Five factors that assess well-being of science predict support for increasing US science funding
2023-09-22
PHILADELPHIA – A study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) identifies five factors that Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC) researchers say reflect public assessments of science and are associated with public support for increasing funding of science and support for federal funding of basic research. These factors are whether science and scientists are perceived to be credible and prudent, and whether their work is perceived to be untainted by bias, self-correcting, and beneficial.
Drawing on 13 questions in APPC’s 2022 nationally representative ...
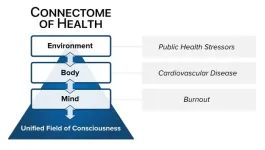
Editorial addresses clinician burnout with unifying systems medicine model
2023-09-22
A new editorial published in the Heart and Mind journal proposes an innovative systems medicine approach to address the epidemic of clinician burnout and holistically improve clinician mental health and wellbeing (Heart and Mind: September 18, 2023. | DOI: 10.4103/hm.HM-D-23-00013, published ahead of print).
In the US and globally, clinician burnout has reached epidemic levels, with over 50% of physicians and healthcare providers reporting symptoms. Besides impairing quality of life, burnout increases risk of mental health disorders, cardiovascular disease and impaired ...
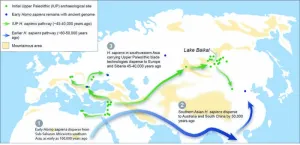
Pollen analysis suggests peopling of Siberia and Europe by modern humans occurred during a major Pleistocene warming spell
2023-09-22
LAWRENCE — It’s an Ice Age mystery that’s been debated for decades among anthropologists: Exactly when and how did the flow of Homo sapiens in Eurasia happen? Did a cold snap or a warming spell drive early human movement from Africa into Europe and Asia?
A new study appearing in Science Advances compares Pleistocene vegetation communities around Lake Baikal in Siberia, Russia, to the oldest archeological traces of Homo sapiens in the region. The researchers use the “remarkable evidence” to tell a compelling story from 45,000-50,000 years ago with new detail: how the first humans migrated across ...
Many low- or middle-income countries unprepared for the battle against cardiovascular disease
2023-09-22
Most healthcare facilities in many Low- and Middle-income Countries (LMICs) are unprepared to treat patients with cardiovascular diseases – despite these conditions leading to millions of people dying prematurely every year, a new study reveals.
Experts analysed health survey data from eight LMICs across four World Health Organisation world regions to discover that most facilities are unprepared to deliver services to treat or manage cardiovascular disease risk factors (CVDRF) such as diabetes and hypertension.
However, the increased ...
Probing the deep genetic structure of Africa
2023-09-22
Africa is the birthplace of modern humans and the continent with the highest level of genetic diversity. While ancient DNA studies are revealing some aspects of the genetic structure of Africa before the spread of food production, issues concerning DNA preservation have limited the insights from ancient DNA. Hoping to find clues in modern populations, researchers from a Portuguese-Angolan TwinLab ventured into the Angolan Namib desert – a remote, multi-ethnic region where different traditions met. “We were able to locate groups which were thought to have disappeared more than 50 years ago”, states Jorge ...
UC San Diego Health named national leader in delivering high-quality patient care
2023-09-22
UC San Diego Health has been recognized as a top performer in the 2023 Bernard A. Birnbaum, MD, Quality Leadership Ranking by Vizient, Inc. for its excellence in delivering high-quality patient care. This achievement represents the fifth consecutive year that UC San Diego Health has been ranked among the top ten academic health systems in the United States.
“This incredible accomplishment is a direct result of the exceptional care provided each day by our multidisciplinary teams throughout our health system,” said Patty Maysent, CEO of UC San Diego Health. “We are extremely proud to have achieved this national honor now for five years in a row, which ...
Louisiana Cancer Research Center Associate Director of Administration Sven Davisson named Treasurer of Association of Independent Research Institutes
2023-09-22
Louisiana Cancer Research Center (LCRC) Associate Director of Administration Sven Davisson has been appointed to the board of the Association of Independent Research Institutes (AIRI).
During his two-year term, Davisson will serve as the organization’s treasurer. He has served the organization in various roles since 2012.
AIRI is a national association of independent, not-for-profit biomedical and behavioral research institutes whose mission is to enhance the ability of its members to improve human health and advance knowledge through networking, education, and involvement in the development of science ...
Discovery in mosquitoes could lead to new strategy against dengue fever and other mosquito-borne vectors
2023-09-22
Researchers from the Johns Hopkins Malaria Research Institute at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health have made an important finding about Aedes aegypti mosquitoes—one that could one day lead to better methods for reducing the mosquito-to-human transmission of dengue, yellow fever, Zika, and other harmful and sometimes deadly viruses.
Ae. aegypti mosquitoes do not succumb to these viruses when infected and continue to move and feed normally. As such, the ...
