Can public financing for political campaigns affect voter participation?
2023-10-04
Policies that provide public financing for political campaigns have gained popularity in the United States. One example is the Democracy Vouchers program that was implemented in Seattle, Washington in 2017 to potentially reduce candidates' reliance on large donations. Research published in Contemporary Economic Policy studied the effects of this program on voter registration and turnout.
In Seattle’s Democracy Vouchers program, every registered voter in the city receives $100 worth of publicly funded vouchers to donate to candidates for municipal office, and candidates ...
Study reveals novel therapeutic target to eliminate unwanted and misfolded proteins
2023-10-04
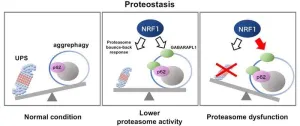
Biological cells contain in-built "housekeeping" mechanisms for taking care of damaged cellular structures. This includes the ubiquitin‒proteasome system (UPS), which selectively tags unwanted proteins with the ubiquitin molecule, and then clears them. When the UPS mechanism fails, cells activate a compensatory protein clearance process called "aggrephagy," in which protein aggregates are degraded by the cell in a controlled manner. However, thus far, the mechanism behind aggrephagy has been unknown.
Now, a landmark paper published on 1 September ...
Women living in more walkable neighborhoods have lower rates of obesity-related cancers
2023-10-04
Residing in a more walkable neighborhood protects against the risk of overall obesity-related cancers in women, specifically postmenopausal breast cancer, but also ovarian cancer, endometrial cancer, and multiple myeloma, according to a new study by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and NYU Grossman School of Medicine. Obesity has been linked to increased risk for 13 types of cancer in women, and physical activity, independent of body size, lowers risk for some of these cancers. Neighborhood walkability ...
Extreme fires and heavy rainfall driving platypuses from their homes
2023-10-04
Australia’s emerging pattern of severe mega bushfires and heavy rainfall may be driving platypuses from their homes, a new study by University of Melbourne researchers has shown.
Analysis of platypus DNA in rivers and creek water samples collected before and after the Black Summer 2019-2020 megafires suggest Australia’s beloved semi-aquatic monotremes might be abandoning severely bushfire-affected areas for up to 18 months after a fire, especially if heavy rainfall has followed the fire.
The study uses the recent technique of environmental DNA sampling, where animal DNA is collected from water, soil, air, or snow ...
Antigen testing can reduce, but not eliminate, the risk of COVID-19 clusters according to mathematical model
2023-10-04
A research group has created a new model to calculate the probability of the occurrence of localized clusters caused by novel coronavirus infections. Led by Shingo Iwami at Nagoya University with collaborators in the United Kingdom and South Korea model, they revealed that screening of infected persons by antigen testing is effective in significantly reducing the probability of cluster occurrence. However, their findings also suggest that it is not sufficient to prevent clusters caused by highly infectious mutant strains, such as Omicron.
With the availability of COVID-19 vaccines and population immunity, countries around the world are seeking to ...
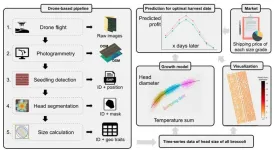
AI drones to help farmers optimize vegetable yields
2023-10-04
For reasons of food security and economic incentive, farmers continuously seek to maximize their marketable crop yields. As plants grow inconsistently, at the time of harvesting, there will inevitably be variations in quality and size of individual crops. Finding the optimal time to harvest is therefore a priority for farmers. A new approach making heavy use of drones and artificial intelligence demonstrably improves this estimation by carefully and accurately analyzing individual crops to assess their likely growth characteristics.
Some optimistic science fiction stories talk about a post-scarcity future, where human needs are catered for and hard labor ...
Wastewater detects signs of antimicrobial resistance in aged care
2023-10-04
A new study published today, analysing wastewater samples from several aged care and retirement homes in Adelaide, has uncovered worrying signs of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in at least one facility.
High levels of bacterial resistance against three common antibiotics – ceftazidime, cefepime and ciprofloxacin – were identified in one aged care residential home. A second facility recorded above average levels of antimicrobial resistance to gentamicin, putting residents’ health at risk.
The listed antibiotics are used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including pneumonia, ...
Unique voice print in parrots
2023-10-04
Parrots are exceptional talkers. They can learn new sounds during their entire lives, amassing an almost unlimited vocal repertoire. At the same time, parrots produce calls so they can be individually recognized by members of their flock—raising the question of how their calls can be very variable while also uniquely identifiable. A study on monk parakeets conducted by the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior and Museu de Ciències Naturals de Barcelona might have the answer: individuals have a unique tone of voice, known as a voice print, similar to that in humans. This finding in a wild parrot raises the possibility that a voice print ...
