Detecting microplastics(MPs) with light!!
2023-10-05
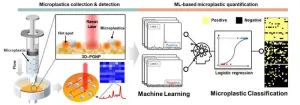
A research team led by Dr. Ho Sang Jung of the Department of Nano-Bio Convergence at the Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS), a government-funded research institute under the Ministry of Science and ICT, in collaboration with the KOTITI Testing & Research Institute, has developed the world's first technology to rapidly and highly sensitively detect microplastics(MPs) in the field, which are well known to cause human and genetic toxicity through environmental pollution and the food chain.
The on-site applicable MPs detection technology developed ...
Comfort with a smaller carbon footprint
2023-10-05
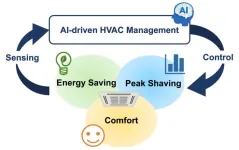
Osaka, Japan – As organizations work to reduce their energy consumption and associated carbon emissions, one area that remains to be optimized is indoor heating and cooling. In fact, HVAC – which stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning – represents, on average, about 40% of a building’s total energy use. Methods that conserve electricity while still providing a comfortable indoor environment for workers could make a significant difference in the fight against climate change.
Now, researchers from Osaka University have demonstrated significant energy savings through the application of a new, AI-driven algorithm ...
Study shows enhanced pandemic-related infection prevention and control practices reduced incidence of healthcare-associated infections
2023-10-05
A new study conducted by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center suggests that enhanced infection prevention and control (IPC) measures implemented to address the COVID-19 pandemic contributed to a significant decrease in many healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) and a reduction in respiratory viral infections (RVIs). The findings, published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC), provide some of the first evidence that strict pandemic-related IPC interventions reduced HAI rates among vulnerable patient populations.
“Previous, large-scale ...
New study reveals Australian Long COVID response lagging
2023-10-05
New research by RMIT University and Northern Health has examined Australia’s Long COVID services, guidelines and public health information, compared with international standards.
The researchers found Australia lacking in several categories, including early investigation, accessibility and availability of trustworthy public health information, and adequate multidisciplinary Long COVID services to meet demand.
Dean of RMIT’s School of Health and Biomedical Sciences and co-author on the paper, Professor Catherine Itsiopoulos, warned that this problem will only worsen over time.
“Long ...
Vaccine via the nasal passage could be the new line of defence against Strep A
2023-10-05
As Streptococcus A cases continue to be prevalent in Queensland and internationally, a new nasal vaccine could provide long-term protection from the deadly bacteria.
Associate Professor Manisha Pandey, Professor Michael Good, and their team from Griffith University’s Institute for Glycomics, are leading the development of a Strep A vaccine which is currently in Phase 1 clinical trials in Canada and quickly advancing to Phase 2 efficacy trials.
The team’s new preclinical research, recently published in Nature Communications, shows an experimental liposome-based vaccine approach incorporating a conserved M-protein epitope from Strep A and an immunostimulatory glycolipid (3D(6-acyl) ...
Mays Cancer Center at UT Health San Antonio identifies possible markers for early metastatic lung cancer
2023-10-05
SAN ANTONIO, Oct. 5, 2023 – Researchers at Mays Cancer Center at The University of Texas Health Science at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) have identified protein markers that could signal for early development of metastatic lung cancer, providing possibilities for new treatment.
The findings already have led to a five-year, $1.6 million grant from the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health that will pave the way for a clinical trial next year for patients with advanced lung cancer. The research is detailed in a new article in Cell Reports, ...
WHO director praises London’s ULEZ expansion as politically courageous
2023-10-05
London mayor Sadiq Khan’s efforts to expand the capital’s Ultra Low Emission Zone (ULEZ) as part of a push to reduce air pollution and improve health, is politically courageous and an example for mayors around the world, says the World Health Organization’s environment, climate change and health director, Maria Neira.
In an exclusive interview for The BMJ’s climate issue, Neira says she is tired of listening to politicians speak on climate change as if they didn't have the power to ...
Software can detect hidden and complex emotions in parents
2023-10-05
Researchers have conducted trials using a software capable of detecting intricate details of emotions that remain hidden to the human eye.
The software, which uses an ‘artificial net’ to map key features of the face, can evaluate the intensities of multiple different facial expressions simultaneously.
The University of Bristol and Manchester Metropolitan University team worked with Bristol’s Children of the 90s study participants to see how well computational methods could capture authentic human emotions amidst everyday ...
$2 million grant boosts technological advancements in cutting-edge cell therapy manufacturing facility
2023-10-05
The Keck School of Medicine of USC has received $2 million from the California Institute of Regenerative Medicine (CIRM) to further augment its newly launched cGMP Laboratory, a state-of-the-art facility designed to advance early-stage research into clinically viable cell and gene therapies. To expedite the translation of these therapies from the lab to the clinic, the facility needs advanced technological know-how, streamlined operations and strict protocols for developing and testing these products, all of which ...
