A cheaper, safer alternative to lithium-ion batteries: Aqueous rechargeable batteries
2023-10-13
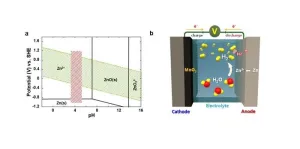
This summer, the planet is suffering from unprecedented heat waves and heavy rainfalls. Developing renewable energy and expanding associated infrastructure has become an essential survival strategy to ensure the sustainability of the planet in crisis, but it has obvious limitations due to the volatility of electricity production, which relies on uncertain variables like labile weather conditions. For this reason, the demand for energy storage systems (ESS) that can store and supply electricity as needed is ever-increasing, but lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) currently employed in ESS are not only highly expensive, but also prone to potential fire, so there is an urgent need to ...
Most accurate test to date developed to measure biological aging
2023-10-13
A team of European researchers has developed a new test that can accurately measure biological aging in a clinical setting. The discovery was made while studying patients for the aging effects of chronic kidney disease.
The new test is an epigenetic clock – a type of biochemical assessment that looks at DNA to understand how well the body is aging in contrast to its chronological age – and is the first of these cutting-edge tests to be proven to perform accurately in a clinical setting, in ...
International experts push for innovation to improve stroke recovery
2023-10-13
Scientists from The Florey are among the world’s leading stroke experts who have mapped out how researchers and clinicians can improve outcomes for people who have survived a stroke.
The third Stroke Recovery and Rehabilitation Roundtable, an initiative of the International Stroke Recovery and Rehabilitation Alliance, has made a series of key recommendations about managing fatigue, measuring mobility, harnessing non-invasive brain stimulation technologies and improving how trials are designed. The highly influential gathering of world stroke experts published their findings in a special ...
Using closed-loop in type 1 pregnancy associated with type 1 diabetes
2023-10-13
A new study endorses closed-loop use in type 1 diabetes pregnancy and highlights how the technology can facilitate positive pregnancy experiences. The study is published in the peer-reviewed journal Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics (DTT). Click here to read the article now.
Julia Lawton, from the University of Edinburgh, and coauthors, on behalf of the AiDAPT Collaborative Group, interviewed closed-loop participants in the Automated insulin Delivery Amongst Pregnant women with T1D (AiDAPT) trial. “Women described how closed-loop lessened the physical and mental demands ...
A step towards understanding early interventions for Huntington’s Disease
2023-10-13
Huntington’s Disease is the most common neurodegenerative disorder controlled by a single gene and is characterized by motor and cognitive deficits and psychiatric symptoms. Currently, no treatments can stop or reverse the disease, but new research from Boston Children’s Hospital suggests that there might be a way to protect the brain and prevent or slow cognitive decline.
Research from the lab of Beth Stevens, PhD suggests that parts of the immune system – complement proteins and microglia – mediate the loss of specific synapses connecting the brain’s cortex and striatum. The findings, recently published in Nature Medicine, could ...
Landmark publication calls for increased attention to workplace mental health
2023-10-13
A landmark scientific article on the workplace as a major determinant of health is published today (Thursday, 12 October) in The Lancet, and reveals a global picture of the work-related causes of mental health conditions.
Carried by University College Cork (UCC) researchers for the Lancet Series on work and health, the paper illustrates that major progress in population health can be made by an increased focus on improving people’s work environments.
The paper, ‘Work-related causes of mental health conditions and interventions for their improvement in workplaces’, ...
DNA methylation: The hidden mechanism enabling plants to adapt in a warmer world
2023-10-13
As global warming continues to redefine ecosystems, plants are increasingly tasked with swift adaptation to ensure their survival. One primary mechanism facilitating such rapid adaptation is epigenetic memory, specifically DNA methylation. DNA methylation, a form of epigenetic modification, involves the addition of a methyl group to the cytosine bases of the DNA, altering its accessibility in chromatin and modulating gene expression. In the context of a warming climate, changes in DNA methylation can be triggered by environmental factors like increased temperature. Such epigenetic adaptations ...
Unlocking the secrets of cold tolerance: a deep dive into tomato plants' molecular responses to chilling stress
2023-10-13
Cold sensitivity poses a significant challenge for certain essential crops. While there's an indication that these plants may possess cold acclimation capabilities, the molecular dynamics, particularly involving the CRT binding factor (CBF) family, are not fully explored. One primary concern has been the disparity in cold tolerance between temperate plants and tropical species such as the tomato. Additionally, the accumulation of small metabolites, termed cryoprotectants, plays a crucial role in enabling plants to resist damage from low temperatures. Adding ...