Potential genetic screening for aggressive melanoma
2023-10-04
Researchers from The University of Queensland and The Alfred hospital in Melbourne have identified gene variants which may contribute to people being at higher risk for nodular melanoma.
Dr Mitchell Stark from UQ’s Frazer Institute said nodular melanoma only accounts for around 14 per cent of invasive melanoma cases, but the aggressive subtype is the largest contributor to melanoma deaths.
“Melanoma is highly curable by surgery when diagnosed early, but nodular melanoma is often detected ...
Striking inequalities in provision of life-saving heart valve replacement in England
2023-10-04
Public health initiatives to understand and tackle these inequalities should be prioritised, say the researchers.
The aortic valve keeps blood flowing from the heart's lower left chamber (left ventricle) to the aorta—the main artery bringing blood from the heart to the body. Aortic stenosis occurs when the aortic valve narrows as a result of calcium build-up, impeding normal blood flow. This causes shortness of breath, light headedness, and chest pain (angina).
Aortic valve replacement (AVR) not only relieves these symptoms, but increases life expectancy, and improves quality of life, say the researchers, adding that up to 1 in 4 of those with severe or very severe aortic stenosis ...
Critical data gaps on doctor assisted deaths in Oregon amid rise in participants
2023-10-04
Information on clinical complications is often missing, while key information on the factors behind medical decision-making, the effectiveness of the lethal drugs used, and the extent of palliative care support isn’t even collected, reveals the review.
Physician assisted suicide as it’s formally known has been legal in the US state of Oregon since 1997 under the Death with Dignity Act.
The legislation allows terminally ill residents over the age of 18 to hasten their death by taking lethal drugs prescribed by a doctor, providing they are capable of making and communicating healthcare ...
New robot could help diagnose breast cancer early
2023-10-04
A device has been created that could carry out Clinical Breast Examinations (CBE).
The manipulator, designed by a team at the University of Bristol and based at the Bristol Robotics Laboratory, is able to apply very specific forces over a range similar to forces used by human examiners and can detect lumps using sensor technology at larger depths than before.
This could revolutionise how women monitor their breast health by giving them access to safe electronic CBEs, located in easily accessible places, such as pharmacies and health centres, which provide accurate results.
Precision, repeatability and ...
A prehistoric cosmic airburst preceded the advent of agriculture in the Levant
2023-10-04
Agriculture in Syria started with a bang 12,800 years ago as a fragmented comet slammed into the Earth’s atmosphere. The explosion and subsequent environmental changes forced hunter-gatherers in the prehistoric settlement of Abu Hureyra to adopt agricultural practices to boost their chances for survival.
That’s the assertion made by an international group of scientists in one of four related research papers, all appearing in the journal Science Open: Airbursts and Cratering Impacts. The papers ...
Is universal screening for type 1 diabetes around the corner?
2023-10-04
The the latest data on universal screening for type 1 diabetes (T1D) is reveiwed in a session at this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Hamburg, Germany (2-6 October). The talk will be given by Dr Emily K. Sims, Associate Professor of Pediatrics, Center for Diabetes and Metabolic Diseases, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN, USA.
Research by various groups has established that individuals with multiple islet autoantibodies (biomarkers showing that the body is attacking and killing its own insulin producing beta cells in ...
Metabolic signature can help predict which smokers will develop type 2 diabetes
2023-10-04
New research being presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of The European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), Hamburg (2-6 Oct) finds that cigarette smoking increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in part by affecting a variety of metabolites—small chemicals produced in the processes of metabolism—that circulate in the bloodstream.
The influence of these metabolic changes on diabetes risk appears to be amplified in individuals with genetic susceptibility to type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance.
The analysis of over 93,000 UK Biobank participants also identified a metabolic ...
Metabolically healthy obesity: fact or fiction?
2023-10-04
A session at this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes will explore the latest data on the concept of metabolically healthy obesity (MHO) – more commonly known by the public as ‘fat but fit’. Professor Matthias Blüher, University of Leipzig, Leipzig and Helmholtz Center Munich, Germany will explain how we define MHO and ask if it can really be described as healthy.
“Some 15-20% of people living with obesity have none ...
Emergency department screening could detect thousands of undiagnosed prediabetes and diabetes cases, UK study suggests
2023-10-04
The introduction of screening for type 2 diabetes in Accident and Emergency (A&E) departments could uncover thousands of previously undiagnosed cases every year, suggests new research being presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of The European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), Hamburg (2-6 Oct).
“Early diagnosis is the best way to avoid the devastating complications of type 2 diabetes, and offers the best chance of living a long and healthy life”, says Professor Edward Jude, Tameside and Glossop Integrated Care NHS Foundation Trust, UK. “Symptoms of type 2 diabetes may be absent and can be tricky ...
