Ultrasound enables gene delivery throughout the brain
2023-09-27
HOUSTON – (Sept. 27, 2023) – Rice University researchers tested the safety and feasibility of gene delivery to multiple brain regions using a noninvasive, ultrasound-based technique in rodents, and their findings suggest that the efficiency of gene delivery improves within each targeted site when more sites are opened.
Shirin Nouraein, a doctoral student working in the lab of Rice bioengineer Jerzy Szablowski, is the lead author on the study recently published in the journal Gene Therapy.
The paper, “Acoustically Targeted Noninvasive Gene Therapy in Large Brain Volumes,” ...
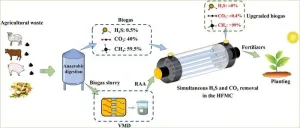
Elevating biogas upgrading performance on renewable aqueous ammonia solution via a novel “membrane method”
2023-09-27
Biogas is usually produced by anaerobic digestion of organic waste such as animal manures and straw wastes, which is a typical green renewable energy and can be used as a fuel for power generation and heat production. China has owned large scale of biogas production, with an annual output of about 15 billion m3 biogas, and the biogas development and utilization provide a new choice for coping with the energy crisis. Factually, biogas contains about 60% CH4 and about ...
Golden Goose Award announces 2023 awardees for discoveries in DNA sequencing technique, a bacteria-inspired method that saves crops and chicken pedigree lines
2023-09-27
WASHINGTON, D.C. – The Golden Goose Award, which celebrates federally funded research that sounds silly, but ultimately benefits society, has selected five researchers across the fields of biology, agriculture and genomics for their unexpected breakthroughs as 2023 awardees. On September 27, 2023, the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS), the world’s largest multidisciplinary scientific society, will co-host the 12th annual Golden Goose Award ceremony with the Association of American Universities, a founding member of the Golden Goose Award, at the Library ...
Inventors of nanopore sequencing honored at Library of Congress
2023-09-27
Two UC Santa Cruz researchers were honored on September 27 at the Library of Congress for the invention of nanopore sequencing, which became a new and revolutionary method to read DNA and RNA.
David Deamer and Mark Akeson, both emeritus professors of biomolecular engineering at the Baskin School of Engineering, received the American Association for the Advancement of Science’s (AAAS) Golden Goose Award for the invention. Their colleague and friend Daniel Branton, a Havard biologist and co-inventor of the technology, was also honored.
The Golden Goose award is given to scientists whose federally-funded research ...
Experimental nasal spray may offer quick, easy remedy for treating rapid heartbeat
2023-09-27
Research Highlights:
In a new study, etripamil, a rapid- and short-acting investigational medication formulated to be delivered via nasal spray, restored a normal heart rhythm in less than 30 minutes in most users with intermittent rapid heartbeats, sparing them a trip to the emergency room to receive intravenous medication.
Participants were able to detect when they were experiencing tachycardia (heart rate over 100 beats/minute) and use the medication appropriately and safely.
The self-administered treatment may help the approximately 1 in 300 adults in the U.S. ...
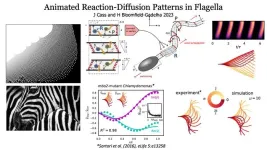
Sperm swimming is caused by the same patterns that are believed to dictate zebra stripes
2023-09-27
Patterns of chemical interactions are thought to create patterns in nature such as stripes and spots. This new study shows that the mathematical basis of these patterns also governs how sperm tail moves.
The findings, published today in Nature Communications, reveal that flagella movement of, for example, sperm tails and cilia, follow the same template for pattern formation that was discovered by the famous mathematician Alan Turing.
Flagellar undulations make stripe patterns in space-time, generating waves that travel along the tail to drive the sperm and microbes forward.
Alan Turing is most well-known for helping ...
New insights into soil liquefaction during earthquakes research reveals
2023-09-27
In a new study, the conventional understanding of soil liquefaction is being challenged, significantly reshaping our comprehension of earthquake-related soil deformation. Traditionally, soil liquefaction has been linked to undrained conditions near earthquake epicenters, but this research reveals that liquefaction can take place under drained conditions, even at considerably lower seismic-energy density levels. This discovery sheds new light on far-field liquefaction events that have long perplexed scientists. The study highlights how seismic shaking, even in drained conditions, triggers interstitial fluid flow within the soil, leading ...
Byzantine Greek inscription of Psalms 86 found in Hyrcania: unearthing ancient faith
2023-09-27
A Koine Greek inscription paraphrasing Psalms 86 was discovered by Hebrew University archaeologists at the site of Hyrcania Fortress in the Judean Desert. Adorned with a cross, the Byzantine-era inscription was likely made by a knowledgeable monk and holds significance as a well-known prayer in the Masoretic text and Christian liturgy. Analysis of the script's style suggests a dating no later than the first half of the 6th century CE, the height of the Byzantine era, with minor grammatical errors revealing the scribe’s ...
