Should older adults with fewer years to live keep getting cancer screenings? Poll explores attitudes
2023-09-28
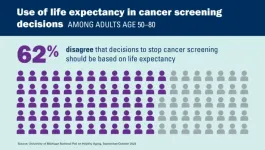
A majority of older adults disagree with the idea of using life expectancy as part of guidelines that say which patients should get cancer screenings such as mammograms and colonoscopies, a new poll finds.
In all, 62% of people aged 50 to 80 said that national guidelines for stopping cancer-detecting tests in individual patients should not be based on how long that person might have left to live, according to new results from the University of Michigan National Poll on Healthy Aging.
That goes against a trend in such guidelines, which national organizations develop based on medical evidence. Guidelines ...
Elk hoof disease likely causes systemic changes
2023-09-28
PULLMAN, Wash. – Elk treponeme-associated hoof disease, previously thought to be limited to deformations in elks’ hooves, appears to create molecular changes throughout the animal’s system, according to epigenetic research from Washington State University.
The findings, published in the journal Scientific Reports, also suggest those changes may be heritable. It remains to be seen though whether this means subsequent generations of elk may be more, or less, prone to catching the devastating disease that severely impairs the elk’s ability to find food and escape predators.
“It’s not just the ...
Wearable device data reveals that reduced sleep and activity in pregnancy is linked to premature birth risk
2023-09-28
A lack of sleep and reduced physical activity during pregnancy are linked to risk of preterm birth, according to new research led by the Stanford School of Medicine.
In the study, which will publish online Sept. 28 in npj Digital Medicine, the researchers collected data from devices worn by more than 1,000 women throughout pregnancy. With a machine learning algorithm, the scientists sifted through participants’ activity information to detect fine-grained changes in sleep and physical activity patterns.
“We showed that an artificial intelligence algorithm can build a ‘clock’ of physical activity and sleep ...
Predicting condensate formation by cancer-associated fusion oncoproteins
2023-09-28
(Memphis, Tenn – September 28, 2023) Many cancers are caused by fusion oncoproteins, molecules that aberrantly form when a rearrangement of DNA results in parts of two different proteins being expressed as one. Several fusion oncoproteins spontaneously form condensates inside cells that promote cancer development. New research by St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital established a method to study this biophysical process in cells, then used that information as a launchpad to predict the behavior of other fusion oncoproteins. The findings, which offer insight into ...
Biological particles play crucial role in Arctic cloud ice formation
2023-09-28
An international team of scientists from Sweden, Norway, Japan, and Switzerland, has presented research findings that reveal a crucial role of biological particles, including pollen, spores, and bacteria, in the formation of ice within Arctic clouds. These findings, published today in Nature Communications, have far-reaching implications for climate science and our understanding of the rapidly changing Arctic climate.
The research, whose outcomes have unveiled the connection between biological particles and the formation of ...
Fitness and staving off weight gain may be more important than weight loss for preventing kidney disease in obese adults, Drexel study says
2023-09-28
Fitness and Staving Off Weight Gain May Be More Important than Weight Loss for Preventing Kidney Disease in Obese Adults, Drexel Study Says
As obesity is a contributing factor to chronic kidney disease, weight loss can help mitigate a patient’s risk. But new research suggests that fitness and preventing weight gain could actually play a more important role in reducing risk than weight loss. The findings were published today in the journal Obesity from researchers at Drexel University’s College of Medicine and Dornsife School of Public Health.
The researchers followed 1,208 overweight ...
Child Development journal Q&A: Music intervention programs can enhance parent and baby language interactions
2023-09-28
Previous research shows that conversational turns (interactive conversations) between parents and children are important for a child’s long-term language development and academic achievement and that these conversations can be enhanced via parent-coaching language interventions. The neural networks responsible for language develop rapidly even before a child can talk, making these interactive conversations especially important during infancy.
Music is an engaging and social experience between parents and children that is often part of daily routines during infancy. Emerging literature also documents links between music experiences and child language outcomes. Researchers ...
New program helps improve toddlers’ self-control skills and healthy eating habits
2023-09-28
Two of the best predictors of life-long health and well-being are early childhood self-control skills and healthy eating habits. A new program that teaches parents how to cook with their 2-year-olds is helping toddlers excel on both fronts. Doing things like stirring ingredients together without spilling and singing a song while something is in the microwave helps toddlers learn multiple important self-control skills, like paying attention, controlling their bodies, waiting patiently, and cooperating with their parents. Toddlers also get excited about being involved in the “grown-up” activity and are more likely to try the new foods they help make. Previous research has shown that ...
Cannabis use disorder may be linked to increased risk of cardiovascular disease
2023-09-28
A new study has found that Canadian adults with cannabis use disorder appear to have an approximately 60% higher risk of experiencing their first heart attack, stroke, or other major cardiovascular event than those without cannabis use disorder.