The potential of solar cars in the world
2023-09-22
A new study, modeling the potential of solar-powered vehicles in the urban context in 100 cities across the world, shows that solar energy provides a range between 11 and 29 km per day, reducing charging needs by half.
Despite the rapid adoption of electric vehicles, the transport sector is still responsible for around a third of global carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions worldwide. Therefore, to achieve decarbonization targets, it is required to significantly decrease the emissions associated with mobility.
Integrating photovoltaic modules into ...
Fruit flies offer clues to how brains make reward-based decisions
2023-09-22
Like many collectors of L.P. records, James Fitzgerald’s brother-in-law has a favorite store where he consistently finds the best vinyl for his collection. But there are times when he spends hours at the store and comes up empty. He also knows that occasionally he should venture to the record store on the other side of town, where he sometimes scores a hard-to-find gem that was stocked since his last visit.
Fitzgerald’s brother-in-law is making a calculation: weighing probable outcomes to guide his behavior. His favorite record store ...
Pioneering health tracker for stroke survivors will use the body to transmit data
2023-09-22
AMHERST, Mass.—An interdisciplinary team led by University of Massachusetts Amherst researchers has been awarded $1.14 million over four years by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to develop a revolutionary way of tracking body movements, with a primary application in stroke survivors’ rehabilitation and huge potential for future applications across a wide range of disciplines, health-related and beyond.
More than 795,000 Americans suffer from strokes annually, and nearly 80% of stroke survivors experience some degree ...
Brazilian researchers develop method of purifying water contaminated by glyphosate
2023-09-22
Researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP) in Brazil have developed a strategy for removing glyphosate, one of the world’s most frequently used herbicides, from water. Inspired by the concept of the circular economy, the technique is based on sugarcane bagasse, a waste material produced by sugar and ethanol plants.
“Isolated and chemically functionalized sugarcane bagasse fibers can be used as adsorbent material. Glyphosate adheres to its surface and is removed as a water contaminant by filtration, decantation or centrifugation,” Maria ...
Vizient awards UCSF Health top marks for quality patient care
2023-09-22
Hospital quality ratings assess safety, equity and effectiveness in hospitals nationwide
Vizient Inc. has named UCSF Health as a Top Performer for its high-quality patient care in the 2023 Bernard A. Birnbaum, MD, Quality Leadership Ranking.
This is the second year in a row that Vizient has recognized UCSF Health as a leader in health care quality. This year, UCSF Health ranked seventh among comprehensive academic medical centers, out of 116 medical centers that were evaluated in that cohort and ...
New research adds evidence to the benefits of ginger supplements for treating autoimmune diseases
2023-09-22
New research has revealed a potentially important role ginger supplements can play in controlling inflammation for people living with autoimmune diseases.
The research published today in JCI Insight focused on studying the impact of ginger supplementation on a type of white blood cell called the neutrophil. The study was especially interested in neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation, also known as NETosis, and what it may mean for controlling inflammation.
The study found ginger consumption by healthy individuals makes their neutrophils more resistant to NETosis. This is important because NETs are microscopic spider web-like structures that propel inflammation and clotting, which ...
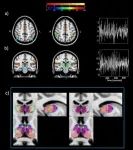
The role of the locus coeruleus. A blue stain linked to sleep
2023-09-22
A study conducted by researchers at the University of Liège (BE) Institute, using ultra-high field 7 Tesla MRI, are providing a better understanding of how sleep is regulated.
We've known for a long time that sleep is good for the brain. We also know that light is not just for seeing, but also plays an important role in other aspects such as mood. What we don't know is how all this happens in our brains. Two separate studies, carried out by researchers at the University of Liège using the 7 Tesla MRI on the GIGA-Centre de Recherche du Cyclotron platform, offer the ...
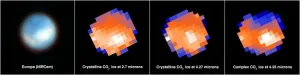
NASA’s Webb finds carbon source on surface of Jupiter’s moon Europa
2023-09-22
Jupiter’s moon Europa is one of a handful of worlds in our solar system that could potentially harbor conditions suitable for life. Previous research has shown that beneath its water-ice crust lies a salty ocean of liquid water with a rocky seafloor. However, planetary scientists had not confirmed if that ocean contained the chemicals needed for life, particularly carbon.
Astronomers using data from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have identified carbon dioxide in a specific region on the icy surface of Europa. Analysis indicates that this carbon likely originated in the subsurface ocean and ...
Wildlife mitigating measures no help for Ottawa’s freshwater turtles
2023-09-22
Local turtles facing extinction within a decade due to urban growth, says uOttawa study.
Urban sprawl and insufficient relief measures have left an Ottawa-area freshwater turtle facing extinction within the decade, says new research from the University of Ottawa and Trent University, which tracked changes to the turtle’s habitat over a 10-year period.