Why an unusual global export industry keeps growing in a developing country
2023-09-27
The global citrus export industry based in South Africa is a surprising outlier in many ways, not least for its vigorous growth. Somehow, the diverse industry has emerged as the second biggest in the world after Spain.
Researchers Ms Shingie Chisoro and Prof Simon Roberts unpack the key factors driving this exceptional success in a study published in The European Journal of Development Research.
Chisoro is a PhD candidate and Roberts the Lead Researcher at the Centre for Competition, Regulation and Economic Development (CCRED), within the College of Business & Economics at the University of Johannesburg.
Resilient ...
Race matters when prescribing hormone therapy for menopausal women
2023-09-27
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Sept 27, 2023)—Michael Jackson may have sung “it don’t matter if you’re black or white,” but when it comes to prescribing hormone therapy, it appears that race may definitely matter. That is according to a new study that found even though Black patients have more menopause symptoms, they receive less treatment. Study results will be presented during the 2023 Annual Meeting of The Menopause Society in Philadelphia September 27-30.
Women experience menopause differently with no two women having the exact same symptoms. Prior research has confirmed that ...
Shedding pounds during midlife is difficult, but not impossible
2023-09-27
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Sept 27, 2023)—Unwanted weight gain is a common problem associated with the menopause transition. Not only does it harm a woman’s self-esteem, but it is also associated with the development of heart disease, cancer, and declines in cognition and mental health. Tips for managing weight during midlife will be provided as part of a presentation at the 2023 Annual Meeting of The Menopause Society in Philadelphia September 27-30.
Weight gain in midlife women is the result of changes related to aging, menopause, and lifestyle. As women age, they are likely to expend less energy because of a reduction in physical activity and a decrease in lean mass. As a double whammy, ...
Can you actually have a hot flash in cold weather?
2023-09-27
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Sept 27, 2023)—It seems counter-intuitive for women to experience hot flashes in cold temperatures but, thanks to declining estrogen levels that cause narrowing of the thermoneutral zone, changes in body core temperature can induce sweating responses in any weather. According to a new study, brown adipose tissue activity may be a key reason why. Study results will be presented during the 2023 Annual Meeting of The Menopause Society in Philadelphia, September 27-30.
“How can I be hot and cold at the same time?” It’s a common question asked by perimenopausal ...
New technologies aid in accurately identifying bone fragility
2023-09-27
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Sept 27, 2023)—Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is the gold standard for assessing bone mass and evaluating fracture risk. But new technologies shed light on knowledge gaps not filled by DXA alone and sometimes suggest the need for additional procedures to accurately assess bone health. A presentation at the 2023 Annual Meeting of The Menopause Society in Philadelphia September 27-30 will focus on the evolution of technology to better diagnose bone fragility.
The discussion of bone health is especially relevant for postmenopausal women who are more vulnerable to osteoporosis and osteopenia because of declining estrogen levels that occur ...
Hot flashes yet another early indicator for Alzheimer's disease
2023-09-27
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Sept 27, 2023)—As if hot flashes alone weren’t bad enough for women going through the menopause transition, a new study suggests that, especially when they occur during sleep, hot flashes may be early indicators of a woman’s increased risk for Alzheimer’s disease (AD). And, the more hot flashes, the greater the disease risk. Study results will be presented during the 2023 Annual Meeting of The Menopause Society in Philadelphia September 27-30.
Women comprise two-thirds of individuals with AD, and there are ...
Post-traumatic stress symptoms can cause problems in the bedroom for midlife women
2023-09-27
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Sept 27, 2023)—Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) has been associated with a number of adverse mental and physical health outcomes. Little is known, however, regarding its impact on sexual functioning among midlife women. A new study is shedding light on the topic, suggesting that greater PTSD symptoms lead to worse sexual functioning. Study results will be presented during the 2023 Annual Meeting of The Menopause Society in Philadelphia, September 27-30.
PTSD is more common among women than many ...
The effects of sexual orientation on sexual function and distress
2023-09-27
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Sept 27, 2023)—In recent years, there has been debate around the topic of who is happier, healthier, and more satisfied sexually—traditional heterosexual or sexual minority women. A new study suggests that cisgender heterosexual women have higher relationship scores and less anxiety and depression than their less traditional counterparts. Study results will be presented during the 2023 Annual Meeting of The Menopause Society in Philadelphia September 27-30.
Satisfaction with one’s relationship and sex life has been shown to ...
Hot flashes linked with risk factors for cardiovascular disease
2023-09-27
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Sept 27, 2023)—Hot flashes have long been known to be linked to a number of adverse health effects. Emerging data suggests an association between them and cardiovascular disease. A new study is the first to link physiologically assessed hot flashes with heightened systemic inflammation which is a risk factor for heart disease. Study results will be presented during the 2023 Annual Meeting of The Menopause Society in Philadelphia September 27-30.