The study, published in Addiction, measured the association between problematic marijuana use and the first-time occurrence of adverse cardiovascular disease events such as heart attack, stroke, cardiac dysrhythmias, and peripheral vascular disease.
Researchers used five Canadian health databases to create a cohort of nearly 60,000 participants, half with a cannabis use disorder ...
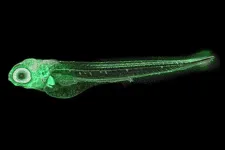
Fish reveal cause of altered human facial development
2023-09-28
Some substances in medicines, household items and the environment are known to affect prenatal child development. In a study published in Toxicological Sciences, researchers tested the effects of five drugs (including caffeine and the blood thinner warfarin) on the growth of zebrafish embryos. They found that all five had the same effect, impairing the migration of bone-forming cells which resulted in the onset of facial malformation. Zebrafish embryos grow quickly, are transparent and develop outside of the parent’s body, ...
How safe is your sushi?
2023-09-28
Sushi has become everyday fare in Norway and elsewhere around the globe, and many people opt for sashimi and other raw fish when they want to treat themselves to something tasty.
It is important to emphasise here that, as a general rule, it is completely safe to eat this type of food in Norway. However, despite the fact that sushi can be delicious, it also carries a health hazard, both for individuals and for society at large.
“Bacteria in sushi, sashimi and cold-smoked fish products can pose a risk to people who eat such foods frequently, especially people with weak immune systems, children and the elderly,” says Hyejeong Lee.
She recently completed her PhD at the Department ...
Job loss is linked to increased risk of miscarriage and stillbirth
2023-09-28
Researchers have found a link between a pregnant woman or her partner losing their job and an increased risk of miscarriage or stillbirth.
The study, which is published today (Thursday) in Human Reproduction [1], one of the world’s leading reproductive medicine journals, found a doubling in the chances of a pregnancy miscarrying or resulting in a stillbirth following a job loss.
The researchers, led by Dr Selin Köksal from the Institute for Social and Economic Research at the University of Essex, UK, ...
Protein p53 regulates learning, memory, sociability in mice
2023-09-28
Researchers have established the protein p53 as critical for regulating sociability, repetitive behavior, and hippocampus-related learning and memory in mice, illuminating the relationship between the protein-coding gene TP53 and neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders like autism spectrum disorder.
“This study shows for the first time that p53 is linked directly to autism-like behavior,” said Nien-Pei Tsai, an associate professor of molecular and integrative biology at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and a researcher at the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology.
In living systems, ...
New report adds heat to Levelling Up debate by revealing England's most 'insecure' regions
2023-09-28
Accessing stable employment with fair pay and predictable hours is harder for workers in the North and Midlands, which can severely affect their living standards, health, and future job prospects.
A new report published by the Work Foundation at Lancaster University reveals the regions with the highest and lowest levels of ‘severely insecure’ work (employment that is involuntarily temporary or part-time, or when multiple forms of insecurity come together, such as casual or zero-hours contracts, or low or unpredictable ...
Swapping starch and refined carbs for whole grains and fruit linked to less midlife weight gain
2023-09-28
Increased consumption of carbohydrate from refined grains, starchy vegetables, and sugary drinks is associated with greater weight gain throughout midlife, while increased fibre and carbohydrate from whole grains, fruit, and non-starchy vegetables is linked to less weight gain, finds a large US study published by The BMJ today.
Most of these associations were stronger for people with excessive body weight, highlighting the potential importance of carbohydrate quality and source for long term weight management, say the researchers.
The role of carbohydrates in weight gain and obesity remains controversial, and few studies have evaluated ...
The BMJ reveals ‘silent scandal’ of missing lung tests across England
2023-09-28
Patients in some of the most deprived areas of England, where respiratory conditions including chronic lung disease (COPD) and asthma are most prevalent, have limited or no access to vital diagnostic tests to confirm their diagnosis, reveals a survey by The BMJ today.
Despite NHS England’s promise of access via Community Diagnostic Centres (CDCs), journalist Sally Howard speaks to GPs in some of the worst affected areas who say having no means of referring patients for lung function tests is “troubling” and “a silent scandal.”
And last month, a report by the charity Asthma + Lung UK ...
Students made Oxford the murder capital of late medieval England, research suggests
2023-09-28
A project mapping medieval England’s known murder cases has now added Oxford and York to its street plan of London’s 14th century slayings, and found that Oxford’s student population was by far the most lethally violent of all social or professional groups in any of the three cities.
The team behind the Medieval Murder Maps – a digital resource that plots crime scenes based on translated investigations from 700-year-old coroners’ inquests – estimate the per capita homicide ...
