Contagious cancers in cockles sequenced, showing unexpected instability
2023-10-02
CONTAGIOUS CANCERS IN COCKLES SEQUENCED, SHOWING UNEXPECTED INSTABILITY
Transmissible cancers in cockles — marine cancers that can spread through the water — have been sequenced for the first time, unearthing new insight into how these cancers have spread across animal populations for hundreds, possibly thousands, of years.
The study, from researchers at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, the CiMUS research centre at the Universidade de Santiago de Compostela in Spain, and collaborators across multiple countries, found that these cockle tumours are highly genetically unstable. The cancer ...
Massive low earth orbit communications satellites could disrupt astronomy
2023-10-02
Observations of the BlueWalker 3 prototype satellite show it is one of the brightest objects in the night sky, outshining all but the brightest stars.
Astronomers have raised concerns that without mitigation, groups of large satellites could disrupt our ability to observe the stars from Earth and perform radio astronomy.
Several companies are planning ‘constellations’ of satellites – groups of potentially hundreds of satellites that can deliver mobile or broadband services anywhere in the world.
However, these satellites need to be in ‘low-Earth’ orbit and can be relatively large, ...
Nerve cells can detect small numbers of things better than large numbers of things
2023-10-02
When two, three or four apples are placed in front of us, we are able to recognize the number of apples very quickly. However, we need significantly more time if there are five or more apples and we often also guess the wrong number. In fact, the brain does actually register smaller numbers of things differently than larger ones. This has been demonstrated in a recent study by the University of Tübingen, University of Bonn and the University Hospital Bonn. The results were published in the magazine Nature ...
Boston Children’s Hospital researchers uncover insights into the developmental trajectory of autism
2023-10-02
In a groundbreaking study published in JAMA Pediatrics on October 2, 2023, researchers at Boston Children’s Hospital shed new light on the evolving nature of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) diagnoses in early childhood. Diagnosing ASD at a young age is important for early intervention and treatment, but this new study suggests that not all kids continue to meet the criteria for ASD as they get older.
The team found that 37% of children diagnosed with ASD as toddlers no longer meet the criteria for ASD around the age of six. Children with lower adaptive skills—essential everyday abilities encompassing communication, self-care, and decision-making—tend ...
Sustainable protection of rapidly subsiding coastlines with mangroves
2023-10-02
Vulnerable coastlines
Unfortunately, precisely in these rural densely populated Asian regions, mangroves have in the past been cleared to free up land for other uses such as aquaculture. This has made these coasts vulnerable to rapid erosion. Restoring mangroves seems a logical solution to reverse this process and protect these densely populated coastlines. However, this requires understanding if mangroves can cope with extreme rates of relative sea level rises, as experienced in these subsiding areas.
Since 2015 NIOZ researcher Celine van Bijsterveldt visited Indonesia regularly during her studies and her Phd. ...
Boreal and temperate forests now main global carbon sinks
2023-10-02
Using a new analysis method for satellite images, an international research team, coordinated by the French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission (CEA) and INRAE, mapped for the first time annual changes in global forest biomass between 2010 and 2019. Researchers discovered that boreal and temperate forests have become the main global carbon sinks. Tropical forests, which are older and degraded by deforestation, fire and drought, are nearly carbon neutral. The findings, published in Nature Geoscience, highlight the importance of accounting for young forests and forest ...
Differences in mortality rates for fatal cerebral haemorrhage between Finnish university hospitals
2023-10-02
Subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) is one of the most dangerous cerebrovascular disorders, with as many as 40% of patients dying within one month of the event.
A study recently published in the esteemed Neurology journal investigated whether there are differences in the prognosis of SAH patients between the university hospital districts in Finland. The research dataset was composed of nearly 10,000 SAH cases from 1998 to 2017, including information on patients who died before receiving neurosurgical care.
Prognoses ...
Smooth avatar-user synchronization for the metaverse
2023-10-02
Mobile phones, smartwatches and earbuds are some gadgets that we carry around physically without much thought. The increasingly digitalised world sees a shrinking gap between human and technology, and many researchers and companies are interested in how technology can be further integrated into our lives.
What if, instead of incorporating technology into our physical world, we assimilate ourselves into a virtual environment? This is what Assistant Professor Xiong Zehui from the Singapore University of Technology ...
Defense against the enemy within
2023-10-02
The research teams of Professor René Ketting at the Institute of Molecular Biology (IMB) in Mainz, Germany, and Dr. Sebastian Falk at the Max Perutz Labs in Vienna, Austria, have identified a new enzyme called PUCH, which plays a key role in preventing the spread of parasitic DNA in our genomes. These findings may reveal new insights into how our bodies detect and fight bacteria and viruses to prevent infections.
