New insights into how the human brain organises language
2023-09-29
Language is the most important tool for human communication and essential for life in our society. “Despite a great deal of neuroscientific research on the representation of language, little is known about the organisation of language in the human brain. Much of what we do know comes from single studies with small numbers of subjects and has not been confirmed in follow-up studies,” says Dr Sabrina Turker from the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences in Leipzig. This meta-analysis aims to help change that.
Based on more than 400 ...
Visual search: Context facilitates more effective strategies
2023-09-29
Study by LMU psychologists shows that distractor objects can help the visual system develop more effective search strategies.
People are continuously provided with an overwhelming stream of events flooding the sensory organs. However, while the brain has impressive processing capabilities, its capacity is strongly limited. Thus, an observer cannot consciously experience all the events and information available at any one time, but has to focus on some limited subset of the whole.
For many decades, researchers have investigated the neuro-cognitive mechanisms of this selective attention through the use of visual search and have shown that contextual cueing plays ...
Malaria: Treatment of Plasmodium falciparum malaria patients under threat in the Horn of Africa
2023-09-29
Diagnosis of Plasmodium falciparum malaria using rapid diagnostic tests and treatment with artemisinin derivatives, the main component of the malaria treatments recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO), are under threat in the Horn of Africa. Scientists from the Laboratory of Parasitology and Medical Mycology at the University of Strasbourg and Strasbourg University Hospital, in collaboration with the Eritrean Ministry of Health, the Institut Pasteur, Columbia University in New York and WHO, have detected the emergence and spread in Eritrea of parasites with both artemisinin resistance and genome modifications ...
New post-translational modification of the glycolytic enzyme enolase
2023-09-29
Tsukuba, Japan—Proteins are subject to post-translational chemical modifications that result in functional diversity. Methylation is one such modification that is generally believed to occur on lysine and arginine residues. Recently, this modification has been shown to occur on histidine residues as well. Furthermore, it has been suggested that histidine methylation occurs in a wide range of proteins. However, many details remain unknown: for example, which are the proteins that are methylated and ...
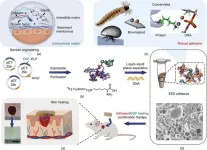
New frontier in biomedical engineering: Protein coacervates engineered into adhesive for unprecedented skin repair speed
2023-09-29
A team of researchers from China has made a significant breakthrough in biomedical engineering by developing a novel adhesive that promises to revolutionize wound management and tissue repair. The research, published in Engineering, unveils a biocomposite adhesive that exhibits robust adhesion and real-time skin healing properties.
Adhesives have long been recognized as a valuable tool in biomedical engineering. However, current adhesive systems face challenges in achieving strong and durable adhesion, limiting their effectiveness in wound healing. ...
New study unveils insights into ethylene copolymerization with linear and end-cyclized olefins using a metallocene catalyst
2023-09-29
A research team led by Changjiang Wu at SINOPEC (Beijing) Research Institute of Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. in China has made important progress in understanding the polymerization behavior and thermal properties of copolymers formed through ethylene copolymerization with linear and end-cyclized olefins. The findings, published in the journal Engineering, shed light on the potential of utilizing different comonomers in olefin solution polymerization to obtain high-performance polyolefin materials.
Polyolefin elastomers (POEs) are widely used in various industries due to their exceptional properties. However, the high cost ...
Study identifies new pathway to suppressing autoimmunity
2023-09-29
Researchers at Stanford University School of Medicine, Yale University School of Medicine, and the Hospital for Special Surgery Research Institute have uncovered new details about how the immune system prevents the production of antibodies that can recognize and damage the body’s own, healthy tissues. The study, to be published September 29 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), also reveals how this process is impaired in autoimmune disorders such as systemic sclerosis and systemic lupus ...
Diabetes may accelerate blood cancer growth, yet survival outcomes differ by race
2023-09-29
(WASHINGTON, Sept. 29, 2023) – Patients with multiple myeloma, a blood cancer of plasma cells in the bone marrow, who also have diabetes have a reduced overall survival when compared to those without diabetes. In a subgroup analysis, this difference in survival due to diabetes was seen in white patients but not in Black patients, according to a study published today in Blood Advances.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, diabetes affects 13% of the U.S. population, and this prevalence is growing rapidly. Multiple myeloma is the second most common blood cancer in the U.S. and disproportionately ...
Groundbreaking mathematical proof: new insights into typhoon dynamics unveiled
2023-09-29
In a remarkable breakthrough in the field of Mathematical Science, Professor Kyudong Choi from the Department of Mathematical Sciences at UNIST has provided an irrefutable proof that certain spherical vortices exist in a stable state. This groundbreaking discovery holds significant implications for predicting weather anomalies and advancing weather prediction technologies.
