Study explains why certain immunotherapies don’t always work as predicted
2023-09-14
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- This block is broken or missing. You may be missing content or you might need to enable the original module.
Cancer drugs known as checkpoint blockade inhibitors have proven effective for some cancer patients. These drugs work by taking the brakes off the body’s T cell response, stimulating those immune cells to destroy tumors.
Some studies have shown that these drugs work better in patients whose tumors have a very large number of mutated proteins, which scientists believe is because those proteins offer plentiful ...
Growth of large operators threatens existence of grassroots coworking spaces, study warns
2023-09-14
The growing number of large operators and developers opening coworking premises threatens to end the availability of grassroots community-oriented spaces designed to bring isolated workers together, a new study warns.
These coworking communities were originally set up to create serendipitous encounters, knowledge-sharing opportunities, and social capital. But the increasing numbers of big companies running flexible offices means they are less likely to offer services matching these aims.
Smaller operators see the incursion by large commercial real estate developers ...
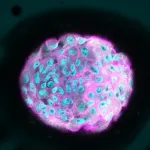
Using topology, Brown researchers advance understanding of how cells organize themselves
2023-09-14
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — The fact that humans and other living organisms can develop and grow from a single cell relies on a process called embryonic development. For healthy tissue to form, cells in the embryo have to organize themselves in the right way in the right place at the right time. When this process doesn’t go right, it can result in birth defects, impaired tissue regeneration or cancer. All of which makes understanding how different cell types organize into a complex tissue ...
A call for better energy system models to enable a decarbonized future
2023-09-14
Energy system models fail to accurately represent energy storage and might recommend decarbonization strategies that make electric grids less reliable.
Policy makers and utilities need robust energy system models to determine the best strategies to decarbonize the world’s electric grids. But most existing models were designed for grids operating more than a decade ago. Today’s grids are much different. New technologies such as solar power and grid energy storage are being rapidly deployed. To accommodate these and other technologies, utilities must run grids in completely new ways.
Improvements are needed in energy system ...
Stretching the truth: New research reveals negative effects of exaggerative political statements
2023-09-14
Justifying policies through unsubstantiated or slightly invalid arguments can have a significantly negative effect on the public opinion of politicians, according to new research from City, University of London.
With increasing scrutiny on global government policies in a ‘post-truth’ era, and in the aftermath of the Covid-19 pandemic that polarised international responses and reactions to the virus, an increased focus has been placed on policymakers to justify their actions and validate reasons for taking decisions.
Short of lying, this can often politicians “stretching arguments” – making invalid claims that are difficult to both prove and disprove.
The study, ...
Aegis Consortium funds research aimed at reducing the threat of future pandemics
2023-09-14
The Aegis Consortium, an initiative of the University of Arizona Health Sciences, awarded approximately $650,000 in seed funding to eight pilot research projects in the areas of pandemic control, prediction or preparedness; post-acute effects of pandemics on individuals and societies; and the resilience of built and natural environments.
“As we explore the challenges of pandemics such as COVID-19, we will continue to expand our investigative reach with domestic and international research teams to provide a range ...
UNIST releases generative AI utilization guide to promote smart usage of ChatGPT
2023-09-14
Under the leadership of UNIST Education Innovation Task Force, a comprehensive guidebook titled ‘A Guide to the Use of Generatvie AI‘ was released on July 28, 2023. This guidebook presents alternative approaches to utilize generative AI, like ChatGPT more efficiently rather than simply prohibiting their use. With a focus on teachers, researchers, and students, the 50-page guidebook provides practical examples of generative AI utilization.
To gain insights into the purpose and development ...
Preventing the tissue's response to stiffness may be key to slowing the progression of breast tumors
2023-09-14
Cells are capable of translating mechanical changes into biological responses. This process is known as mechanotransduction and plays a fundamental role in the progression of solid tumors, such as breast cancer.
It is well-established that a common mechanical alteration in cancer progression involves tissue hardening. This stiffness is precisely what is detected during self-examinations or breast palpations for potential tumor detection. The stiffness of breast tissue triggers a chain reaction, inducing tension within cells and distorting their nuclei. Ultimately, this nuclear deformation activates genes responsible for controlling cell proliferation, which are closely associated ...
Members of the National Association of Neonatal Nurses support efforts to promote racial equity
2023-09-14
September 14, 2023 — More than 90% of the active members of the National Association of Neonatal Nurses (NANN) believe the organization should pursue racial equity work, and many have specific suggestions for a strategic plan. This feedback comes from the survey results the association released this month in its journal, Advances in Neonatal Care. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Neonatal care has advanced significantly in recent years, yet ...
