New method can improve assessing genetic risks for non-white populations
2023-09-25
A team led by researchers at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and the National Cancer Institute has developed a new algorithm for genetic risk-scoring for major diseases across diverse ancestry populations that holds promise for reducing health care disparities.
Genetic risk-scoring algorithms are considered a promising method to identify high-risk groups of individuals who could benefit from preventive interventions for various diseases and conditions, such as cancers and heart diseases. ...
Wearable devices show who may need more help managing diabetes
2023-09-25
A new Dartmouth study in the journal Science Advances suggests that how well people with diabetes manage their blood sugar depends on their experience with the condition and their overall success in controlling their glucose levels, as well as on the season and time of day. The findings could help physicians identify those patients who could benefit from more guidance in regulating their blood sugar, particularly at certain times of year.
The researchers accessed data from wearable glucose monitors that showed how 137 people in the U.S. aged 2 to 76 living primarily with type 1, aka juvenile, diabetes managed their blood sugar on a daily basis. By analyzing more ...
Light and sound waves reveal negative pressure
2023-09-25
As a physical quantity pressure is encountered in various fields: atmospheric pressure in meteorology, blood pressure in medicine, or even in everyday life with pressure cookers and vacuum-sealed foods. Pressure is defined as a force per unit area acting perpendicular to a surface of a solid, liquid, or gas. Depending on the direction in which the force acts within a closed system, very high pressure can lead to explosive reactions in extrem cases, while very low pressure in a closed system can cause the implosion of the system itself. Overpressure ...
Predicting how climate change affects infrastructure without damaging the subject
2023-09-25
A digital twin may sound like something out of a science fiction film, but Pitt engineers are developing new technology to make them a reality in our campus and beyond.
Digital twins – a model that serves as a real-time computational counterpart – can be used to help simulate the effects of multiple types of conditions, such as weather, traffic, and even climate change. Still, life-cycle assessments (LCAs) of climate change’s effects on infrastructure are still a work-in-progress, leaving a need ...
New qubit circuit enables quantum operations with higher accuracy
2023-09-25
In the future, quantum computers may be able to solve problems that are far too complex for today’s most powerful supercomputers. To realize this promise, quantum versions of error correction codes must be able to account for computational errors faster than they occur.
However, today’s quantum computers are not yet robust enough to realize such error correction at commercially relevant scales.
On the way to overcoming this roadblock, MIT researchers demonstrated a novel superconducting qubit ...
Could this new hydrogel make HIV therapy more convenient?
2023-09-25
A new injectable solution that self-assembles into a gel under the right conditions could help manage HIV unlike any currently available methods, researchers have found.
The gel releases a steady dose of the anti-HIV drug lamivudine over six weeks, suggesting people living with HIV could have new therapy that doesn’t require a daily pill regimen to prevent AIDS.
“The primary challenge in HIV treatment is the need for lifelong management of the virus, and one way to address this is to reduce dosing frequencies to help patients stick to medical regimens,” said Honggang Cui, a Johns Hopkins University chemical and biomolecular engineer ...
Study finds immune cells in older adults resemble those in newborns and children, but fall short in virus detection
2023-09-25
Study finds immune cells in older adults resemble those in newborns and children, but fall short in virus detection
A world-first discovery has revealed special immune cells called ‘killer T cells’ in older adults, directed against influenza viruses, closely resemble those found in newborns and children, but struggle to recognise infected cells – a finding that unlocks the potential for the development of better vaccines and therapies tailored to different age groups.
Killer T cells (also known as CD8+ T cells) play a critical role in the immune system by eliminating virus-infected cells. ...
Wang studying novel & interpretable statistical learning for brain imaging data
2023-09-25
Wang Studying Novel & Interpretable Statistical Learning For Brain Imaging Data
Lily Wang, Professor, Statistics, has received a total grant of $1,199,772 ($299,987 for the first year) from the National Institutes of Health for the project: "SCH: Novel and Interpretable Statistical Learning for Brain Images in AD/ADRDs." This funding began in Sept. 2023 and will end in late April 2027. This grant was reviewed by the joint NSF/NIH Smart Health and Biomedical Research in the Era of Artificial Intelligence and Advanced Data Science (SCH) program.
Alzheimer’s ...