Texas Children’s Bariatric Surgery Program receives prestigious national accreditation
2023-10-05
HOUSTON (October 4, 2023) – Texas Children’s Hospital is proud to announce that its Adolescent Bariatric Surgery Program has received national accreditation from the Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program (MBSAQIP).
Texas Children’s Hospital The Woodlands is the only Bariatric Surgery Center in the state of Texas that serves to an adolescent-only patient population with a multidisciplinary clinical staff who is certified to meet the surgical, medical and psychological needs of ...
Two-dimensional compounds can capture carbon from the air
2023-10-05
Some of the thinnest materials known to mankind may provide solutions to scientists in their quest to curb the effects of global warming.
Known as MXene and MBene compounds, these substances are only a few atoms thick, making them two-dimensional. Because of their large surface area, the materials have the potential to absorb carbon dioxide molecules from the atmosphere, which could help reduce the harmful effects of climate change by safely sequestering carbon dioxide.
In a paper published Oct. 4 in the journal Chem, UC Riverside professor Mihri Ozkan and her co-authors explain the potential of MXenes and MBenes in carbon capture technologies.
“In this review, ...
New type of tiny wasp comes with mysterious, cloud-like structures at ends of antennae
2023-10-05
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Fossil researchers have discovered a novel genus and species of tiny wasp with a mysterious, bulbous structure at the end of each antenna.
The female micro-wasp was described from 100-million-year-old Burmese amber in a study led by George Poinar Jr., who holds a courtesy appointment in the Oregon State University College of Science.
Poinar and Fernando Vega, an independent researcher based in Silver Spring, Maryland, have some ideas about the “clouds” on the ...
Tirzepatide is as effective at treating early-onset type 2 diabetes as diabetes diagnosed later in life
2023-10-05
Tirzepatide is as effective at treating early-onset type 2 diabetes (T2D), a more aggressive form of the condition that normally responds less well to treatment, as it is at treating T2D diagnosed later in life, new research being presented at the Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Hamburg, Germany (2-6 Oct) has found.
Tirzepatide belongs to a new class of drugs that mimic the effect of two hormones involved in blood sugar control and appetite suppression, ...
Commonly prescribed antibiotic, antipsychotic and prokinetic drugs are associated with a higher risk of sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) in people with type 2 diabetes, study finds
2023-10-05
New research being presented at the Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Hamburg, Germany (2-6 Oct) has identified a range of characteristics associated with a higher risk of sudden cardiac arrest in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
These include the some commonly prescribed antibiotic and antipsychotic drugs, prokinetics (drugs used to treat gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea and vomiting) and low fasting blood sugar.
Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is a leading cause of death. ...
Study reveals distinct illness trajectory in the years leading up to type 2 diabetes diagnosis
2023-10-05
New research presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of The European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), Hamburg (2-6 Oct), reveals a marked increase in several common conditions in the years leading up to, and immediately prior to, type 2 diabetes diagnosis, suggesting considerably earlier diagnosis might be possible in some patients.
“These novel insights into the onset and natural progression of type 2 diabetes, suggest an early phase of inflammation-related disease activity long before any clinical diagnosis of type 2 diabetes is made”, says senior author Dr Adrian Heald from Manchester ...
Is lasting remission of type 2 diabetes feasible in the real-world setting?
2023-10-05
At this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Hamburg, Germany (2-6 Oct) experts will discuss if lasting remission from diabetes is feasible in the real-world setting.
Professor Roy Taylor of Newcastle University, Newcastle, UK, will be speaking in support of the motion
Professor Taylor will argue that through a series of studies in which people with type 2 diabetes were put on low calorie diets, he has shown that lasting remission of type 2 diabetes is indeed feasible in the real world.
He will begin ...
Second international consensus report - clinical translation of precision diabetes medicine
2023-10-05
Precision medicine is part of the logical evolution of contemporary evidence-based medicine that seeks to reduce errors and optimise outcomes when making medical decisions and health recommendations. Diabetes affects hundreds of millions of people worldwide, many of whom will develop life-threatening complications and die prematurely.
“Diabetes recommendations often focus on what works well for the average person. However, because diabetes is an incredibly heterogeneous disease, few people are Mr or Mrs “average” and one-size-fits-all ...
Wastewater surveillance research provides a 12-day lead time for RSV season: new study
2023-10-04
In a first-of-its-kind study, researchers using wastewater surveillance over conventional indicators have predicted the start of the annual respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) season 12 days early, providing more lead time for hospital preparedness and the timely initiation of RSV prevention therapy provided by the province for at risk-infants and young children.