Our cells are under constant attack from millions of foreign intruders, such as viruses and bacteria. To keep us from getting sick, ...
New tool reveals how drugs affect men, women differently -- and will make for safer medications
2023-10-02
UVA Health researchers have developed a powerful new tool to understand how medications affect men and women differently, and that will help lead to safer, more effective drugs in the future.
Women are known to suffer a disproportionate number of liver problems from medications. At the same time, they are typically underrepresented in drug testing. To address this, the UVA scientists have developed sophisticated computer simulations of male and female livers and used them to reveal sex-specific differences in how the tissues are affected by drugs.
The new model has already provided ...
Researchers develop mixture of compounds to help preserve organs before transplantation
2023-10-02
Using zebrafish as a model, investigators have determined a suitable combination of chemical compounds in which to store hearts, and potentially other organs, when frozen for extended periods of time before transplantation.
The work, which is published in The FASEB Journal, involved a variety of methods, including assays at multiple developmental stages, techniques for loading and unloading agents, and the use of viability scores to quantify organ function.
These methods allowed scientists to perform the largest and most comprehensive screen of cryoprotectant agents to determine their toxicity and efficiency at preserving ...
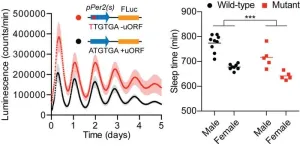
A surprising way to disrupt sleep
2023-10-02
Osaka, Japan - Circadian rhythms, the internal biological clocks that regulate our daily activities, are essential for maintaining health and well-being. While the role of transcription in these rhythms is well-established, a new study sheds light on the critical importance of post-transcriptional processes. The research, titled “Circadian ribosome profiling reveals a role for the Period2 upstream open reading frame in sleep,” to be published in PNAS, redefines our understanding of how translation and post-transcriptional processes influence the body’s internal clock and its impact on sleep patterns.
Timing Is Everything: ...
To Eat or Not to Eat: Targeting autophagy to enhance memory immune responses
2023-10-02
Osaka, Japan – Memory B cells depend on autophagy for their survival, but the protein Rubicon is thought to hinder this process. Researchers from Osaka University have discovered a shorter isoform of Rubicon called RUBCN100, which enhances autophagy in B cells. Mice that lacked the longer isoform, RUBCN130, produced more memory B cells in a way that relied on autophagy. These findings provide further insight into the role of Rubicon in autophagy.
Autophagy is a mechanism that degrades and ...
Researchers find a cause of Parkinson’s disease
2023-10-02
Until recently, our understanding of Parkinson's disease has been quite limited, which has been apparent in the limited treatment options and management of this debilitating condition.
Our recent understanding has primarily revolved around the genetic factors responsible for familial cases, while the causative factors in the vast majority of patients remained unknown.
However, in a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen have unveiled new insights into the workings of the brain in Parkinson's patients. Leading the groundbreaking discovery is Professor Shohreh Issazadeh-Navikas.
“For the first time, we can show that mitochondria, ...
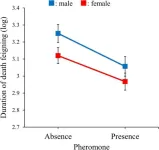
Pheromones influence death feigning behavior in beetles
2023-10-02
Predation is a driving force in the evolution of anti-predator strategies, and death feigning, characterized by immobility in response to threats, is a common defensive mechanism across various animal species. While this behavior can enhance an individual's survival prospects by reducing a predator's interest, it also carries costs, such as limited opportunities for feeding and reproduction. Recently, researchers from Okayama University, Japan, investigated how pheromones, important chemical signals that affect foraging and reproduction, might influence death-feigning behavior in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum.
“Male beetles release an aggregation pheromone called ...
Genetics of attraction: mate choice in fruit flies
2023-10-02
Genetic quality or genetic compatibility? What do female fruit flies prioritize when mating? Researchers at the University of Zurich show that both factors are important at different stages of the reproductive process and that females use targeted strategies to optimize the fitness of their offspring.
Breeding female fruit flies face a difficult decision: do they mate with the male that has the best genes, or with the one whose genes best match their own? Evolutionary biologists from the University of Zurich and Concordia University have now investigated ...
FAU Engineering study employs deep learning to explain extreme events
2023-10-02
Identifying the underlying cause of extreme events such as floods, heavy downpours or tornados is immensely difficult and can take a concerted effort by scientists over several decades to arrive at feasible physical explanations.
Extreme events cause significant deviation from expected behavior and can dictate the overall outcome for a number of scientific problems and practical situations. For example, practical scenarios where a fundamental understanding of extreme events can be of vital importance include rogue waves in the ocean that could endanger ships and offshore structures or increasingly ...