NCCN Senior Director Evelyn Handel Zapata is named a ‘40 Under 40 in Cancer: Emerging Leader’ for milestone work improving safe use of chemotherapy
2023-09-25
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [September 25, 2023] —Evelyn Handel Zapata, PharmD, BCPS, BCOP, Senior Director of Drugs & Biologics Programs at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®) was named a 40 Under 40 in Cancer: Emerging Leader at a national reception in Chicago in June. This achievement comes as the NCCN Chemotherapy Order Templates (NCCN Templates®) program celebrates its 15th anniversary and launches new resources for a type of pediatric lymphoma today.
40 Under 40 in Cancer is an awards initiative that recognizes ...
Modelling of adhesive technology sheds new light on prehistoric cognition
2023-09-25
Studying prehistoric production processes of birch bark tar using computational modelling reveals what kinds of cognition were required for the materials produced by Neanderthal and early modern humans. Researchers of Team Langejans in the Materials Science and Engineering (MSE) department (TU Delft) recently published two papers on one of the world’s oldest transformative technologies, publishing their findings in Nature Scientific Reports.
Measuring complexity
Birch bark tar is the first time we see evidence of creating a new material, ...
Two Salk Institute faculty members earn V Foundation awards for cancer research
2023-09-25
LA JOLLA (September 25, 2023)—Salk Institute Assistant Professors Christina Towers and Deepshika Ramanan were named V Scholars by the V Foundation for Cancer Research. They will each receive $600,000 over three years to fund their unique cancer research goals.
“On behalf of all our Salk colleagues, we are proud to congratulate Christie and Shika on this outstanding recognition,” says Salk President Gerald Joyce. “Through their dedication and innovative approaches, they both embody Salk’s mission to push the boundaries of knowledge and make meaningful impact in the world.”
Towers was named to the first class of recipients of V Foundation’s A Grant ...
People with long COVID have distinct hormonal and immune differences from those without this condition
2023-09-25
Long COVID patients have clear differences in immune and hormone function from patients without the condition, according to a new study led by the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and Yale School of Medicine.
The research, published in the September 25 issue of Nature, is the first to show specific blood biomarkers that can accurately identify patients with long COVID.
“These findings are important—they can inform more sensitive testing for long COVID patients and personalized treatments for long COVID that have, until now, not had a proven scientific rationale,” says Principal Investigator David Putrino, ...
New vaccine technology could protect from future viruses and variants
2023-09-25
Studies of a ‘future-proof’ vaccine candidate have shown that just one antigen can be modified to provide a broadly protective immune response in animals. The studies suggest that a single vaccine with combinations of these antigens – a substance that causes the immune system to produce antibodies against it – could protect against an even greater range of current and future coronaviruses.
The vaccine antigen technology, developed by the University of Cambridge and spin-out DIOSynVax in early 2020, provided protection against all known variants of SARS-CoV-2 – the virus that causes COVID-19 – as well as other ...
Racial disparities in emergency department physical restraint use
2023-09-25
About The Study: In this systematic review and meta-analysis of 10 studies, physical restraint was uncommon, occurring in less than 1% of encounters, but adult Black patients experienced a significantly higher risk of physical restraint in emergency department settings compared with other racial groups. Emergency departments should carefully consider, and take steps to address, how racism may affect disparate use of restraints among adult patients.
Authors: Vidya Eswaran, M.D., of the Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Access to marijuana by minors via online dispensaries
2023-09-25
About The Study: This analysis of 80 online marijuana dispensaries based in 32 states found that most lacked adequate age verification features and most accepted nontraceable payment methods, enabling youth to hide their transactions. Almost 1 in 5 online dispensaries required no formal age verification at any stage of the purchasing process.
Authors: Ruth L. Milanaik, D.O., of Steven and Alexandra Cohen Children’s Medical Center of New York in Lake Success, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.3656)
Editor’s ...
Racial, ethnic, and sex diversity in academic medical leadership
2023-09-25
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that select specialties in academic medicine have bridged diversity gaps in academic medical leadership whereas others continue to lag behind.
Authors: Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A., of Henry Ford Health in Detroit, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.35529)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and ...
Distinct immune, hormone responses shed light on mysteries of long COVID
2023-09-25
New Haven, Conn. — People who have experienced brain fog, confusion, pain, and extreme fatigue for months or longer after being infected with the COVID-19 virus exhibit different immune and hormonal responses to the virus than those not diagnosed with long COVID, according to a new study by researchers at Yale School of Medicine and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
The discovery of these distinct responses can help scientists for the first time identify the causes — and potentially ...