Specifically, the development of Terry Fox Drive in the city’s west end has led to a dangerous decline in the Blanding’s turtle’s (Emydoidea blandingii) habitat, leading to a 70% decline in adult population size, despite mitigating measures such as wildlife fencing, new wetlands ...
A network that spreads light and the role of thalamus in our brain
2023-09-22
New research conducted at the University of Liège, using ultra-high field 7 Tesla MRI, provides a better understanding of how light stimulates our brain and could provide new insights into how it works.
A research team at the ULiège GIGA Institute tried to understand better how light stimulates our cognition. Light acts like a cup of coffee and helps keep us awake. That's why we recommend not using too much light on our smartphones and tablets in the evening. This can disrupt our sleep. On the other hand, the same light can help us during the day. Many studies have shown that good lighting can help students in schools, ...
Unraveling the mysteries of glassy liquids
2023-09-22
Glass, despite its apparent transparency and rigidity, is a complex and intriguing material. When a liquid is cooled to form a glass, its dynamics slows down significantly, resulting in its unique properties.
This process, known as “glass transition”, has puzzled scientists for decades. But one of its intriguing aspects is the emergence of "dynamical heterogeneities," where the dynamics become increasingly correlated and intermittent as the liquid cools down and approaches the glass transition temperature.
In a new study, researchers propose a new theoretical framework to explain these dynamical heterogeneities in glass-forming ...
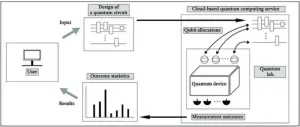
Can cloud-based quantum computing really offer a quantum advantage?
2023-09-22
A quantum machine can drastically speed up certain kinds of computation, but only if two or more quantum bits in the machine are entangled---that is, capable of displaying related behavior despite being separated. Seeking a way for users of cloud-based quantum computing services to detect qubit entanglement, Jiheon Seong and Joonwoo Bae of the Korea Advanced Institute of science and Technology developed and tested an entanglement witness circuit. It works to certify entanglement even when the cloud-based service allows only limited control ...
UNC-Chapel Hill research presents new development model for the world's third-longest river
2023-09-22
A new research paper published in Science Advances reveals how changes in the size of the Yangtze River watershed may have led to the carving of deep canyons.
In this study, UNC-Chapel Hill professor Eric Kirby and his co-authors explore the impact of drainage basin expansion on the growth of the Yangtze River.
“This study presents a new model for when and how the Yangtze River was born,” said Kirby, “The Yangtze is one of the world’s great rivers, rising on the Tibetan Plateau at altitudes over 17,000 feet and descending ...
Why are you better at recognizing upright faces? Clues from a person who sees the world differently
2023-09-22
When you see a familiar face upright, you’ll recognize it right away. But if you saw that same face upside down, it’s much harder to place. Now researchers who’ve studied Claudio, a 42-year-old man whose head is rotated back almost 180 degrees such that it sits between his shoulder blades, suggest that the reason people are so good at processing upright faces has arisen through a combination of evolution and experience. The findings appear September 22 in the journal iScience.
“Nearly everyone has far more experience with upright faces and ancestors whose reproduction ...
Jellyfish shown to learn from past experience for the first time
2023-09-22
Even without a central brain, jellyfish can learn from past experiences like humans, mice, and flies, scientists report for the first time on September 22 in the journal Current Biology. They trained Caribbean box jellyfish (Tripedalia cystophora) to learn to spot and dodge obstacles. The study challenges previous notions that advanced learning requires a centralized brain and sheds light on the evolutionary roots of learning and memory.
No bigger than a fingernail, these seemingly simple jellies have a complex visual system with 24 eyes embedded in their bell-like body. Living ...
Jellyfish are smarter than you think
2023-09-22
Jellyfish are more advanced than once thought. A new study from the University of Copenhagen has demonstrated that Caribbean box jellyfish can learn at a much more complex level than ever imagined – despite only having one thousand nerve cells and no centralized brain. The finding changes our fundamental understanding of the brain and could enlighten us about our own mysterious brains.
After more than 500 million years on Earth, the immense evolutionary success of jellyfish is undeniable. Still, we've always thought of them as simple creatures with very limited learning abilities.
The prevailing opinion is that ...
Vulnerability of older adults to government impersonation scams
2023-09-22
About The Study: In this study using a behavioral experiment designed to mimic a real-world imposter scam among 644 older adults, a sizable number of older adults engaged without skepticism. The results suggest that many older adults, including those without cognitive impairment, are vulnerable to fraud and scams.
Authors: Lei Yu, Ph.D., of Rush University Medical Center in Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.35319)
Editor’s ...
[1] ... [1670]
[1671]
[1672]
[1673]
[1674]
[1675]
[1676]
[1677]
1678
[1679]
[1680]
[1681]
[1682]
[1683]
[1684]
[1685]
[1686]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.