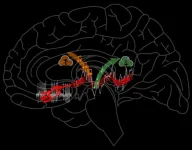
Mount Sinai researchers first to develop age prediction model on human brain tissue using artificial intelligence
2023-10-10
Paper Title: Histopathologic Brain Age Estimation via Multiple Instance Learning
Journal: Acta Neuropathologica, October 10, 2023
Authors: John F. Crary, MD, PhD, Professor of Pathology, Molecular and Cell-Based Medicine, Neuroscience, and Artificial Intelligence and Human Health at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai; Kurt W. Farrell, PhD, Assistant Professor of Pathology, Molecular and Cell-Based Medicine, Neuroscience, and Artificial Intelligence and Human Health at Icahn Mount Sinai; Gabriel A. Marx, MD, MS, Resident in Neurology at Icahn Mount Sinai; and other coauthors.
Bottom Line: The aging brain undergoes structural ...
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance call for papers theme issue on preventive strategies
2023-10-10
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance Editor-in-Chief: Travis Sanchez and guest editors Dr. Roy Rillera Marzo, Dr. Adnan Kisa, Petra Heidler and Shekhar Chauhan welcome submissions to a special theme issue examining "Scaling Up Effective Public Health Interventions for Long-Term Population Health Benefits."
This special issue aligns with the journal’s commitment to advancing knowledge in public health and disease prevention. It provides an opportunity to showcase cutting-edge research in preventive strategies, with ...
John D. Carpten, Ph.D., City of Hope’s chief scientific officer, elected to prestigious National Academy of Medicine
2023-10-10
LOS ANGELES — John D. Carpten, Ph.D., chief scientific officer at City of Hope, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States and a leading research center for diabetes and other life-threatening illnesses, was presented with one of the highest honors in health and medicine today when he was elected to the National Academy of Medicine (NAM).
NAM recognized Carpten “for leading the genomics field in understanding how racial and ethnic backgrounds affect cancer predisposition,” sharing that ...
Can immunity from routine vaccines be used to fight cancer?
2023-10-10
A University of Massachusetts Amherst team has demonstrated in theory that a protein antigen from a childhood vaccine can be delivered into the cells of a malignant tumor to refocus the body’s immune system against the cancer, effectively halting it and preventing its recurrence.
The bacteria-based intracellular delivering (ID) system uses a non-toxic form of Salmonella that releases a drug, in this case a vaccine antigen, after it’s inside a solid-tumor cancer cell.
“As an off-the-shelf immunotherapy, this bacterial system has ...
X-rays reveal microstructural fingerprints of 3D-printed alloy
2023-10-10
ITHACA, N.Y. -- Cornell researchers took a novel approach to explore the way microstructure emerges in a 3D-printed metal alloy: They bombarded it with X-rays while the material was being printed.
By seeing how the process of thermomechanical deformation creates localized microscale phenomena such as bending, fragmentation and oscillation in real time, the researchers will be able to produce customized materials that incorporate such performance-enhancing characteristics.
The group’s paper, “Dendritic Deformation Modes in Additive ...
New study offers improved strategy for social media communications during wildfires
2023-10-10
In the last 20 years, disasters have claimed more than a million lives and caused nearly $3 trillion in economic losses worldwide, according to the United Nations.
Disaster relief organizations (DROs) mobilize critical resources to help impacted communities, and they use social media to distribute information rapidly and broadly. Many DROs post content via multiple accounts within a single platform to represent both national and local levels.
Specifically examining wildfires in collaboration with the Canadian Red Cross (CRC), new research from the University of Notre Dame contradicts ...
Powering AI could use as much electricity as a small country
2023-10-10
Artificial intelligence (AI) comes with promises of helping coders code faster, drivers drive safer, and making daily tasks less time-consuming. But in a commentary published October 10 in the journal Joule, the founder of Digiconomist demonstrates that the tool, when adopted widely, could have a large energy footprint, which in the future may exceed the power demands of some countries.
“Looking at the growing demand for AI service, it’s very likely that energy consumption related to AI will significantly increase in the coming years,” says author Alex de Vries (@DigiEconomist), a Ph.D. candidate at Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam.
Since 2022, generative AI, which ...
Sweet Victory: Sensor detects adulteration in honey
2023-10-10
Adulteration is a bitter truth in the sweet world of honey. As consumers seek nature’s nectar for its purity and health benefits, a shadowy industry taints this golden elixir with hidden additives, most commonly water.
Standard detection methods of honey adulteration are expensive, and either have complicated operation methods or low detection accuracy.
In Review of Scientific Instruments, from AIP Publishing, a team of scientists from the Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics ...
