Surrogate adiposity markers and mortality
2023-09-20
About The Study: Waist-to-hip ratio had the strongest and most consistent association with mortality irrespective of body mass index in this study consisting of 387,000 UK adult participants from the UK Biobank. Clinical recommendations should consider focusing on adiposity distribution compared with mass.
Authors: Guillaume Pare, M.D., M.Sc., of the Vascular and Stroke Research Institute in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.34836)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional ...
Strengthening artificial immune cells to fight cancer
2023-09-20
Among available immunotherapies, the use of «CAR-T» cells is proving extremely effective against certain blood cancers, but only in half of patients. A main reason for this is the premature dysfunction of these immune cells, which have been artificially modified in vitro. A team from the Universities of Geneva (UNIGE), Lausanne (UNIL), the Geneva University Hospitals (HUG) and the Vaud University Hospital (CHUV), all part of the Swiss Cancer Center Léman (SCCL), has discovered how to prolong the functionality of CAR-T cells. By inhibiting a very specific metabolic mechanism, the team has succeeded ...
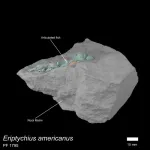
Prehistoric fish fills 100 million year gap in evolution of the skull
2023-09-20
A 455-million-year-old fossil fish provides a new perspective on how vertebrates evolved to protect their brains, a study has found.
In a paper published in Nature today (Wednesday 20th September), researchers from the University of Birmingham, Naturalis Biodiversity Centre in Leiden, Netherlands; and the Natural History Museum have pieced together the skull of Eriptychius americanus.
The research, funded by the Leverhulme Trust, suggests that the ancient jawless fish found in ancient deposits in ...
Study finds firearm injuries increased in gentrified neighborhoods
2023-09-20
Brigham researchers reported that gentrified neighborhoods had a 62 percent higher firearm injury incidence rate than non-gentrified communities with comparable sociodemographic characteristics
Understanding the reason for this increase is vital to reducing future firearm injuries
Gentrification can have a ripple effect on communities. While it can improve certain conditions in typically low-income areas, rising housing costs can displace residents, causing social disruption and other downstream effects. Investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, conducted a study using national data to examine the relationship ...
Scientists reveal how the effects of psychosis spread throughout the brain
2023-09-20
Psychoses like schizophrenia cost billions of dollars annually and derail the lives of people struggling with the disease. Now Monash University researchers have modelled how the effects of psychosis spread through the brain, allowing them to isolate areas where these changes may originate from and which could be targeted by therapies designed to reduce the disease’s progression.
The study, published today in the prestigious Journal of the American Medical Association Psychiatry, details how the scientists were able to map and model the spread of brain changes in people with different stages of psychoses such as schizophrenia,from people newly ...
Ya-Chieh Hsu, Ph.D. (Harvard) and Xuebing Wu, Ph.D. (Columbia) receive inaugural Glenn Foundation Discovery Awards
2023-09-20
Santa Barbara, CA and New York, NY -- The Glenn Foundation for Medical Research (GFMR) and the American Federation for Aging Research (AFAR) are pleased to announce the inaugural recipients of the
2023 Glenn Foundation Discovery Awards:
Ya-Chieh Hsu, PhD, Professor of Stem Cell and Regenerative Biology at Harvard University, and a Principal Faculty Member at the Harvard Stem Cell Institute.
Xuebing Wu, PhD, Assistant Professor of Medical Sciences (in Medicine and in Systems Biology), Columbia University.
The Glenn Foundation Discovery Award was created to support research projects with strong potential to develop pioneering discoveries ...
Decoding depression: Researchers identify crucial biomarker that tracks recovery from treatment-resistant depression
2023-09-20
A team of leading clinicians, engineers, and neuroscientists has made a groundbreaking discovery in the field of treatment-resistant depression. By analyzing the brain activity of patients undergoing deep brain stimulation (DBS), a promising therapy involving implanted electrodes that stimulate the brain, the researchers identified a unique pattern in brain activity that reflects the recovery process in patients with treatment-resistant depression. This pattern, known as a biomarker, serves as a measurable indicator of disease recovery and represents a significant ...
CityU researchers develop novel photo-oxidation therapy for anticancer treatment
2023-09-20
A research team led by scientists from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has achieved a significant breakthrough by inventing a new class of near-infrared-activated photo-oxidants that can effectively kill cancer cells without requiring oxygen. The photo-oxidants induce a unique form of cancer cell death that can overcome cancer cell resistance. The findings offer a new strategy, called ‘photo-oxidation therapy’, and provide a promising direction for the development of anti-cancer drugs.
Photodynamic therapy, an innovative ...