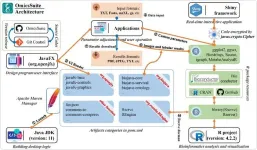
OmicsSuite: A customized and pipelined suite for analysis and visualization of multi-omics big data
2023-10-13
Abstract:
With the advancements in high-throughput sequencing technologies such as Illumina, PacBio, and 10X Genomics platforms, and gas/liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, large volumes of biological data in multiple formats can now be obtained through multi-omics analysis. Bioinformatics is constantly evolving and seeking breakthroughs to solve multi-omics problems, however it is challenging for most experimental biologists to analyze data using command-line interfaces, coding, and scripting. Based on experience with multi-omics, we have developed OmicsSuite, a desktop suite that comprehensively integrates statistics and multi-omics analysis and visualization. The suite ...
Stress wrecks male big brown bat fertility during breeding season
2023-10-13
Even on a good day the environment can be wildly unpredictable, from unexpected gusts of wind to food scarcity, and as humans continue to edge out the natural world, the stress on wild populations is increasing. ‘Bats are critical for the maintenance and stability of many terrestrial ecosystems’, say Mattina Alonge [University of California, Berkeley (UCB), USA] and Lucas Greville (McMaster University, Canada) and the animals are known to be particularly sensitive when under strain. But little was known about the impact that stress might have on their ability to reproduce. Concerned about the effect of stress on already vulnerable bat populations, Alonge and her colleagues ...
Almost half of patients with skin disease suffer from sleep disturbances, global study finds
2023-10-13
(Friday, 13 October 2023, Berlin, Germany) Almost half (42%) of patients with skin disease experience sleep disturbances, a major study presented today at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) Congress 2023 has revealed.1
The ALL PROJECT, a comprehensive international research initiative, analysed over 50,000 adults across 20 countries to assess the impact of skin diseases.2
Notably, these sleep disturbances were found to have broader implications on patients' quality of life. Nearly half (49%) of patients with skin disease reported reduced productivity at work, in contrast with just one in five (19%) participants without a skin disease.1
The ...
Kraft Family Blood Donor Center expands eligibility for donors
2023-10-12
Boston – The Kraft Family Blood Donor Center, which provides lifesaving blood products to patients at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, announced today that it has finished implementing a more inclusive blood donation process, in alignment with updated guidelines issued by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that will allow many gay and bisexual men to donate blood and platelets.
On May 11, 2023, the FDA changed its policy to reflect that deferring prospective blood donors based on sexual orientation is no longer supported by data. ...
200-year-old DNA helps map tiny fly’s genetic course to new lands, modern times
2023-10-12
Back when the biggest fly enthusiasts of 19th century Sweden — Carl Fredrik Fallén, for one, and later Johan Wilhelm Zetterstedt — were collecting insects for what would become Lund University’s entomological collections, they wondered exactly what was that buzzing coming from their can of raisins.
Skip forward 200 years, and the humble fruit fly, known better to geneticists as Drosophila melanogaster, is one of the most thoroughly studied animals on the planet. And DNA from Fallén and Zetterstedt’s centuries-old curiosities are still revealing new insights into the fly’s evolution as it spread alongside ...
Study highlights concerns and preferences of residents regarding police involvement in mental health crisis response
2023-10-12
PHILADELPHIA (October 11, 2023) – Police officers often respond to incidents that do not involve crime or immediate threats to public safety but instead deal with community members facing unmet mental health needs. In response to this, many cities are experimenting with co-deploying police officers alongside health professionals or deploying teams entirely composed of civilian health professionals.
Recently, researchers from the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing (Penn Nursing) explored the perspectives and preferences about these programs among residents in structurally disadvantaged areas where mental health distress is ...
More Aggressive treatment doesn’t impact quality of life for metastatic colorectal cancer patients, according to new study in JNCCN
2023-10-12
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [October 12, 2023] — New research in the October 2023 issue of JNCCN—Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network finds that intensive local-regional treatment to remove as much tumor as possible (known as “debulking”), in addition to standard systemic therapy, does not impact overall quality of life significantly for people with metastatic colorectal cancer.
The researchers examined the ongoing ORCHESTRA trial (NCT01792934) to compare patients treated with standard palliative chemotherapy alone to those who received palliative chemotherapy plus either surgery, ablative therapy, and/or radiotherapy ...
Honey bees may inherit altruistic behavior from their mothers
2023-10-12
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — True altruism is rare behavior in animals, but a new study by Penn State researchers has found that honey bees display this trait. Additionally, they found that an evolutionary battle of genetics may determine the parent they inherit it from.
For the study, published in the journal Molecular Ecology, the researchers examined the genetics behind “retinue” behavior in worker honey bees, who are always female. After the worker bees are exposed to the queen bee’s pheromone, they deactivate their own ovaries, help spread the pheromone to the other worker bees, and tend to the queen ...
Researchers develop technology to tabulate and characterize every cell in the human brain
2023-10-12
BOSTON – The brain is made up of numerous types of cells that are organized into different structures and regions.
Although several important steps have been made towards building models of the human brain, the advances have not produced undistorted 3D images of cellular architecture that are needed to build accurate and detailed models.