New study uncovers potential treatment for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
2023-10-02
A breakthrough study, jointly led by Professor Jang Hyun Choi and Professor Sung Ho Park from the Department of Biological Sciences at UNIST has identified an important factor involved in the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) caused by obesity. The research team discovered that Thrap3, a protein associated with thyroid hormone receptors, plays a significant role in exacerbating NAFLD by inhibiting the activity of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key regulator of fat metabolism in the liver.
NAFLD encompasses various metabolic diseases such as fatty hepatitis and cirrhosis resulting from excessive fat accumulation. ...
Susan G. Komen® analysis shows many breast cancer patients struggle to afford basic needs: Housing, transportation, utilities
2023-10-02
Lower income breast cancer patients often struggle to afford life’s necessities such as housing, transportation and utilities due to direct and incidental costs related to their treatment, according to a new analysis by Susan G. Komen®, the world’s leading breast cancer organization. These top needs were identified by Susan G. Komen’s Patient Care Center, which provided nearly $9.1 million in grants to more than 16,000 breast cancer patients from April 1, 2022 to March 31, 2023, as part of Komen’s direct-to-patient ...
Dense measurement network revealed high level of PM2.5 in Punjab due to crop residue burning and its transport to Haryana and Delhi NCR
2023-10-02
A group of international collaborators led by the Research Institute for Humanity and Nature (RIHN) team performed the first quantitative study of air pollution in the north-western India region using 29 low-cost and reliable instruments, demonstrating the advantages of source region observations to link crop residue burning (CRB) and air pollution at local to regional scales.
Exposure to particulate matter less than 2.5 µm in diameter (popularly known as PM2.5) causes health hazards in cities and major emission regions of the world. Although the major sources ...
Next-generation printing: precise and direct, using optical vortices
2023-10-02
Osaka, Japan – Will printed photographs ever match the precision of a mirror's reflection? Even though the answer may still be no for a while, Osaka Metropolitan University scientists have made significant strides in precision printing with their innovative optical vortex laser-based technique that allows for the precise placement of minuscule droplets with micrometer-scale accuracy.
Inkjet technology is a well-known printing technique that emits microdroplets from a nozzle directly onto a surface. However, when the ink droplets are viscous, with high density, ...
Pharmacists can improve access to life-saving vaccines
2023-10-02
HPV, or human papillomavirus, is the most common sexually transmitted infection. It is also the leading cause of cervical cancer. Over 1,400 Canadian women are affected yearly, with almost 400 deaths, according to the Canadian Cancer Society. It is completely preventable with the HPV vaccine, and yet, unfortunately, many people are unvaccinated.
University of Waterloo researchers have found a possible solution to this on-going issues. Using an electronic questionnaire at the time of appointment scheduling for seasonal influenza or COVID-19 vaccines, researchers have found, is a quick and efficient way to identify people in Ontario willing to receive additional life-saving vaccines.
“This ...
Researchers studied thousands of fertility attempts hoping to improve IVF
2023-10-02
By genetically testing nearly one thousand embryos, scientists have provided the most detailed analysis of embryo fate following human in vitro fertilization.
Nearly half the embryos studied underwent developmental arrest because of genetic mishaps in early development — a revealing insight that suggests more IVF babies could come to term with changes in the fertility treatment process. The unique combination of data from arrested embryos also sheds new light on the still largely mysterious earliest stages of pregnancy through natural ...
Precision medicine navigators increase genomic testing rates for Black patients with prostate cancer
2023-10-02
SAN DIEGO, October 1, 2023 — The presence of a clinical navigator to act as a liaison between people with prostate cancer and the health care system greatly increases the likelihood that patients, especially Black patients, will receive advanced testing that can help predict the severity of their disease and guide treatment, a new study suggests.
The study showed patients seen by a precision medicine navigator were substantially more likely to receive genomic testing than those not seen by the navigator. Black patients, whose genomic testing rates traditionally ...
Play in early childhood helps build a better brain, says leading expert
2023-10-02
Dr Jacqueline Harding, director of Tomorrow’s Child and an early childhood expert at Middlesex University, argues that the young child’s brain is inherently designed to be playful and this is crucial for its development.
In her new book, The Brain that Loves to Play, she challenges the traditional division between play and learning, emphasizing the essential role of play in early years education and holistic child development.
With a renewed vision for the fusion of play and learning, the book aims to contribute to the ...
[1] ... [1638]
[1639]
[1640]
[1641]
[1642]
[1643]
[1644]
[1645]
1646
[1647]
[1648]
[1649]
[1650]
[1651]
[1652]
[1653]
[1654]
... [8821]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.