FAU Engineering study employs deep learning to explain extreme events
2023-10-02
Identifying the underlying cause of extreme events such as floods, heavy downpours or tornados is immensely difficult and can take a concerted effort by scientists over several decades to arrive at feasible physical explanations.
Extreme events cause significant deviation from expected behavior and can dictate the overall outcome for a number of scientific problems and practical situations. For example, practical scenarios where a fundamental understanding of extreme events can be of vital importance include rogue waves in the ocean that could endanger ships and offshore structures or increasingly ...
New study uncovers potential treatment for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
2023-10-02
A breakthrough study, jointly led by Professor Jang Hyun Choi and Professor Sung Ho Park from the Department of Biological Sciences at UNIST has identified an important factor involved in the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) caused by obesity. The research team discovered that Thrap3, a protein associated with thyroid hormone receptors, plays a significant role in exacerbating NAFLD by inhibiting the activity of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key regulator of fat metabolism in the liver.
NAFLD encompasses various metabolic diseases such as fatty hepatitis and cirrhosis resulting from excessive fat accumulation. ...
Susan G. Komen® analysis shows many breast cancer patients struggle to afford basic needs: Housing, transportation, utilities
2023-10-02
Lower income breast cancer patients often struggle to afford life’s necessities such as housing, transportation and utilities due to direct and incidental costs related to their treatment, according to a new analysis by Susan G. Komen®, the world’s leading breast cancer organization. These top needs were identified by Susan G. Komen’s Patient Care Center, which provided nearly $9.1 million in grants to more than 16,000 breast cancer patients from April 1, 2022 to March 31, 2023, as part of Komen’s direct-to-patient ...
Dense measurement network revealed high level of PM2.5 in Punjab due to crop residue burning and its transport to Haryana and Delhi NCR
2023-10-02
A group of international collaborators led by the Research Institute for Humanity and Nature (RIHN) team performed the first quantitative study of air pollution in the north-western India region using 29 low-cost and reliable instruments, demonstrating the advantages of source region observations to link crop residue burning (CRB) and air pollution at local to regional scales.
Exposure to particulate matter less than 2.5 µm in diameter (popularly known as PM2.5) causes health hazards in cities and major emission regions of the world. Although the major sources ...
Next-generation printing: precise and direct, using optical vortices
2023-10-02
Osaka, Japan – Will printed photographs ever match the precision of a mirror's reflection? Even though the answer may still be no for a while, Osaka Metropolitan University scientists have made significant strides in precision printing with their innovative optical vortex laser-based technique that allows for the precise placement of minuscule droplets with micrometer-scale accuracy.
Inkjet technology is a well-known printing technique that emits microdroplets from a nozzle directly onto a surface. However, when the ink droplets are viscous, with high density, ...
Pharmacists can improve access to life-saving vaccines
2023-10-02
HPV, or human papillomavirus, is the most common sexually transmitted infection. It is also the leading cause of cervical cancer. Over 1,400 Canadian women are affected yearly, with almost 400 deaths, according to the Canadian Cancer Society. It is completely preventable with the HPV vaccine, and yet, unfortunately, many people are unvaccinated.
University of Waterloo researchers have found a possible solution to this on-going issues. Using an electronic questionnaire at the time of appointment scheduling for seasonal influenza or COVID-19 vaccines, researchers have found, is a quick and efficient way to identify people in Ontario willing to receive additional life-saving vaccines.
“This ...
Researchers studied thousands of fertility attempts hoping to improve IVF
2023-10-02
By genetically testing nearly one thousand embryos, scientists have provided the most detailed analysis of embryo fate following human in vitro fertilization.
Nearly half the embryos studied underwent developmental arrest because of genetic mishaps in early development — a revealing insight that suggests more IVF babies could come to term with changes in the fertility treatment process. The unique combination of data from arrested embryos also sheds new light on the still largely mysterious earliest stages of pregnancy through natural ...
Precision medicine navigators increase genomic testing rates for Black patients with prostate cancer
2023-10-02
SAN DIEGO, October 1, 2023 — The presence of a clinical navigator to act as a liaison between people with prostate cancer and the health care system greatly increases the likelihood that patients, especially Black patients, will receive advanced testing that can help predict the severity of their disease and guide treatment, a new study suggests.
The study showed patients seen by a precision medicine navigator were substantially more likely to receive genomic testing than those not seen by the navigator. Black patients, whose genomic testing rates traditionally ...
Play in early childhood helps build a better brain, says leading expert
2023-10-02
Dr Jacqueline Harding, director of Tomorrow’s Child and an early childhood expert at Middlesex University, argues that the young child’s brain is inherently designed to be playful and this is crucial for its development.