In new research published in Science Advances, a team led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of Mass General Brigham (MGB), has overcome this challenge to offer scientists and clinicians a comprehensive cellular atlas of a part of the human brain known as Broca’s area, with ...
Americans will spend half their lives taking prescription drugs, study finds
2023-10-12
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — An American born in 2019 will spend a larger share of their lifetime taking prescription drugs than being married or receiving an education, according to new research by Jessica Ho, associate professor of sociology and demography at Penn State. She found that American males will spend approximately 48% of their lives taking prescription drugs. The number jumped to 60% for females.
Ho reported her findings this week (Oct. 1) in the journal Demography.
“As an American, I’d like ...
Advertising rental housing in Spanish puts off many potential renters
2023-10-12
Publishing an ad for an apartment or rental home in Spanish may seem like it would broaden the pool of potential renters, but new research shows it can harm rental-seekers’ perception of the property and its neighborhood.
Finding a new apartment or home to rent can be nerve-wracking and tedious. It is increasingly digital and there are thousands of websites and Facebook groups for prospective renters to peruse. It can be a fraught endeavor — from vetting Craigslist listings to scrolling through hundreds of different listings to find the ...
Scientists generate first single-cell “atlas” of the primate brain to help explore links between molecules, cells, brain function and disease
2023-10-12
A longstanding mystery in science is how the over 100 million individual neurons work together to form a network that forms the basis of who we are – every human thought, emotion and behavior.
Mapping these constellations of cells and discovering their function have been long-standing goals of scores of 21st century molecular cartographers working worldwide as part of the National Institutes of Health’s “Brain Initiative Cell Census Network” project. The overarching ...
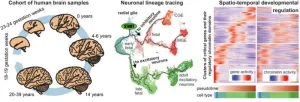
Researchers construct first “multiome” atlas of cell development in the human cerebral cortex from before birth to adulthood
2023-10-12
A team of researchers from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and Yale University School of Medicine has created the first “multiome” atlas of brain cell development in the human cerebral cortex across six broad developmental time points from fetal development into adulthood, shedding new light on their roles during brain development and disease.
“Multiome” refers to the simultaneous analysis of multiple types of genetic information within the same biological sample. They can include the genome, the DNA encoded in our cells; the transcriptome, the RNA copies that the cell makes from the ...
Boom-and-bust cycles in grey whale population associated with changing Arctic ecosystem
2023-10-12
Even highly mobile, large, and long-lived species are sensitive to dynamic and changing conditions as the Arctic warms. A new study reports that population swings in eastern North Pacific grey whales – some of which have resulted in recent mass mortality events – are driven by changing prey biomass and ice cover in the Arctic. Climate change is driving rapid change in Arctic ecosystems, including the highly productive shallow basins of the Pacific Arctic, which are critical marine areas that support seasonal foraging opportunities for various migratory marine species. While climate impacts affect lower-trophic level and short-lived species most directly, ...
About 2 million years ago, Homo Erectus lived at high altitudes and produced both Oldowan and Acheulean tools
2023-10-12
Two million years ago, Homo erectus had expanded beyond the lowland savanna environments of East Africa and into the high-altitude regions of the Ethiopian highlands, where they produced both Oldowan and Acheulean tools, according to a new study. It presents a reanalysis of an early hominin fossil first discovered in 1981. The findings provide novel insights into the evolution, migration and adaptive capacities of early human ancestors. In Africa, the limited number of hominin fossils found in direct association with stone tools has hindered attempts to link Homo habilis and Homo erectus with ...
Engineered bacteria guide CAR-T cells to poorly infiltrated solid tumors
2023-10-12
A new probiotic-guided chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T platform uses engineered bacteria to infiltrate and produce synthetic antigen targets, enabling CAR-T cells to find, identify, and destroy tumor cells in situ, according to a new study. The combined cell therapy platform expands the scope of CAR-T cell therapy to include difficult-to-target solid tumors. Immunotherapies using CAR-T cells have proven successful in treating some types of blood cancers. However, their efficacy against solid tumors remains elusive. A key challenge facing tumor-antigen targeting immunotherapies like CAR-T is the identification of suitable ...
An electrical switch to control chemical reactions
2023-10-12
New pharmaceuticals, cleaner fuels, biodegradable plastics: in order to meet society’s needs, chemists have to develop new synthesis methods to obtain new products that do not exist in their natural state. A research group at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), in collaboration with Cardiff University, has discovered how to use an external electric field to control and accelerate a chemical reaction, like a ‘‘switch’’. This work, to be read in Science Advances, could have a considerable impact on the development of new molecules, enabling not only more environmentally friendly synthesis, but also very simple external control of a chemical reaction.
In ...
[1] ... [1627]
[1628]
[1629]
[1630]
[1631]
[1632]
[1633]
[1634]
1635
[1636]
[1637]
[1638]
[1639]
[1640]
[1641]
[1642]
[1643]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.