Webb Confirms accuracy of universe’s expansion rate measured by Hubble, deepens mystery of Hubble constant tension
2023-09-14
The rate at which the universe is expanding, known as the Hubble constant, is one of the fundamental parameters for understanding the evolution and ultimate fate of the cosmos. However, a persistent difference called the “Hubble Tension” is seen between the value of the constant measured with a wide range of independent distance indicators and its value predicted from the big bang afterglow.
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope provides new capabilities to scrutinize and refine some of the strongest observational evidence for this tension. Nobel Laureate Adam Riess from the Johns Hopkins University and ...
Penn Medicine’s Carl June, MD, to receive 2024 Breakthrough Prize in Life Sciences
2023-09-14
PHILADELPHIA – CAR T cell therapy pioneer Carl June, MD, the Richard W. Vague Professor in Immunotherapy in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and director of the Center for Cellular Immunotherapies (CCI) at Penn Medicine’s Abramson Cancer Center, has been named a winner of the 2024 Breakthrough Prize in Life Sciences for the development of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell immunotherapy, a revolutionary cancer treatment approach in which each patient’s T cells are modified to target and kill their cancer cells. The invention sparked a new path in cancer care, harnessing the power of patients’ own immune systems, a once-elusive ...
New research published by Nature Food reveals food is primary driver of the EU-27’s outsized Ecological Footprint
2023-09-14
One quarter of food consumed in the EU-27 originates from outside the region, highlighting the vulnerability of the EU’s food system.
New research coordinated by Global Footprint Network’s sustainability scientists in collaboration with food system experts published the article “EU-27 Ecological Footprint was primarily driven by food consumption and exceeded regional biocapacity from 2004 to 2014” today in Nature Food. The way food is provided to and consumed by Europeans represents ...
Rivers are rapidly warming, losing oxygen; aquatic life at risk, study finds
2023-09-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Rivers are warming and losing oxygen faster than oceans, according to a Penn State-led study published today (Sept. 14) in the journal Nature Climate Change. The study shows that of nearly 800 rivers, warming occurred in 87% and oxygen loss occurred in 70%.
The study also projects that within the next 70 years, river systems, especially in the American South, are likely to experience periods with such low levels of oxygen that the rivers could “induce acute death” for certain species of fish and threaten aquatic diversity at large.
“This is a wake-up call,” ...
London has the fastest increase in cooling demand in the world, shows new model
2023-09-14
A model to map energy demand down to street level shows cooling demand in the capital grew by 5% per year between 1980 and 2022 as summers heat up.
The Demand.ninja model, created by researchers at Imperial College London and TU Delft, was designed to show how the weather influences hourly energy consumption in buildings. It can also account for changes in demand as the climate changes, including the increase in cooling demand in the summer as heatwaves become more common and more intense.
Countries ...
New research signals a quantum leap for brain tumour treatment
2023-09-14
Researchers have discovered a new way to target and kill cancer cells in hard-to-treat brain tumours using electrically charged molecules to trigger self-destruction, that could be developed into a spray treatment used during surgery.
A multidisciplinary team of researchers from the University of Nottingham, led by the School of Pharmacy found a new way to harness the extraordinary capabilities of bio-nanoantennae—gold nanoparticles intricately coated with specialised redox active molecules to induce programmed cell death, or apoptosis, in cancer cells on electrical stimulation. The research ...
Use of physical therapy and subsequent falls among patients with dizziness
2023-09-14
About The Study: The findings of this study of 805,000 patients ages 18 or older suggest that receipt of physical therapy (PT) after presentation for dizziness was associated with a reduction in fall risk during the subsequent 12 months; thus, timely PT referral for dizziness may be beneficial for these patients. Future research, ideally with a clinical trial design, is needed to explore the independent impact of PT on subsequent falls for adults with dizziness.
Authors: Meredith E. Adams, M.D., M.S., of ...
Geographical variation in social determinants of female breast cancer mortality across US counties
2023-09-14
About The Study: The results of this study of 2,176 counties suggest that breast cancer mortality in the U.S. can be affected by where individuals live, and that more comprehensive and geographically targeted interventions may lead to healthier communities.
Authors: Taylor Anderson, Ph.D., of George Mason University in Fairfax, Virginia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.33618)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
Combination immunotherapy treatment effective before lung cancer surgery
2023-09-14
Combination immunotherapy with the anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody durvalumab and other novel agents outperforms durvalumab alone in the neoadjuvant (pre-surgical) setting for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), according to researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
The findings, published today in Cancer Discovery, were first presented at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2022.