Improving follow-up of abnormal cancer screening results
2023-10-10
About The Study: A multilevel primary care intervention that included electronic health record reminders and patient outreach with or without patient navigation improved timely follow-up of overdue abnormal cancer screening test results for breast, cervical, colorectal, and lung cancer.
Authors: Steven J. Atlas, M.D., M.P.H., of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.18755)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
Pingpong balls score big as sound absorbers
2023-10-10
Long-term exposure to low-frequency noise can cause numerous health problems, but the solution may be found in an unexpected object, a pingpong ball. Conventionally thought of as the hollow plastic balls that speed through the air during a fast-tempo game of table tennis, with a few modifications, pingpong balls can help absorb the city din.
Low-frequency noise is ubiquitous in cities, near roads, and by airports. Though potentially heard as background in the acoustic landscape, it can trigger earaches, respiratory impairment, irritability, and other ...
Postsurgery memory impairment in middle-aged Chinese patients
2023-10-10
About The Study: This study of middle-aged Chinese surgery patients found subjective cognitive and short-term memory impairment within 12 months after both cardiac and noncardiac surgery, with multiple identified risk factors, underscoring the potential of preoperative psychological interventions and optimized perioperative management for postoperative cognitive impairment prevention.
Authors: Huan Song, M.D., Ph.D., and Qian Li, M.D., of Sichuan University in Chengdu, China, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
Use of prenatal telehealth in the first year of the pandemic
2023-10-10
About The Study: This cross-sectional study found that most survey respondents who gave birth between June and December 2020 did not use prenatal telehealth, and a personal preference for in-person care was the most common reason. Patients’ preferences should influence how prenatal telehealth, which has both benefits and drawbacks, is incorporated into their care.
Authors: Rebecca A. Gourevitch, Ph.D., of the University of Maryland in College Park, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: ...
Titanium oxide material can remove toxic dyes from wastewater
2023-10-10
Discharged in large quantities by textile, cosmetic, ink, paper and other manufacturers, dyes carry high-toxicity and can bring potential carcinogens to wastewater. It’s a major concern for wastewater treatment—but researchers in Drexel University’s College of Engineering may have found a solution, using a tiny nanofilament.
A study lead Michel Barsoum, Ph.D., Distinguished University professor in the College of Engineering, and his team, including researchers from Drexel’s College of Arts and Sciences, found that a ...
Role of methylation in vernalization and photoperiod pathway: a potential flowering regulator?
2023-10-10
Recognized as a pivotal developmental transition, flowering marks the continuation of a plant's lifecycle. Flowering time determines the length of plant reproductive period and environmental adaptability. The correct flowering time is very significant for plants to reproduce fruit successfully and is controlled by environment and endogenous signals. Vernalization and photoperiod are the two main flowering pathways orchestrating a large number of floral signals. Methylation is one of the most important epigenetic modifications, which is involved in many key plant growth and development events. Methylation, including histone methylation, DNA methylation ...
Wireless, battery-free electronic ‘stickers’ gauge forces between touching objects
2023-10-10
Engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed electronic “stickers” that measure the force exerted by one object upon another. The force stickers are wireless, run without batteries and fit in tight spaces. That makes them versatile for a wide range of applications, from arming robots with a sense of touch to elevating the immersive experience of VR and AR, making biomedical devices smarter, monitoring the safety of industrial equipment, and improving the accuracy and efficiency of inventory management in warehouses.
They could be used, for example, in knee implants to measure the forces that implants exert on the joint. ...
How to cope when your values clash with your co-workers’
2023-10-10
COLUMBUS, Ohio – In our increasingly polarized society, more people may find themselves in a workplace where they are one of the few conservatives or few liberals around.
A new study found that those whose values – political or otherwise – don’t match the majority in their organization felt they received less respect and as a result were less engaged at work. Moreover, their co-workers noticed their lack of engagement.
“It is a real issue that organizations face,” said Tracy Dumas, lead author of the study and associate professor of management and human resources at The Ohio State University’s ...
Source of electron acceleration and X-ray aurora of Mercury ̶ local chorus waves detected
2023-10-10
Background
Since Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun among the solar system planets, it is strongly influenced by the solar wind, a high-speed (several hundred km/s) stream of plasma blowing from the Sun. Explorations of Mercury was first carried out by the Mariner 10 spacecraft in 1974 and 1975, which revealed that Mercury has a magnetic field, and thus a magnetosphere, similar to that of Earth. In the 2000s, the MESSENGER spacecraft provided a detailed picture of the Mercury's magnetic field and magnetosphere, and revealed that Mercury's magnetic field center is shifted northward from the planet’s center by approximately ...