Risk of premature birth from smoking while pregnant more than double previous estimates
2023-09-28
Cambridge researchers have found that women who smoke during pregnancy are 2.6 times more likely to give birth prematurely compared to non-smokers – more than double the previous estimate.
The study, published today in the International Journal of Epidemiology, also found that smoking meant that the baby was four times more likely to be small for its gestational age, putting it at risk of potentially serious complications including breathing difficulties and infections.
But the team found no evidence that caffeine intake was linked to adverse outcomes.
Women are currently recommended to stop smoking and limit their caffeine intake during pregnancy because of the risk of complications ...
Women seeking credibility in health care feel ‘on trial,’ struggle with constraints of double binds
2023-09-28
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Having a chronic illness is a great deal of work, communication researchers have long known. But having an illness that is stigmatized, not well understood or not perceived as a priority by clinicians is uniquely burdensome for many women, who find themselves struggling to establish both the legitimacy of their medical problems and their credibility with clinicians, family members and friends, a recent study suggests.
Sasha, a 25-year-old woman interviewed for the project, told the researchers she has a binder 3 inches thick containing all her medical records that she lugs to every doctor’s appointment to provide documentation ...
Chi-Nu experiment ends with data to support nuclear security, energy reactors
2023-09-28
The results of the Chi-Nu physics experiment at Los Alamos National Laboratory have contributed essential, never-before-observed data for enhancing nuclear security applications, understanding criticality safety and designing fast-neutron energy reactors. The Chi-Nu project, a years-long experiment measuring the energy spectrum of neutrons emitted from neutron-induced fission, recently concluded the most detailed and extensive uncertainty analysis of the three major actinide elements — uranium-238, uranium-235 and plutonium-239.
“Nuclear fission and related nuclear chain ...
Researchers dynamically tune friction in graphene
2023-09-28
The friction on a graphene surface can be dynamically tuned using external electric fields, according to researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign led by Professor Rosa Espinosa-Marzal of the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering. The work is detailed in the paper, “Dynamically tuning friction at the graphene interface using the field effect,” published September 19, 2023, in the journal Nature Communications.
Friction plays a key role in both natural and engineered systems, dictating the behavior of sliding contacts, affecting ...
Polyps as pixels: innovative technique maps biochemistry of coral reefs
2023-09-27
Using an innovative new approach to sampling corals, researchers at the University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa are now able to create maps of coral biochemistry that reveal with unprecedented detail the distribution of compounds that are integral to the healthy functioning of reefs. Their study was published today in Communications Biology.
“This work is a major step in understanding the coral holobiont [the coral animal and all of its associated microorganisms], which is critical for reef restoration and management,” said lead author Ty Roach, who conducted this study as a postdoctoral researcher at the Hawai‘i Institute of Marine Biology (HIMB) in the UH ...
Study shows how brain tumors make certain immune cells turn traitor
2023-09-27
September 27, 2023, NEW YORK – A Ludwig Cancer Research study has for the first time exhaustively analyzed immune cells known as neutrophils that reside in brain tumors, including gliomas, which develop in the brain itself, and cancers that spread there from the lung, breast and skin.
Led by Ludwig Lausanne’s Johanna Joyce and Roeltje Maas, an MD-PhD student in her laboratory, the study also details the key role neutrophils play in ensuring the survival of brain cancers and exposes the mechanisms by which the tumor microenvironment (TME) tweaks their biology to turn them into enablers of malignant growth. Its findings suggest new approaches ...
State politics, industry drive planetary health education for K-12 students in US
2023-09-27
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — As much of the U.S. broils under record-setting temperatures, battles wildfires and is rocked by fierce storms, a new study suggests that the science learning standards for many public schools are not preparing young people to understand and respond to problems such as climate change that will dramatically impact their lives and those of millions of people around the globe.
Published in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Science, the findings raise troubling questions about political bias shaping if and what the nation’s ...
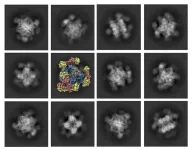
UCLA-led team develops key improvement to Nobel Prize-winning technology
2023-09-27
The scientists who received the 2017 Nobel Prize in chemistry were honored for their development of a technique called cryo-electron microscopy, or cryo-EM. The technology was revolutionary because it enabled scientists to see the atomic structure of biological molecules in high resolution.
But cryo-EM still had a catch: It was only effective for imaging large molecules.
Now, UCLA biochemists, working with pharmaceutical industry scientists, have developed a solution that will make it possible for cryo-EM to acquire high-quality images of smaller protein molecules, too. The scientists engineered a 20 nanometer, cube-shaped ...
[1] ... [1659]
[1660]
[1661]
[1662]
[1663]
[1664]
[1665]
[1666]
1667
[1668]
[1669]
[1670]
[1671]
[1672]
[1673]
[1674]
[1675]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.