In her new book, The Brain that Loves to Play, she challenges the traditional division between play and learning, emphasizing the essential role of play in early years education and holistic child development.
With a renewed vision for the fusion of play and learning, the book aims to contribute to the ...
Faith primary schools admitting fewer children with special educational needs
2023-10-02
Faith primary schools are admitting fewer children with special educational needs and disabilities (SEND) than local authority community primaries, according to new research from the London School of Economics and Political Science (LSE).
In research funded by the British Academy, Dr Tammy Campbell analysed Reception year admissions to mainstream state schools from 2010-2020 in England using the National Pupil Database census. She concluded that many faith primary schools ‘serve as hubs of relative advantage, seeming disproportionately to serve ...
Food insecurity doubles rate of severe hypoglycaemia in adults with diabetes
2023-10-02
New research being presented at the Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Hamburg, Germany (2-6 Oct) has found that severe hypoglycaemia is more than twice as common among adults with diabetes who struggle to afford food.
Severe hypoglycaemia occurs when a person’s blood sugar levels fall to such an extent that it can cause loss of consciousness, seizures, coma and, in rare cases, death.
Severe hypoglycaemia is rare in people with diabetes unless they are taking insulin or secretagogues – two commonly prescribed ...
Breastfeeding is associated with lower levels of body fat at the age of nine
2023-10-02
New research being presented at the Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Hamburg, Germany (2-6 Oct) has linked infant formula and the early introduction of fizzy drinks with higher levels of body fat later in childhood.
Youngsters who were breastfed for at least six months or longer had a lower percentage of body fat by age nine compared to those who did not receive breast milk for six months (a group that includes children who were never breastfed or received breast milk for less than 6 months).
Children ...
Exposure to daylight rather than artificial light improves blood sugar control and nutrient use in individuals with type 2 diabetes, small Dutch study finds
2023-10-02
Exposure to natural light could help treat and prevent type 2 diabetes, new research being presented at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Hamburg, Germany (2-6 Oct), suggests.
“The misalignment of our internal circadian clock with the demands of a 24/7 society is associated with an increased incidence of metabolic diseases, including type 2 diabetes,” says Ivo Habets, of Maastricht University, Maastricht, the Netherlands, who co-led the research. “Natural daylight is the strongest zeitgeber, or environmental cue, of the circadian ...
Shorter course of radiation therapy is safe for patients with early-stage breast cancer who have undergone mastectomy and reconstruction
2023-10-01
Boston – Researchers at Dana-Farber Brigham Cancer Center have found that a shorter course of radiation therapy after mastectomy and breast reconstruction surgery provides the same protection against breast cancer recurrence and equivalent physical side-effects but substantially reduces life disruption and financial burden for patients.
The results of the multicenter randomized clinical trial – the FABREC Study (Hypofractionated versus Conventionally Fractionated Postmastectomy Radiation Therapy After Implant-Based Reconstruction) – were presented ...
Short-course radiation as effective as standard treatment for patients who opt for breast reconstruction after mastectomy
2023-10-01
SAN DIEGO, October 1, 2023 — In a first-of-its-kind study, people with breast cancer who underwent implant-based breast reconstruction immediately following a mastectomy reported that getting fewer, higher doses of radiation was just as effective as standard radiation, did not increase side effects and saved them time and money. There also was a small improvement in quality of life for women under 45 who received the shortened treatment regimen.
The FABREC study is the first prospective randomized study comparing quality-of-life and clinical outcomes following accelerated versus conventional radiation therapy specifically for patients with ...
Sexual activity and vaginal dilation associated with fewer side effects after cervical cancer treatment
2023-10-01
SAN DIEGO, October 1, 2023 — People who engage in sexual activity or vaginal dilation after chemoradiation treatment for cervical cancer are at lower risk for long-term side effects, according to a new study from researchers in Austria. Findings of the EMBRACE study will be presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) Annual Meeting.
“Curing cancer is always our first priority,” said lead study author Kathrin Kirchheiner, MSc, PhD, a clinical psychologist in the department of radiation oncology at the Medical University of Vienna. “But with a growing number of relatively young cervical cancer survivors, ...
High-dose radiation offers new treatment option for older patients with inoperable kidney tumors
2023-10-01
SAN DIEGO, October 1, 2023 — Older adults diagnosed with kidney tumors that are not suitable for surgery may benefit from targeted, high-dose radiation, a new study from Australian and Dutch researchers suggests.
A multi-institutional phase II study – TransTasman Radiation Oncology Group (TROG) FASTRACK II – found 100% local control and cancer-specific survival for longer than three years among patients who were treated non-invasively for inoperable kidney cancer with stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy (SABR). Findings will be presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) ...