Vasomotor symptoms, more often referred to as hot flashes, are one of the most common symptoms identified during the menopause transition, with roughly 70% of midlife ...
The impact of menopause stage on age-related changes in the brain
2023-09-27
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Sept 27, 2023)—Driven by changing estrogen levels, the menopause transition has a major influence on physiology during aging. Estrogen receptors populate numerous brain regions which explains why cerebral glucose metabolism is affected during the perimenopause stage. A new study investigated the association between the menopause stage and cerebral hemodynamics during typical aging. Study results will be presented during the 2023 Annual Meeting of The Menopause Society in Philadelphia September 27-30.
It has been suggested that changes in cerebral physiology during aging may ...
What your hair and saliva say about your risk for depression and cognitive shortfalls during menopause
2023-09-27
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Sept 27, 2023)—Stress affects the body and brain in many ways by causing the endocrine system to increase cortisol levels. These spiked levels can be found throughout the body. A new study suggests that elevated cortisol levels in the hair and saliva may affect cognitive and mental health in late peri/early postmenopausal women. Study results will be presented during the 2023 Annual Meeting of The Menopause Society in Philadelphia September 27-30.
It’s no secret that stress can take a major toll on the body and ...
Obese women have worse menopause symptoms nd get less relief from hormone therapy
2023-09-27
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Sept 27, 2023)—Obesity has already been associated with a number of adverse health conditions and can interfere with a person’s quality of life. A new study suggests that, in addition to these other problems, it may also worsen a woman’s menopause symptoms and limit the amount of relief she gets from hormone therapy (HT). Study results will be presented during the 2023 Annual Meeting of The Menopause Society in Philadelphia, September 27-30.
HT remains the most effective ...
New research identifies genetic links between schizophrenia and cardiovascular disease risk factors
2023-09-27
WASHINGTON, D.C., Sept. 27, 2023 — New research finds that people with schizophrenia have a genetic propensity to smoking and a reduced genetic risk of obesity. The study, published in The American Journal of Psychiatry, revealed genetic overlap between schizophrenia and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors, particularly body mass index (BMI) and smoking. The findings highlight the importance of environmental factors in the development of obesity and other CVD comorbidities.
Schizophrenia is associated with an increased ...
Workshop synthesis paper describes value of prescribed fire in wilderness areas
2023-09-27
GUNNISON, Colorado, September 18, 2023 - Many of the wilderness areas that we treasure were historically shaped by fire. Yet today, many wilderness landscapes are caught in the wildfire paradox – widespread suppression and exclusion of burning over the last century have increased the likelihood of high-intensity fires, which are more damaging rather than restorative. In December of 2022, experts from land management agencies, Tribes, and organizations across the country convened at the Wilderness and Fire Workshop in Gunnison to consider solutions to this dilemma, including the use of prescribed fire. Today, ...
Patients who quit smoking after percutaneous coronary intervention do as well as non-smokers – unless they had smoked heavily
2023-09-27
Patients who quit smoking after undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for narrowed arteries have similar outcomes as non-smokers during four years of follow-up after the procedure, according to a large study published in the European Heart Journal [1] today (Wednesday). However, if they had been heavy, long-term smokers, no improvement was seen.
The study of 74,471 patients who had a PCI between 2009 and 2016 is the first, large population-based study to examine the impact of smoking on cardiovascular outcomes, such as death, heart ...
USC launches liver disease study as part of $50.3 million “multi-omics” consortium
2023-09-27
The Keck School of Medicine of USC has received funding from the National Institutes of Health as part of a five-year, $50.3 million “multi-omics” study of human health and disease involving six sites. Researchers in the Multi-Omics for Health and Disease consortium will study fatty liver disease, hepatocellular carcinoma, asthma, chronic kidney disease, preeclampsia and other conditions, with a focus on underrepresented racial and ethnic groups.
Throughout the study, researchers will use ...
How silencing a gene-silencer could lead to new cancer drugs
2023-09-27
Deep inside our cells—each one complete with an identical set of genes—a molecular machine known as PRC2 plays a critical role in determining which cells become heart cells, versus brain or muscle or skin cells.
When the machine is missing or broken, normal fetal development can’t occur. If it’s mutated, cells can grow uncontrollably, and cancer can arise—a fact that has made PRC2 a source of keen interest for drug developers.
New research by scientists at CU Boulder and Harvard Medical School offers an unprecedented ...
[1] ... [1645]
[1646]
[1647]
[1648]
[1649]
[1650]
[1651]
[1652]
1653
[1654]
[1655]
[1656]
[1657]
[1658]
[1659]
[1660]
[1661]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.