New stem cell-derived islet therapy improves blood sugar control in all treated patients, with three achieving insulin independence
2023-10-04
Six adults with type 1 diabetes (T1D) treated with stem cell-derived islet cells (VX-880) have shown improved blood sugar control with three participants achieving insulin independence, according to new research being presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of The European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), Hamburg (2-6 Oct).
All patients treated with VX-880 have demonstrated improved glycaemic control, as evidenced by elimination of severe hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar), improvements in HbA1c (a measure of long-term sugar levels) and the amount of time their ...
New pipeline makes valuable organic acid from plants — saving money and emissions
2023-10-03
In a breakthrough for environmentally friendly chemical production, researchers at the Center for Advanced Bioenergy and Bioproducts Innovation (CABBI) have developed an economical way to make succinic acid, an important industrial chemical, from sugarcane.
The team of University of Illinois and Princeton University researchers created a cost-effective, end-to-end pipeline for this valuable organic acid by engineering a tough, acid-tolerant yeast as the fermenting agent, avoiding costly steps in downstream processing. Succinic acid is a widely ...
PARMESAN: An AI-based predictive tool to find new treatments for genetic disorders
2023-10-03
To discover new treatments for genetic disorders, scientists need a thorough knowledge of prior literature to determine the best gene/protein targets and the most promising drugs to test. However, biomedical literature is growing at an explosive rate and often contains conflicting information, making it increasingly time-consuming for researchers to conduct a complete and thorough review.
To address this challenge, Cole Deisseroth, a graduate student enrolled in the M.D./Ph.D. program and mentored by Drs. Huda Zoghbi and Zhandong Liu at the Jan and Duncan ...
PPPL awarded $5 million to lead an Energy Earthshot Research Center focused on clean hydrogen
2023-10-03
Lessening the effects of climate change will require a variety of innovations and a lot of ingenuity. Now, a new center led by the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) will help these efforts by advancing the understanding of plasma-based clean hydrogen production.
PPPL was selected to lead a DOE Energy Earthshot Research Center (EERC) as part of the Hydrogen Shot™, which aims to reduce the cost of hydrogen by 80%. With funding from the DOE’s Office of Science, the EERCs support fundamental ...
Illinois-led project to sequence 400 soybean genomes, improve future crops
2023-10-03
As a source of protein and biodiesel for cleaner renewable energy, soybean is an important crop worldwide. But is it performing to its full potential? An ambitious effort led by the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and the U.S. Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute (JGI) will sequence 400 soybean genomes to develop a “pangenome” — an attempt to characterize all the useful diversity in the genome to create an even more robust and resilient crop.
The soybean pangenome project will sequence and analyze at least 50 soybean genomes from cultivated lines and wild relatives at reference quality, the gold standard of modern sequencing. A further ...
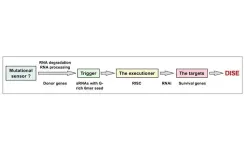
An ancient anti-cancer mechanism: DISE
2023-10-03
“DISE is effective against all cancers we tested.”
A new editorial paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on September 25, 2023, entitled, “DISE, an ancient anti-cancer mechanism that senses mutational load in cancerous cells?”
In their new editorial, researchers Monal Patel and Marcus E. Peter from Northwestern University discuss a recent breakthrough in cancer therapy. Despite the multiple advances in therapy, cancer remains one of the most common causes of death globally. ...
Project aims to develop all-in-one semiconductor that stores, processes data
2023-10-03
A multi-institutional project led by a Penn State researcher is focused on developing an all-in-one semiconductor device that can both store data and perform computations. The project recently received $2 million in funding over three years as part of the new National Science Foundation Future of Semiconductors (FuSe) program, a $45.6 million investment to advance semiconductor technologies and manufacturing through 24 research and education projects across the United States.
“The goal of ...
Nemours Children’s Health hosts first-ever pediatric session at HLTH
2023-10-03
Nemours Children’s Health will host the first-ever dedicated pediatric session at HLTH, the leading platform bringing together the entire health ecosystem focused on health innovation and transformation. This invited program, “Elevating Kids Health Well Beyond Medicine,” will extend HLTH’s 2023 theme, “Elevating Humanity,” to focus on health in childhood and why it is the only way to build good health across the lifespan.
“The child health perspective is an essential viewpoint for the attendees of HLTH to consider and we are proud to offer ...
[1] ... [1629]
[1630]
[1631]
[1632]
[1633]
[1634]
[1635]
[1636]
1637
[1638]
[1639]
[1640]
[1641]
[1642]
[1643]
[1644]
[1645]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.