How an audience changes a songbird’s brain
2023-09-27
NEW YORK, NY — His mind might have been set on finding water or on perfecting a song he learned as a chick from his dad. But all of that gets pushed down the to-do list for an adult male zebra finch when he notices a female has drawn nigh.
“The males stop worrying about anything else and, for the first time, we have found signs of that re-prioritization in the behavior of specific brain cells,” said Vikram Gadagkar, PhD, a principal investigator at Columbia’s Zuckerman Institute and a co-first author, along with graduate student Andrea Roeser of Cornell ...
Organic lasers have a bright future
2023-09-27
Scientists at St Andrews are leading a significant breakthrough in a decades-long challenge to develop compact laser technology.
Lasers are used across the world for a huge range of applications in communications, medicine, surveying, manufacturing and measurement. They are used to transmit information across the internet, for medical treatments, and even in the face scanner on phones. Most of these lasers are made from rigid, brittle, semiconductor crystals such as gallium arsenide.
Organic semiconductors are a newer class of electronic material. Flexible, based on carbon and emitting visible ...
Women’s mood worsens during ‘pill pause’ period of monthly contraceptive pill cycle
2023-09-27
Type of work: peer-reviewed/observational study/people
Barcelona: Most contraceptive pills are based on a cycle of taking the pill for 21 days, and then stopping the pill for 7 days. Now researchers have found that women’s mood worsens during the 7 pill-free days. This work will be presented at the ECNP congress in Barcelona on 8th October, after recent publication (see notes).
Lead researcher, Professor Belinda Angela Pletzer (of Paris Lodron University, Salzburg, Austria) said “We investigated women’s mental health during the pill pause in long-term pill users: since they are long-term ...
Teams investigate material degradation process of carbon-based catalyst
2023-09-27
Although a plethora of carbon-based catalysts have been developed to promote oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in different electrochemical systems, the degradation process of those catalysts remains obscure to date. During certain steps of the ORR on a catalyst's surface in electrochemical systems, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is generated. This compound can be detrimental to the catalyst itself because the highly oxidative species produced from H2O2 can attack different moieties of the catalyst, leading to the degradation of its chemical structure. A team of researchers has elucidated how H2O2 affects the degradation of a carbon-based catalyst named N-G/MOF. This catalyst ...
Team examines importance of zeolite in catalysts for syngas conversion
2023-09-27
The fuels used today depend heavily on petroleum. As the demand grows, scientists are looking for ways to produce fuels that do not require petroleum. A research team set out to examine the role of zeolites in the conversion of synthetic gas to fuels. Wanting to better understand how zeolites regulate the reaction pathways, they reviewed the most recent advancements in synthetic gas conversion with catalysts containing zeolites.
Their review paper is published in the journal Carbon Future on July 28, 2023.
As an alternative ...
AI chest X-ray model analysis reveals race and sex bias
2023-09-27
OAK BROOK, Ill. – An AI chest X-ray foundation model for disease detection demonstrated racial and sex-related bias leading to uneven performance across patient subgroups and may be unsafe for clinical applications, according to a study published today in Radiology: Artificial Intelligence, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). The study aims to highlight the potential risks for using foundation models in the development of medical imaging artificial intelligence.
“There’s ...
Integration propels machine vision
2023-09-27
A joint research team in China wrote a review on in-sensor visual computing, a three-in-one hardware solution that is more efficient, economical and secure than conventional machine vision systems, which collect, store, and interpret visual signals on separate hardware units. This review was published Sept. 26 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
In-sensor visual computing systems are inspired by how humans and other mammals collect, extract and process visual signals, an intricate biological mechanism showing low latency and low energy cost. By integrating sensing, storage and computation onto the ...
Blocking abnormal stem cell signal during aging lessens related bone loss
2023-09-27
A cellular signal essential to the development of the skeleton increases during aging to weaken bones, finds a new study in mice.
The study, led by researchers from NYU Grossman School of Medicine, found that blocking the signaling pathway, called Notch, in aging skeletal stem cells caused a “massive increase” in bone mass and restored lost bone-healing ability during aging.
The study results revolve around immature stem cells, which have the capacity to mature into more than one cell type. Bone is among the tissues that keep pools of stem cells on hand into adulthood, ready to mature into replacement cells that maintain healthy tissue and repair ...
Henry Ford Health first in Michigan to introduce advanced prostate diagnostic technology
2023-09-27
DETROIT (Sept. 27, 2023) – Henry Ford Health is the first health system in Michigan to offer ExactVu, a cutting-edge technology for diagnosing and evaluating prostate cancer. Enhancing the precision and speed of diagnosis, this new technology ensures patients receive timely and appropriate care, while also providing a more efficient and convenient experience than other diagnostic methods.
"Throughout the years, advancements in prostate cancer diagnostic and treatment modalities have made a tremendous difference for patients,” said Craig Rogers, M.D., Chair of the Department of Urology at Henry Ford Cancer. “This is ...