Published in Frontiers in Public Health, the study is the first to describe the relationship between wastewater measurements and clinical data for RSV and to use near real-time wastewater measurements to accurately identify the start of the RSV season.
Working in close collaboration with CHEO Research Institute (RI) ...
Unmet health needs for HIV, hypertension and diabetes in rural South Africa
2023-10-04
The burden of non-communicable diseases like hypertension and diabetes is increasing globally, especially in low-income and middle-income countries where they occur alongside epidemics of communicable diseases like HIV. A large public health survey in South Africa led by Emily Wong, M.D., has assessed the multimorbidity health needs of individuals and communities in rural KwaZulu-Natal and established a framework to quantify met and unmet health needs for individuals living with infectious and non-communicable diseases. The study is published in The Lancet Global Health.
“Applying ...
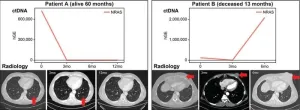
Blood-based biomarker may redefine the future treatment for advanced melanoma
2023-10-04
Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) is emerging as a blood-based biomarker for many solid tumor types, including melanoma. A new study that assessed ctDNA in the blood of patients with BRAF wild-type (BRAF WT) stage III and IV melanoma concludes that measuring ctDNA may lead to alternative treatment options and better outcomes for these patients, report investigators in The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, published by Elsevier.
For patients with BRAF WT stage III and IV melanoma, there is an urgent clinical need to identify prognostic biomarkers and biomarkers to predict treatment ...
Advances from MSK researchers reported at 2023 ASTRO Meeting
2023-10-04
Researchers from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) were recognized for their achievements at the 2023 meeting of ASTRO, the American Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology. Teams reported new findings about radiation-induced secondary cancers, a new guidance system for radiation therapy, and the consequences of insurance denials, among other topics.
At the meeting, held from October 1 to October 4, 2023, in San Diego, Simon Powell, MD, PhD, FRCP, Chair of MSK’s Department of Radiation Oncology and Enid A. Haupt Chair in Radiation Oncology, was honored with ASTRO’s Gold Medal Award. This award is ASTRO’s highest honor, bestowed upon ...
Ketamine-related drug gives better treatment for difficult to treat clinical depression
2023-10-04
Type of work: peer-reviewed/clinical trial/people
A major clinical trial shows that the drug, esketamine, one of the two main forms of ketamine, outperforms one of the standard treatments for treatment-resistant major depression. This industry-funded work is presented for the first time at the 36th ECNP Congress in Barcelona, with publication in the peer-reviewed journal the New England Journal of Medicine (see Notes for details).
Clinical depression (also known as MDD, major depressive disorder) affects a significant number of people at any one time, giving ...
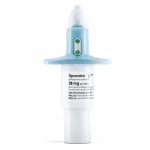
Esketamine nasal spray: an option for patients with treatment-resistant depression
2023-10-04
Understanding Treatment-Resistant Depression
Treatment-resistant depression (TRD) is a particularly challenging form of major depressive disorder. As Albino Oliveira-Maia, head of the Champalimaud Foundation’s Neuropsychiatry Unit and the study’s national coordinator for Portugal, explains, “TRD is defined as the persistence of depressive symptoms despite adequate courses of at least two different antidepressant medications”. Despite repeated therapeutic attempts, these patients’ depressive symptoms ...
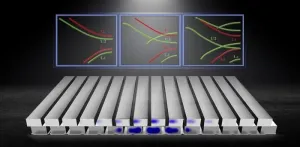
Navigating moiré physics and photonics with band offset tuning
2023-10-04
When two lattices with distinct angles or periodicities come together, they conjure a moiré superlattice — a realm where astonishing phenomena like superconductivity and optical solitons spring to life. At the heart of this realm lies the moiré flatband, a key player in shaping advanced light–matter interactions, such as laser emission and second harmonic generation. In moiré physics and its relevant applications, wielding control over flatbands is a pivotal superpower.
Moiré flatbands are typically generated with special structures, often manipulated ...
Aging in place: U-M study highlights racial disparities among older adults
2023-10-04
Audio
Roughly 40% of older Black adults live with a disability, compared to only one-third of older adults overall.
Disability is one of various disparities highlighted in a new study from the University of Michigan, which used data from the National Poll on Healthy Aging to examine the extent to which 50- to 80-year-olds were prepared to age in place and the racial and ethnic disparities that exist to that end.
Sheria Robinson-Lane, U-M assistant professor of nursing and principal investigator, said many of the disparities were related to "weathering"—stressors connected to environmental, ...
[1] ... [1643]
[1644]
[1645]
[1646]
[1647]
[1648]
[1649]
[1650]
1651
[1652]
[1653]
[1654]
[1655]
[1656]
[1657]
[1658]
[1659]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.