Multimillion-dollar scientific grant program releases third cycle of funding to increase foundational understanding of sarcoidosis
2023-09-20
WASHINGTON (September 20, 2023)—The Ann Theodore Foundation Breakthrough Sarcoidosis Initiative (ATF-BSI), in partnership with the Milken Institute, launched its latest round of funding today. Up to $3.4 million in total funding will be made available to researchers from around the world whose work aims to increase scientific understanding of sarcoidosis. The program is accepting applications for two-year research projects and intends to award four to six research grants from doctorate-level investigators at qualifying research-based institutions worldwide. Awardees may be eligible for a third year of funding.
Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory ...
Zhijian ‘James’ Chen and Glen Barber awarded Horwitz prize for discovering the cGAS-STING pathway
2023-09-20
NEW YORK, NY (September 20, 2023)—Columbia will award the 2023 Louisa Gross Horwitz Prize to Zhijian ‘James’ Chen and Glen Barber for discovering the cGAS-STING pathway, a key component of one of the body’s first line of defenses, the innate immune system.
When pathogens infiltrate our cells, they leave behind traces of their DNA. These molecular fingerprints are detected by our cGAS-STING pathway, which sounds the alarm and mobilizes the immune system to eliminate invading threats. Research on the cGAS-STING pathway has revealed the ...
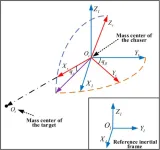
Scientists researched on finite-time anti-saturated proximity control with a tumbling non-cooperative space target
2023-09-20
The past few decades have witnessed the burgeoning development of on-orbit servicing in light of various meaningful space applications such as repair of malfunctioning satellites, debris removal, on-orbit assembly, and so on. As for the orbit-servicing targets, they are usually divided into 2 categories, i.e., cooperative and non-cooperative ones, based on whether the space targets have active cross-link communication and cooperative identifiers with the servicing spacecraft or not. Before executing the orbit-servicing task, close-range rendezvous and proximity is an inevitable process in which ...
Australian biobank aims to discover new treatments for children with genetic muscle diseases
2023-09-20
An Australian-first biobank will be established to improve and discover new treatments for children with genetic muscle diseases.
The National Muscle Disease Bio-databank, co-led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute, Monash University and Alfred Health, will advance research into understanding why children develop genetic muscle diseases. The project forms part of a $2.5 million Medical Research Future Fund grant awarded to the team for research into congenital muscle diseases.
These diseases, spanning dystrophies and myopathies, are characterised by severe muscle weakness, usually from infancy, that can impact swallowing, ...
A study published in Chinese Medical Journal reveals potential of methotrexate to treat liver cancer
2023-09-20
Liver cancer is one of the most prevalent and deadly types of cancer worldwide. Most patients are diagnosed at an advanced stage, which leaves them with few treatment options. Unfortunately, the first-line drugs used in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common type of liver cancer, are not very effective and offer only modest clinical benefits.
Over the past few years, scientists have been trying to develop new therapies for HCC by analyzing specific genetic abnormalities and the ways in which they affect the manifestation and progression of the disease. One of the most common mutations in HCC ...
State Council in Virginia approves new UVA Data Science Major
2023-09-20
The State Council of Higher Education for Virginia (SCHEV) approved Tuesday the creation of an undergraduate major for the University of Virginia’s School of Data Science, a landmark development for the four-year-old school, which was the first of its kind in the nation.
Prior to Tuesday’s announcement, undergraduates could obtain a minor in data science, while graduate students could pursue master’s or doctoral degrees. Now, the establishment of the B.S. in Data Science will allow UVA’s undergraduates to focus their studies on this emerging and growing interdisciplinary field.
“The B.S. in Data Science major is a major milestone ...
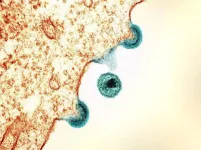
A newly identified virus emerges from the deep
2023-09-20
Highlights:
Organisms, including viruses, live in the deepest, darkest places on the planet
Marine virologists analyzed sediment from the Mariana Trench, the deepest place on Earth, and identified a new bacteriophage
The phage infects Halomonas bacteria, which have been found in deep-sea environments and near hydrothermal vents
The study helps probe how phages and hosts evolve together in secluded, hostile environments
Washington, D.C. — The Mariana Trench, the deepest place on Earth, plunges nearly 11,000 meters at its lowest point on the floor ...
Black holes eat faster than previously expected
2023-09-20
A new Northwestern University-led study is changing the way astrophysicists understand the eating habits of supermassive black holes.
While previous researchers have hypothesized that black holes eat slowly, new simulations indicate that black holes scarf food much faster than conventional understanding suggests.
The study will be published on Wednesday (Sept. 20) in The Astrophysical Journal.
According to new high-resolution 3D simulations, spinning black holes twist up the surrounding space-time, ultimately ripping apart ...
FAU receives $1.3 million grant for Alzheimer’s outreach in Broward County
2023-09-20
Florida Atlantic University’s María de los Ángeles Ortega, DNP, APRN, in the Christine E. Lynn College of Nursing, has been awarded a three-year, $1.3 million grant from the Administration for Community Living’s (ACL) Alzheimer’s Disease Program Initiative for a groundbreaking project designed to advance health equity and improve quality of life for individuals living with or at high risk for Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias (ADRD) and their family caregivers.