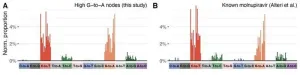
Antiviral drug linked to SARS-CoV-2 mutations
2023-09-25
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00hrs BST 25 September 2023
Peer reviewed
Observational study
People
Antiviral drug linked to SARS-CoV-2 mutations
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute, the University of Cambridge, Imperial College London, the University of Liverpool, the University of Cape Town and UKHSA have uncovered a link between an antiviral drug for COVID-19 infections called molnupiravir and a pattern of mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Molnupiravir works by inducing mutations in the virus’s ...
Pioneering research links the increase of misinformation shared by Republican US politicians to a changing public perception of honesty
2023-09-25
The international study, published in Nature Human Behaviour, analysed millions of tweets by members of Congress over the last decade. Its findings showed both Republican and Democratic politicians were increasingly sharing their beliefs and opinions as well as evidence-based information. But among Republicans, their expression of honestly-held beliefs and opinions was strongly linked to less trustworthy information sources.
Lead author Jana Lasser, a postdoctoral research fellow in computational social science at Graz University of Technology (TU Graz), said: “We wanted to find out what reasons and social changes contribute to people sharing ...
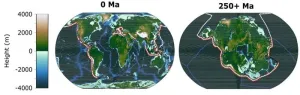
New research reveals extreme heat likely to wipe out humans and mammals in the distant future
2023-09-25
A new study shows unprecedented heat is likely to lead to the next mass extinction since the dinosaurs died out, eliminating nearly all mammals in some 250 million years time.
The research, published today in Nature Geoscience and led by the University of Bristol, presents the first-ever supercomputer climate models of the distant future and demonstrates how climate extremes will dramatically intensify when the world’s continents eventually merge to form one hot, dry and largely uninhabitable supercontinent.
The ...
Theories about the natural world may need to change to reflect human impact
2023-09-25
New research, reported in Nature Ecology & Evolution, (25 September 2023) has for the first time validated at scale, one of the theories that has underpinned ecology for over half a century. In doing so, the findings raise further questions about whether models should be revised to capture human impacts on natural systems.
Scientists working in the 50’s and 60’s developed theories to predict the ecological distribution of species. These theories could be applied across a broad range of environments and variables such as food supply or temperature and when tested on a small scale they were found to be accurate. Amongst the earliest examples of these ...
Ocean acidification research is robust despite ebbs and flows
2023-09-25
A new objective examination of almost a quarter-of-a-century of ocean acidification research shows that, despite challenges, experts in the field can have confidence in their research.
The University of Adelaide’s Professor Sean Connell from the Ecology and Evolutionary Biology unit led the study.
“In our field, the marine science community was galvanised by the demonstration of how ocean acidification impairs shell-building life, which has profound implications for life on the planet,” ...
Systemic cooling poverty: A new facet of deprivation emerging in a warming planet
2023-09-25
OXFORD - 25/09/2023 - A new study in Nature Sustainability - published today by researchers from Oxford University, Ca’ Foscari University of Venice, the Euro-Mediterranean Center on Climate Change, the European Institute on Economics and the Environment and the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine - brings attention to a new relevant dimension of deprivation which is clearly emerging in a warming world: cooling poverty. The study highlights the multidimensional nature of cooling poverty and introduces the new concept of systemic cooling ...
PSU study examines how weather patterns will change in the future
2023-09-25
In a warming Pacific Northwest, summers are getting hotter and winters less cold, but the atmospheric patterns that influence the weather aren’t necessarily expected to become stronger or more frequent by the end of the century, according to a new Portland State University study.
That means that in an overall warmer climate, models suggest we'll have the same variety of atmospheric patterns as we have now but the weather we experience from them will be warmer and, in some cases, wetter.
Graham Taylor, a Ph.D. student in PSU’s ...
Drug discovery on an unprecedented scale
2023-09-25
Boosting virtual screening with machine learning allowed for a 10-fold time reduction in the processing of 1.56 billion drug-like molecules. Researchers from the University of Eastern Finland teamed up with industry and supercomputers to carry out one of the world’s largest virtual drug screens.
In their efforts to find novel drug molecules, researchers often rely on fast computer-aided screening of large compound libraries to identify agents that can block a drug target. Such a target can, for instance, be an enzyme that enables a bacterium to withstand ...
[1] ... [1655]
[1656]
[1657]
[1658]
[1659]
[1660]
[1661]
[1662]
1663
[1664]
[1665]
[1666]
[1667]
[1668]
[1669]
[1670]
[1671]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.