A vortex is a rotating region of fluid, such as air or water, characterized by intense rotation. Common examples include typhoons and tornadoes frequently observed in news reports. Professor Choi’s mathematical proof establishes the stability of specific ...
Teams invent a new metallization method of modified tannic acid photoresist patterning
2023-09-29
The micro/nano metal pattern formation is a key step in the assembly of various devices. However, ex situ approaches of metal patterning limited their industrial applications due to the poor stability and dispersion of metal nanoparticles. The in situ electroless deposition after lithography patterning may be a better choice for avoiding the growth and aggregation of metal particles in the polymers. Tannic acid is rich in natural products, having an adjacent tri-hydroxyl structure, which can realize the in situ reduction of metal ions on the photoresist pattern. A team of scientists ...
MoMFs could be central to liver regeneration
2023-09-29
The liver is a vital organ that plays a role in many essential functions, including digestion, detoxification, and metabolism. When the liver is damaged, it has the remarkable ability to regenerate itself. However, the process of liver regeneration is not fully understood.
A critical aspect of liver regeneration is removing dead tissue and necrotic lesions. In a recent study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, Feng et al. showed that monocyte-derived macrophages (MoMFs) play a crucial role in this process. MoMFs are a type of white blood cell that is recruited to the liver in response to injury. Once in the liver, MoMFs engulf dead cells ...
A lethal parasite’s secret weapon: Infecting non-immune cells
2023-09-29
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The organisms that cause visceral leishmaniasis, a potentially deadly version of the parasitic disease that most often affects the skin to cause disfiguring disease, appear to have a secret weapon, new research suggests: They can infect non-immune cells and persist in those uncommon environments.
Researchers found the Leishmania donovani parasites in blood-related stem cells in the bone marrow of chronically infected mice – precursor cells that can regenerate all types of cells in the blood-forming system. The finding may help explain why some people who develop visceral leishmaniasis, which is ...
Ball milling provides high pressure benefits to battery materials
2023-09-29
Cheaper, more efficient lithium-ion batteries could be produced by harnessing previously overlooked high pressures generated during the manufacturing process.
Scientists at the University of Birmingham have discovered that routine ball milling can cause high pressure effects on battery materials in just a matter of minutes, providing a vital additional variable in the process of synthesizing battery materials.
The research (part of the Faraday Institution funded CATMAT project), led by Dr Laura Driscoll, Dr Elizabeth Driscoll and Professor Peter Slater at the University of Birmingham is published in RSC Energy Environmental Science.
The use ...
Congenital Heart Surgeons' Society (CHSS) and fourteen professional organizations announce recommendations for performing pediatric heart surgery in US
2023-09-29
September 29, 2023, Cincinnati, OH — A set of recommendations to address the known variation in outcomes at US congenital heart surgery centers has been endorsed by 15 collaborating societies led by the Congenital Heart Surgeons' Society (CHSS). The guidelines will appear in “Recommendations for Centers Performing Pediatric Heart Surgery in the United States," to be co-published in the World Journal for Pediatric and Congenital Heart Surgery, Annals of Thoracic Surgery, and Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery.
“In ...
Mouthwash for dogs: water additive with pomegranate helps to keep canine teeth healthy
2023-09-29
Periodontal disease is one of the most common canine diseases, affecting at least 80% of dogs aged three and over. Periodontal disease begins as gingivitis, where gums become red and inflamed, and may bleed. Untreated, the disease can progress to periodontitis, where the alveolar bone is progressively damaged so that teeth may loosen or fall out. In turn, periodontitis is a risk factor for other diseases like cardiovascular and lung disease.
A major cause of periodontal disease is poor oral hygiene, ...
Racial/ethnic minority patients may be less likely than white patients to receive palliative care during breast cancer treatment
2023-09-29
ORLANDO, Fla. – Despite a steady increase in palliative care utilization from 2004 to 2020, non-Hispanic Black, Hispanic, and Asian or Pacific Islander patients with metastatic breast cancer were less likely to receive palliative care than non-Hispanic white patients, according to results presented at the 16th AACR Conference on the Science of Cancer Health Disparities in Racial/Ethnic Minorities and the Medically Underserved, held September 29-October 2, 2023.
Palliative care consists of treatments or procedures intended ...
Spanish-speaking men in sexual minority groups may lack knowledge about cancers linked to HPV
2023-09-29
ORLANDO, Fla. – A study found multiple gaps in awareness and knowledge about the connection between the human papillomavirus (HPV) and several types of cancer among Hispanic and Latino men who identified as sexual minorities, according to results presented at the 16th AACR Conference on the Science of Cancer Health Disparities in Racial/Ethnic Minorities and the Medically Underserved, held September 29-October 2, 2023.
“Sexual minority men are a population group at higher risk for HPV infections and ...
