...
[1] ... [1344]
[1345]
[1346]
[1347]
[1348]
[1349]
[1350]
[1351]
1352
[1353]
[1354]
[1355]
[1356]
[1357]
[1358]
[1359]
[1360]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.