Liquid biopsies can rapidly detect residual disease following cervical chemoradiation, study finds
2023-10-01
SAN DIEGO, October 1, 2023 — Two liquid biopsy tests that look for the presence of human papillomavirus (HPV) in the blood accurately identified patients with a high risk of cervical cancer recurrence after the completion of chemoradiation, a new study confirms. Findings will be presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) Annual Meeting.
The study compared two novel tests – a digital polymerase chain reaction (dPCR) test and a sequencing test for genetic material from HPV, the main cause of cervical cancer – and found they were equally effective at identifying residual disease in the blood of patients who ...
Metaphors for human fertilization are evolving, study shows
2023-10-01
New Haven, Conn. — In a common metaphor used to describe human fertilization, sperm cells are competitors racing to penetrate a passive egg. But as critics have noted, the description is also a “fairy tale,” rooted in cultural beliefs about masculinity and femininity.
A new study by Yale sociologist Rene Almeling provides evidence that this metaphor remains widely used despite the profound shift in recent decades in social and scientific views about gender, sex, and sexuality. But her findings, based ...
Study suggests threshold for type 2 diabetes diagnosis in women under 50 years should be lowered
2023-10-01
New research to be presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Hamburg, Germany (2-6 October) and published in the journal Diabetes Therapy suggests that the diagnosis threshold for type 2 diabetes (T2D) should be lowered in women aged under 50 years, since natural blood loss through menstruation could be affecting their blood sugar management. The study is by Dr Adrian Heald, Salford Royal Hospital, UK, and colleagues.
Analysis of the national diabetes ...
Synergistic work of cations in anion exchange membranes for OH- transport in fuel cells
2023-09-30
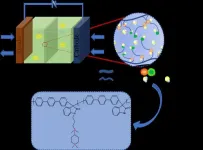
Anion exchange membrane fuel cells (AEMFCs) have gained attention in the process of fuel cell development because they operate in alkaline environments, the redox reaction rate at the electrodes is faster, and non-precious metal catalysts such as Ni, Co, and Ag can be used, which reduces the cost of fuel cells. However, the mobility of OH- is only 56.97% of that of H+ under the same conditions, and its stability is poor, so improving the ionic conductivity and mechanical properties of anion exchange membranes (AEM) is the key to the commercialization ...
Hairy polymer balls help get genetic blueprints inside T-cells for blood cancer therapy
2023-09-30
Tokyo, Japan – Scientists from Tokyo Metropolitan University have realized a new polymer that can effectively transport plasmid DNA into T-cells during chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, a key treatment for blood cancer. Importantly, it can get genes into floating T-cells, not only ones fixed to surfaces. It is stable, non-toxic, and doesn’t use viruses. It outperforms polyion compounds considered a gold standard in the field, paving the way for new therapies.
T-cells, or lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell that helps our immune system fight germs and protect us from disease. Recently, technology has become available that helps reprogram T-cells to fight cancer. ...
Reducing fishing gear could save whales with low impacts to California’s crab fishermen
2023-09-30
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Sometimes simple solutions are better. It all depends on the nature of the problem. For humpback whales, the problem is the rope connecting a crab trap on the seafloor to the buoy on the surface. And for fishermen, it’s fishery closures caused by whale entanglements.
Managing this issue is currently a major item on California’s agenda, and it appears less fishing gear may be the optimal solution. So says a team of researchers led by Christopher Free, at UC Santa Barbara, after modeling the benefits and impacts that several management strategies would have on whales and fishermen. ...
Engineering researchers to study wireless communication and machine learning with NSF grant
2023-09-30
A virtual reality (VR) game crashes. A robot rolls dangerously close to the edge of a cliff. An autonomous vehicle speeds toward a pedestrian. Without intelligent control happening every millisecond, accidents can occur. This control can mean applying the brake of an autonomous vehicle to save a life or creating a more user-friendly augmented reality experience.
Two professors in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Texas A&M University are working to enhance and advance the future ...
Wheat's long non-coding RNAs unveiled: A leap in understanding grain development
2023-09-30
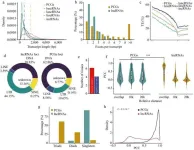
Wheat is a global staple food and plays a pivotal role in the livelihoods of billions of people. Although long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been recognized as crucial regulators of numerous biological processes, our knowledge of lncRNAs associated with wheat (Triticum aestivum) grain development remains minimal.
Seed Biology published an online paper entitled “A comprehensive atlas of long non-coding RNAs provides insight into grain development in wheat” on 04 September 2023.
To ...
[1] ... [1653]
[1654]
[1655]
[1656]
[1657]
[1658]
[1659]
[1660]
1661
[1662]
[1663]
[1664]
[1665]
[1666]
[1667]
[1668]
[1669]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.