Structural racism may play a role in increased cancer mortality rates among racial minorities
2023-09-29
ORLANDO, Fla. – Structural racism was associated with increased county-level cancer mortality rates among minority populations compared with whites, according to results presented at the 16th AACR Conference on the Science of Cancer Health Disparities in Racial/Ethnic Minorities and the Medically Underserved, held September 29-October 2, 2023.
“Applying measures that attempt to capture the multiple and compounding ways racism presents in policies, laws, and practices at a population level shows how racism manifests beyond interpersonal interactions to negatively impact cancer outcomes,” said presenter Joelle N. Robinson-Oghogho, ...
Racial and ethnic minorities may be less willing than others to participate in clinical trials
2023-09-29
ORLANDO, Fla. – A survey conducted in one cancer center’s catchment area found that while a majority of respondents would be willing to participate in a clinical trial, members of racial and ethnic minority groups were significantly less likely to participate than non-Hispanic whites, according to results presented at the 16th AACR Conference on the Science of Cancer Health Disparities in Racial/Ethnic Minorities and the Medically Underserved, held September 29-October 2, 2023. Reasons to participate ...
NCI-sponsored cancer clinical trials have become more diverse over past two decades
2023-09-29
ORLANDO, Fla. – Compared to the year 2000, a greater proportion of NCI-sponsored early-phase clinical trial participants in 2022 were older, from minority racial/ethnic groups, and lived in historically underrepresented regions of the U.S., according to a study presented at the 16th AACR Conference on the Science of Cancer Health Disparities in Racial/Ethnic Minorities and the Medically Underserved, held September 29-October 2, 2023.
“Early-phase clinical trials, which primarily evaluate the safety of new therapies, have historically had insufficient representation of racial minorities, women, elderly ...
Research finds DEI initiatives during certain presidencies can affect bottom line
2023-09-29
DURHAM, N.H. — Corporate initiatives focused on diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI) for vulnerable social groups can change a company in many ways. According to researchers at the University of New Hampshire, how DEI affects a business’ bottom line may depend on the presidential administration and the general public’s perception at the time. They found that DEI initiatives put in place to support a specific social group during a presidential administration perceived as unfriendly to a particular issue related to that community resulted in higher stock prices than during a presidency that had a better relationship ...
Alcohol 'promotion' detracted from success of Women's World Cup
2023-09-29
Broadcasters should avoid focusing on alcohol in crowd shots during major sporting events, such as this summer’s Women’s World Cup final, say researchers.
In a new commentary published in the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine (JRSM), researchers from the Technological University of the Shannon and the University of Galway in the Republic of Ireland suggest that the ‘thorny issue of alcohol’ detracted from the success of the record-breaking tournament.
The authors, Dr Frank Houghton ...
Solving a sticky, life-threatening problem
2023-09-29
In 2009, a mysterious fungus emerged seemingly from out of thin air, targeting the most vulnerable among us. It sounds like Hollywood, but the fungus in question poses a very real threat. Scientists are scrambling to figure out what makes the life-threatening fungus Candida auris tick--and why even the best infection control protocols in hospitals and other care settings often fail to get rid of it.
Researchers at U-M have zeroed in on C. auris’ uncanny ability to stick to everything from skin to catheters and made a startling discovery.
The investigative team, led by Teresa O’Meara, Ph.D. of the U-M Medical School Department of Microbiology and ...
A deep look into the progression of Parkinson's Disease
2023-09-29
Parkinson's disease is a complex neurodegenerative disorder that leads to the deterioration of specific types of neurons in the brain, resulting in a number of motor and non-motor symptoms. It is currently estimated that more than 10 million people in the world are living with Parkinson’s disease, the second most common neurodegenerative disorder after Alzheimer’s. That number is expected to swell up to 14 million by 2040 in what is being referred to as the Parkinson’s pandemic.
One of the key events in Parkinson's disease is the accumulation of a protein called alpha-synuclein inside neurons. That accumulation disrupts the normal functioning ...
Study pinpoints the length of incidental activity linked to health benefits
2023-09-29
A new wearables study tracking over 25,000 people provides the best evidence yet that short bouts of incidental activity, the kind we do as part of daily living, could reduce risk of heart attack, stroke and even premature death – but the length of activity and intensity matters.
“From walking up the stairs to speedily mopping the floors; in recent years we’ve come to understand that it is not just structured exercise that is good for our health, but we know very little about how these short bouts of incidental activity translate to health benefits,” said the study’s senior author Professor Emmanuel Stamatakis from the University ...
[1] ... [1652]
[1653]
[1654]
[1655]
[1656]
[1657]
[1658]
[1659]
1660
[1661]
[1662]
[1663]
[1664]
[1665]
[1666]
[1667]
[1668]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.