NIH provides $1.2 million for ambitious effort to battle antibiotic resistance
2023-10-10
University of Virginia researchers are working to outrace two dangerous germs known for quickly developing resistance to new antibiotics – and the scientists’ efforts could help us better combat antibiotic resistance more broadly.
A team led by Jason Papin, PhD, is developing sophisticated computer models of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, two multi-drug resistant bacteria that infect thousands of Americans every year. The researchers will use their models to better understand the cellular processes and gene activity that make the bacteria ...
Researchers test large language model that preserves patient privacy
2023-10-10
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Locally run large language models (LLMs) may be a feasible option for extracting data from text-based radiology reports while preserving patient privacy, according to a new study from the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center (NIH CC) published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). LLMs are deep-learning models trained to understand and generate text in a human-like way.
Recently released LLM models such as ChatGPT and GPT-4 have garnered attention. However, they are not compatible with healthcare data due to privacy constraints.
“ChatGPT and GPT-4 are proprietary models that require the user ...
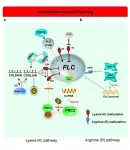
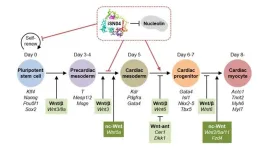
DNA aptamer finds novel application in regulating cell differentiation
2023-10-10
Generating specific cell lineages from induced pluripotent stem cells and embryonic stem cells is the holy grail of regenerative medicine. Guiding iPSCs toward a target cell line has garnered much attention, but the process remains challenging. Now, researchers from Japan have discovered that an anti-nucleolin DNA aptamer, iSN04, can determine a cell’s lineage during differentiation. By demonstrating the generation of cardiomyocytes from murine pluripotent stem cells, their concept shows promise as a regenerative therapy.
Self-renewal ...
Monitoring African copper and cobalt mining emissions from space
2023-10-10
Emissions associated with mining operations in Africa’s Copperbelt can be quantified from space, according to new research led by the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR).
Mining for copper and cobalt in Africa has rapidly increased, the latter in response to growing global demand for electric vehicles, laptops, smartphones, and other devices that rely on lithium-ion batteries, the vast majority of which contain cobalt.
The new study is published in Geophysical Research Letters, ...
Study compares health information exchange data versus patient self-reports to measure cancer screening uptake
2023-10-10
INDIANAPOLIS – Knowing which populations are following cancer screening guidelines is important to public health officials and policy makers as well as researchers developing strategies to improve adherence. A recent study is one of the first to compare using health information exchange (HIE) data with patient self-reported data as a means of gathering this intelligence.
The researchers found that completeness of information differed by data source and screening test. HIE data provided more information than patient self-reports about ...
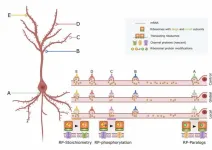
Seamlessly multiplexing memory storage and recall
2023-10-10
Every day we store memories, some of which we are able to recall later. But while we do so, do we keep on storing? Yes! We cannot afford to stop memory formation while we are retrieving prior ones. Imagine, for instance, that you are navigating the city while recalling last night’s events to a friend tagging along. Your brain must memorize aspects of the route even while you are in the story, so that you can find your way back later or reach your next destination.
We seem to perform this task without much conscious effort. Big deal, one could say, as we know that the brain has trillions of synaptic connections, so parallel processing ...
UNIST recognized for design excellence at IDEA 2023!
2023-10-10
The design concept of a disaster alert balloon, capable of changing its color like a chameleon, has been honored for its design excellence at the internationally renowned International Design Excellence Award (IDEA) 2023.
The awarded concept, named SAFEUP, serves as a hazard indicator, providing visual information about the condition of accident sites from a safe distance. Developed by Professor Chajoong Kim and his team in the Department of Design at UNIST, SAFEUP has received the ‘IDEA 2023’ Bronze Award in the category of Concepts & Speculative Design. The ...
The ribosome–depression link
2023-10-10
A group of ribosomal protein genes connect animal models of depression to human patients with major depressive disorder. In order to research depression treatments, scientists use a mouse model, inducing a state with similarities to depression though exposure to variable, unpredictable, and uncontrolled stressors over days or weeks. But is this state molecularly akin to what humans with major depressive disorder experience? To find out, Xiaolu Zhang, Mahmoud Ali Eladawi, and colleagues examine transcriptomics data from postmortem human brain tissue and from several mouse models of stress, seeking to pinpoint conserved ...
[1] ... [1635]
[1636]
[1637]
[1638]
[1639]
[1640]
[1641]
[1642]
1643
[1644]
[1645]
[1646]
[1647]
[1648]
[1649]
[1650]
[1651]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.