ACL was created around the fundamental principle that all people, regardless of age or disability, should be able to live independently ...
New Si-based photocatalyst enables efficient solar-driven hydrogen production and biomass refinery
2023-09-20
A team of researchers, led by Professor Jungki Ryu in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST and Professor Soojin Park from Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), have achieved a significant breakthrough in the development of a hybrid silicon photocatalyst. This innovative catalyst utilizes solar power to produce hydrogen and high-value compounds efficiently, marking a major step forward in green hydrogen production technology.
The newly developed photocatalyst is both non-toxic and eco-friendly, addressing the limitations associated with ...
Chameleon-inspired coating could cool and warm buildings through the seasons
2023-09-20
As summer turns to fall, many people will be turning off the air conditioning and firing up heaters instead. But traditional heating and cooling systems are energy intensive, and because they typically run on fossil fuels, they aren’t sustainable. Now, by mimicking a desert-dwelling chameleon, a team reporting in ACS’ Nano Letters has developed an energy-efficient, cost-effective coating. The material could keep buildings cool in the summers — or warm in the winters — without additional energy.
Many ...
Effective visual communication of climate change
2023-09-20
Boulder, Colo., USA: The consequences of a warming climate frequently dominated the news this summer, from devastating wildfires and floods to deadly heat waves across the globe. Reducing harm from climate change is a challenging endeavor, and it requires comprehensive public education. Thus, the question arises: How can climate change science be made most accessible to the general population, as well as decision-makers and educators?
In a new paper published in the journal Geosphere, Steph Courtney and Karen McNeal explore the effects ...
Clinical trial of HIV vaccine begins in United States and South Africa
2023-09-20
WHAT:
A trial of a preventive HIV vaccine candidate has begun enrollment in the United States and South Africa. The Phase 1 trial will evaluate a novel vaccine known as VIR-1388 for its safety and ability to induce an HIV-specific immune response in people. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, has provided scientific and financial support throughout the lifecycle of this HIV vaccine concept and is contributing funding for this study.
VIR-1388 is designed to instruct the ...
Five new health systems partner with American Thoracic Society on vaccine initiative
2023-09-20
NEW YORK, NY – Sept. 20, 2023 – As cities brace for a confluence of flu, COVID-19, pneumonia, and RSV infections this fall, the American Thoracic Society announced that five new health systems have partnered with the Society to improve vaccination rates. Grady Health System (Atlanta, GA), Meharry Medical College (Nashville, TN), St. Luke’s Health System (Boise, ID), the University of Colorado (Aurora, CO), and Wayne Health (Detroit, MI) join the University of Arizona/ Banner Health, West Virginia University Hospitals, Inc., and San Francisco Health Network/ University of California to help identify barriers to vaccination and find ...
Mount Sinai receives $6.2 million grant from the Steven & Alexandra Cohen Foundation for the clinical care of long Lyme disease
2023-09-20
Mount Sinai’s Department of Rehabilitation and Human Performance has announced a $6.2 million grant from the Steven & Alexandra Cohen Foundation. The grant will expand the Cohen Center for Recovery From Complex Chronic Illnesses (CoRE) to encompass research and clinical care beyond long COVID to include “long Lyme Disease/Lyme+” as well as other infection-associated complex chronic illnesses.
This funding will be used for new research programs focusing on understanding and highlighting the key similarities and differences between long COVID; long Lyme disease/Lyme+, a collection of infection-associated ...
Citizen Science receives a significant boost
2023-09-20
There is a growing interest in incorporating assistance from private citizens into scientific projects globally. Nonetheless, it seems that Anders P. Tøttrup, an Associate Professor at the Natural History Museum of Denmark, might become the world's first professor in Citizen Science.
Anders P. Tøttrup is a trained biologist and leads the section for Citizen Science projects at the Natural History Museum of Denmark. These projects involve scientific endeavours in which citizens are invited to assist in collecting and analyzing data. Now, the Museum is taking a step further as Anders P. Tøttrup enters a 'professor track.' The goal is ...
Urban light pollution linked to smaller eyes in birds
2023-09-20
PULLMAN, Wash. – The bright lights of big cities could be causing an evolutionary adaptation for smaller eyes in some birds, a new study indicates.
Researchers found that two common songbirds, the Northern Cardinal and Carolina Wren, that live year-round in the urban core of San Antonio, Texas, had eyes about 5% smaller than members of the same species from the less bright outskirts. Researchers found no eye-size difference for two species of migratory birds, the Painted Bunting and White-eyed Vireo, no matter which part of the city ...
[1] ... [1673]
[1674]
[1675]
[1676]
[1677]
[1678]
[1679]
[1680]
1681
[1682]
[1683]
[1684]
[1685]
[1686]
[1687]
[1688]
[1689]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.