Resolving a seeming contradiction, study advances understanding of visual recognition memory
2023-09-27
Because figuring out what is new and what is familiar in what we see is such a critically important ability for prioritizing our attention, neuroscientists have spent decades trying to figure out how our brains are typically so good at it. Along the way they’ve made key observations that seem outright contradictory, but a new study shows that the mystifying measures are really two sides of the same coin, paving the way for a long-sought understanding of “visual recognition memory” (VRM).
VRM is the ability to quickly recognize the familiar things in scenes, which can then be de-prioritized so that we can focus on the new things that might be more important ...
The Buck Institute and Phenome Health announce major strategic partnership
2023-09-27
The Buck Institute for Research on Aging and Phenome Health are joining forces in the quest to understand the biology of aging. Phenome Health, a Seattle-based nonprofit research organization led by CEO Lee Hood, MD, PhD, uses a data-driven approach to health and disease that integrates diverse types of biological big data. The new Center for Phenomic Health at the Buck will be co-led by Dr. Hood, who joins the Buck as Chief Innovation Officer and Distinguished Professor, and Eric Verdin, MD, Buck President ...
Revolutionary breakthrough: human stomach micro-physiological system unveiled
2023-09-27
A groundbreaking development in biomedical engineering has led to the creation of a human stomach micro-physiological system (hsMPS), representing a significant leap forward in understanding and treating various gastrointestinal diseases, including stomach cancer. The research team, led by Professor Tae-Eun Park from the Department of Biomedical Engineering at UNIST and Professor Seong-Ho Kong from Seoul National University Hospital, has successfully developed a biomimetic chip that combines organoid and organ-on-a-chip technologies to simulate the complex defense mechanisms of the human gastric mucosa.
Organoids, which mimic human organs using stem cells, have ...
ORNL launches Center for AI Security Research to study AI’s impacts on society, security
2023-09-27
The Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory announced the establishment of its Center for AI Security Research, or CAISER, to address threats already present as governments and industries around the world adopt artificial intelligence and take advantage of the benefits it promises in data processing, operational efficiencies and decision-making.
In partnership with federal agencies such as the Air Force Research Laboratory’s Information Directorate and the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) Science and Technology Directorate ...
Extreme weight loss: Star sheds unexpected amounts of mass just before going supernova
2023-09-27
Cambridge, Mass. — A newly discovered nearby supernova whose star ejected up to a full solar mass of material in the year prior to its explosion is challenging the standard theory of stellar evolution. The new observations are giving astronomers insight into what happens in the final year prior to a star’s death and explosion.
SN 2023ixf is a new Type II supernova discovered in May 2023 by amateur astronomer Kōichi Itagaki of Yamagata, Japan shortly after its progenitor, or origin star, ...
Target: BP™ intitiative helps more than 8.6 million Americans with hypertension improve heart health
2023-09-27
DALLAS, September 27, 2023 — The American Heart Association and American Medical Association (AMA) nationally recognized 1,709 health care organizations (HCOs) — 400 more than in 2022 — for their efforts to prioritize control of their patients’ blood pressure (BP), a leading preventable risk factor for heart disease, stroke and premature death.
According to the 2022 American Heart Association Statistical Update, nearly half of U.S. adults — 121.5 million ...
Tiny CRISPR tool could help shred viruses
2023-09-27
HOUSTON – (Sept. 27, 2023) Small and precise: These are the ideal characteristics for CRISPR systems, the Nobel-prize winning technology used to edit nucleic acids like RNA and DNA.
Rice University scientists have described in detail the three-dimensional structure of one of the smallest known CRISPR-Cas13 systems used to shred or modify RNA and employed their findings to further engineer the tool to improve its precision. According to a study published in Nature Communications, the molecule works differently than other proteins in the same family.
“There are different types of CRISPR systems, and the one ...
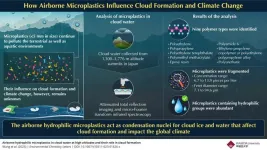
Plastic cloud: New study analyzes airborne microplastics in clouds
2023-09-27
Plastic particles less than 5 mm in size are called “microplastics.” These tiny bits of plastic are often found in industrial effluents, or form from the degradation of bulkier plastic waste. Research shows that large amounts of microplastics are ingested or inhaled by humans and animals alike and have been detected in multiple organs such as lung, heart, blood, placenta, and feces. Ten million tons of these plastic bits end up in the ocean, released with the ocean spray, and find their way into the atmosphere. This implies that microplastics may have become an essential component of clouds, ...