The multicenter, randomized Phase II NeoCOAST clinical trial evaluated neoadjuvant durvalumab alone ...
Verbal nonsense reveals limitations of AI chatbots
2023-09-14
NEW YORK – The era of artificial-intelligence chatbots that seem to understand and use language the way we humans do has begun. Under the hood, these chatbots use large language models, a particular kind of neural network. But a new study shows that large language models remain vulnerable to mistaking nonsense for natural language. To a team of researchers at Columbia University, it’s a flaw that might point toward ways to improve chatbot performance and help reveal how humans process language.
In a paper published online today in Nature Machine Intelligence, ...
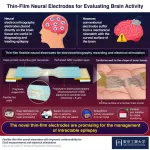
Revolutionizing brain monitoring and stimulation with thin-film neural electrodes
2023-09-14
Flexible thin-film electrodes placed directly on brain tissue show promise for the diagnosis and treatment of epilepsy, as demonstrated recently by scientists at Tokyo Tech. Thanks to an innovative yet straightforward design, these durable electrodes accurately match the mechanical properties of brain tissue, leading to better performance during electrocorticography recordings and targeted neural stimulation.
Measuring brain activity is a useful technique for diagnosing epilepsy and other neuropsychiatric disorders. Among the several approaches adopted, electroencephalography (EEG) is the least invasive. During EEG recordings, electrodes ...
Researchers present novel principle for nitric oxide-mediated signalling in blood vessels
2023-09-14
Although a simple molecule, nitric oxide is an important signal substance that helps to reduce blood pressure by relaxing the blood vessels. But how it goes about doing this has long been unclear. Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden now present an entirely novel principle that challenges the Nobel Prize-winning hypothesis that the substance signals in its gaseous form. Their findings are presented in the journal Nature Chemical Biology.
That the simple molecule nitric oxide or nitrogen monoxide (NO) serves as a signal substance in many important physiological processes has been known for some time. For example, the discovery of the compound’s ...
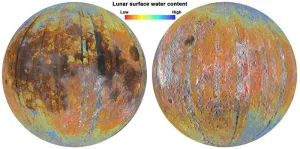
Electrons from Earth may be forming water on the Moon
2023-09-14
A team of researchers, led by a University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa planetary scientist, discovered that high energy electrons in Earth’s plasma sheet are contributing to weathering processes on the Moon's surface and, importantly, the electrons may have aided the formation of water on the lunar surface. The study was published today in Nature Astronomy.
Understanding the concentrations and distributions of water on the Moon is critical to understanding its formation and evolution, and to providing water resources for future human exploration. The new ...
New tool can reveal inequitable distribution of ‘healing’ green spaces
2023-09-14
Areas in Vancouver with the greatest need for restorative nature often have the least exposure to it, according to a new UBC study published recently in Ambio. These neighbourhoods include Strathcona, downtown Vancouver, the West End, southern Sunset and Marpole.
The researchers developed a new tool, the local restorative nature (LRN) index to assess spaces for the presence of qualities that promote mental well-being. While initially applied in Vancouver, the index can also be used in any urban landscape, according to lead author Dr. Tahia Devisscher, an assistant professor in the faculty of forestry.
We sat down with Dr. Devisscher to discuss the study findings and ...
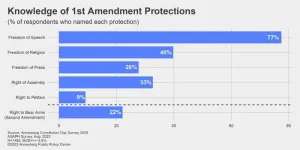
Many don’t know key facts about US Constitution, Annenberg study finds
2023-09-14
PHILADELPHIA – Many Americans do not know what rights are protected under the First Amendment and a substantial number cannot name all three branches of government, according to the 2023 Annenberg Constitution Day Civics Survey.
The Annenberg Public Policy Center’s annual, nationally representative survey finds that when U.S. adults are asked to name the specific rights guaranteed by the First Amendment to the Constitution, only one right is recalled by most of the respondents: Freedom of speech, ...
All work and no play will really make a dull life - new research reveals
2023-09-14
The study across three countries led by the Department of Psychology’s Dr Paul Hanel discovered people who prioritised achievement over enjoyment were less happy on the next day.
Whereas those who aimed for freedom said they had a 13% increase in well-being, recording better sleep quality and life satisfaction.
And participants who tried to relax and follow their hobbies recorded an average well-being boost of 8% and a 10% drop in stress and anxiety.
Dr Hanel worked with colleagues at the University of Bath on the Journal of Personality-published study.
For the first ...
[1] ... [1669]
[1670]
[1671]
[1672]
[1673]
[1674]
[1675]
[1676]
1677
[1678]
[1679]
[1680]
[1681]
[1682]
[1683]
[1684]
[1685]
... [8817]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.