Winners of the ASTRO-Sumitomo Pharma-Pfizer Alliance new combination therapy challenge announced
2023-09-27
ARLINGTON, Va., September 27, 2023 — The American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) today announced the three winning research proposals for the 2022 ASTRO-Myovant Sciences (now known as Sumitomo Pharma)-Pfizer Alliance New Combination (Relugolix-Radiation) Therapy Challenge. The Challenge aims to identify research that addresses ways prostate cancer treatments can be improved with the gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) receptor antagonist relugolix in patients who received radiation therapy.
The Challenge invited researchers to propose the study of relugolix in different scenarios: ...
New evidence for sub-network specializations within the Default Mode Network and the Special Role of Facial Movements in Brain Activation and Self-Perception
2023-09-27
Recent advancements in neuroscience have unveiled new insights into the neural processes responsible for self-referential cognition. This research has brought particular attention to a critical neural network known as the Default Mode Network (DMN), comprising brain regions such as the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), posterior cingulate cortex, temporoparietal junction (TPJ), and both lateral and medial temporal lobes.
Central to self-related processing, is the information associated with one’s ...
Ultrasound enables gene delivery throughout the brain
2023-09-27
HOUSTON – (Sept. 27, 2023) – Rice University researchers tested the safety and feasibility of gene delivery to multiple brain regions using a noninvasive, ultrasound-based technique in rodents, and their findings suggest that the efficiency of gene delivery improves within each targeted site when more sites are opened.
Shirin Nouraein, a doctoral student working in the lab of Rice bioengineer Jerzy Szablowski, is the lead author on the study recently published in the journal Gene Therapy.
The paper, “Acoustically Targeted Noninvasive Gene Therapy in Large Brain Volumes,” ...
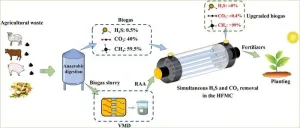
Elevating biogas upgrading performance on renewable aqueous ammonia solution via a novel “membrane method”
2023-09-27
Biogas is usually produced by anaerobic digestion of organic waste such as animal manures and straw wastes, which is a typical green renewable energy and can be used as a fuel for power generation and heat production. China has owned large scale of biogas production, with an annual output of about 15 billion m3 biogas, and the biogas development and utilization provide a new choice for coping with the energy crisis. Factually, biogas contains about 60% CH4 and about ...
Golden Goose Award announces 2023 awardees for discoveries in DNA sequencing technique, a bacteria-inspired method that saves crops and chicken pedigree lines
2023-09-27
WASHINGTON, D.C. – The Golden Goose Award, which celebrates federally funded research that sounds silly, but ultimately benefits society, has selected five researchers across the fields of biology, agriculture and genomics for their unexpected breakthroughs as 2023 awardees. On September 27, 2023, the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS), the world’s largest multidisciplinary scientific society, will co-host the 12th annual Golden Goose Award ceremony with the Association of American Universities, a founding member of the Golden Goose Award, at the Library ...
Inventors of nanopore sequencing honored at Library of Congress
2023-09-27
Two UC Santa Cruz researchers were honored on September 27 at the Library of Congress for the invention of nanopore sequencing, which became a new and revolutionary method to read DNA and RNA.
David Deamer and Mark Akeson, both emeritus professors of biomolecular engineering at the Baskin School of Engineering, received the American Association for the Advancement of Science’s (AAAS) Golden Goose Award for the invention. Their colleague and friend Daniel Branton, a Havard biologist and co-inventor of the technology, was also honored.
The Golden Goose award is given to scientists whose federally-funded research ...
Experimental nasal spray may offer quick, easy remedy for treating rapid heartbeat
2023-09-27
Research Highlights:
In a new study, etripamil, a rapid- and short-acting investigational medication formulated to be delivered via nasal spray, restored a normal heart rhythm in less than 30 minutes in most users with intermittent rapid heartbeats, sparing them a trip to the emergency room to receive intravenous medication.
Participants were able to detect when they were experiencing tachycardia (heart rate over 100 beats/minute) and use the medication appropriately and safely.
The self-administered treatment may help the approximately 1 in 300 adults in the U.S. ...
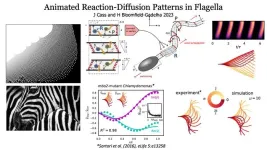
Sperm swimming is caused by the same patterns that are believed to dictate zebra stripes
2023-09-27
Patterns of chemical interactions are thought to create patterns in nature such as stripes and spots. This new study shows that the mathematical basis of these patterns also governs how sperm tail moves.
The findings, published today in Nature Communications, reveal that flagella movement of, for example, sperm tails and cilia, follow the same template for pattern formation that was discovered by the famous mathematician Alan Turing.
Flagellar undulations make stripe patterns in space-time, generating waves that travel along the tail to drive the sperm and microbes forward.
Alan Turing is most well-known for helping ...
[1] ... [1662]
[1663]
[1664]
[1665]
[1666]
[1667]
[1668]
[1669]
1670
[1671]
[1672]
[1673]
[1674]
[1675]
[1676]
[1677]
[1678]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.