Adults with ADHD are at increased risk for developing dementia
2023-10-17
Adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are nearly three times more likely to develop dementia than adults without ADHD, according to a Rutgers study.
The study, coauthored by Michal Schnaider Beeri, director of the Herbert and Jacqueline Krieger Klein Alzheimer’s Research Center at Rutgers Brain Health Institute (BHI) was published in JAMA Network Open. It followed more than 100,000 older adults in Israel over 17 years to examine if adults with ADHD are at increased risk for dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease.
Although more than 3 percent of the adult population in the United States has ADHD, there is limited research ...
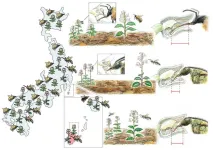
Orchid without bumblebee on island finds wasp, loses self
2023-10-17
Because the bumblebee that an orchid relies on for pollination does not exist on a remote island, the plant gets pollinated by an island wasp. Kobe University researchers found that this came at the cost of being hybridized with another orchid species adapted to being pollinated by the wasp. The finding showcases how plants in ecological relationships adapt to changing circumstances.
Remote islands have been exciting study grounds for biologists since at least the days of Darwin. When studying ecological relationships between different species, the differences between mainland and island ...
Ocean circulation, ice melt and increasing tourism could all be contributing to Arctic microplastics
2023-10-17
Scientists measured microplastic concentrations in the highly productive Barents Sea and suggest that ocean circulation, ice melt, tourism, inadequate waste management, shipping and fishing are all likely contributors.
Numerous studies have shown that global microplastic quantities in the marine environment are increasing, even in remote locations such as the Arctic.
The Barents Sea, which adjoins the Arctic Ocean, is one of the most productive oceanic areas in the world and home to an enormous diversity of organisms.
It is also a key route for Atlantic ...
Boosting weak immune system: scientists find an unusual weapon against virus
2023-10-17
Some viruses can be dormant throughout a person’s life and cause no harm but become dangerous when the immune system is weakened. One of such viruses is human cytomegalovirus (CMV). Harmless to the general public but life-threatening to patients with a supressed immune system.
“Patients undergoing bone marrow transplantations have their blood and immune system fully replaced by that of the donor. In the first months after transplantation they are defenseless. They can either catch CMV or have virus reactivated that was dormant in the patient. At the moment, there is no ideal treatment. The available ones work ...
Depression, anxiety common among college students
2023-10-17
Depression and anxiety among college students is a growing public health problem. And new research from the University of Georgia suggests the problem may be worse for students who aren’t the same race as most of their peers.
The new study found that students who were not the majority race at a predominantly white college reported significantly higher rates of depression than their white peers.
At the mostly white university, more than half of the students who self-identified as races other than white reported feelings of mild depression. An additional 17% said they were experiencing moderate to severe depression.
Students at the predominantly ...
Research finds water quality in Gulf of Mexico improves when adding social costs to carbon emissions
2023-10-17
DURHAM, N.H.—U.S. Climate policies can offer options for putting climate change efforts into place that solve environmental problems like excessive carbon dioxide in the atmosphere created by greenhouse gas emissions. Research led by the University of New Hampshire took a closer look at what would happen to agriculture if there was an extra cost, or so-called social cost, added to fossil fuels, which are essential for making fertilizer used in farming. They found that while CO2 emissions would decline by as much as 50%, the cost of fertilizer would rise leading to a significant benefit on water quality by lessening fertilizer runoff contributing ...
Mitigating electrode-level heterogeneity using phosphorus nanolayers on graphite for fast-charging batteries
2023-10-17
In a major stride towards achieving fast-charging lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) with reliable cyclability, researchers at UNIST have made a groundbreaking discovery. Their study, published in the prestigious ACS Energy Letters, introduces a novel strategy of utilizing phosphorus nanolayers to enhance the lithiation kinetics and performance of graphite-based composites, without compromising safety.
Led by Professor Hyun-Wook Lee from the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST, the research team developed a revolutionary graphite-phosphorus composite using a vaporization-condensation ...
In 2020, 30% of the Pantanal was burned to cinders by wildfires
2023-10-17
In 2020, the Pantanal, the largest tropical freshwater wetland in the world and a biodiversity hotspot, was swept by high-intensity fires that destroyed native vegetation in an area totaling 44,998 square kilometers (km²), or about 30% of the Brazilian portion of the biome, which spans some 150,000 km². The estimate is presented in an article published in the science journal Fire.
The area destroyed by that year’s disastrous fires was far larger than had been thought, according to the article. ...
SwRI will advance impact modeling software for U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
2023-10-17
SAN ANTONIO — October 17, 2023 —Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) will continue advancing the Elastic Plastic Impact Computations (EPIC) dynamic finite-element code as part of an Other Transaction Prototype Agreement with the U.S Army Corps of Engineers. The first year’s funding of $500,000 has been awarded, with optional additional funding across the next three years totaling $3.5 million.
“EPIC uses finite element and particle methods to simulate complex impact and explosion scenarios,” said SwRI Staff Engineer Dr. Stephen Beissel, who leads the EPIC project and has been involved in EPIC’s development since the mid-1990s. ...
The earthworm effect: unraveling soil weathering dynamics
2023-10-17
17 October 2023
The Geological Society of America
Release No. 23-42
Contact: Justin Samuel
+1-303-357-1026
jsamuel@geosociety.org
For Immediate Release
Contributed by Sarah Derouin
Pittsburgh, Pa., USA: Earthworms, the hardworking invertebrates that grace the upper layers of soil, have long been considered helpful in our home gardens. Earthworms are prolific munchers, grinding up organic material and sediment grains that make up soils. Although they are very different animals, worms, like many poultry, have gizzards. “Worms will ingest some larger soil grains, and then they use the strongest and largest of those grains, retaining them in their gizzard,” ...
New dating of cave art reveals history of Puerto Rican people
2023-10-17
17 October 2023
The Geological Society of America
Release No. 23-40
Contact: Justin Samuel
+1-303-357-1026
jsamuel@geosociety.org
For Immediate Release
Leer en español.
Contributed by Sarah Derouin
Pittsburgh, Pa., USA: In the karstic caves of Puerto Rico, cave art paints the rock walls. Previous research has assigned ages to this art based on the ages of nearby archaeological artifacts within the caves, but these ages are relative and may not reflect the true timing of the art creation.
Now, a new study to be presented Wednesday at the Geological Society of America’s GSA Connects 2023 meeting shows that researchers have refined the age of this rupestrian ...
U.S. groundwater is getting saltier—what that means for infrastructure, ecosystems, and human health
2023-10-17
17 October 2023
The Geological Society of America
Release No. 23-41
Contact: Justin Samuel
+1-303-357-1026
jsamuel@geosociety.org
For Immediate Release
Contributed by Sarah Derouin
Pittsburgh, Pa., USA: Scientists from the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) have been monitoring groundwater quality in wells across the country for more than three decades, looking for harmful chemicals or residual substances that may cause harm to ecosystems or humans. In all, they have measured up to 500 chemical constituents, including major ions, metals, pesticides, volatile organic compounds, fertilizers, and radionuclides.
Of ...
Pathogen that plagues food processing plants eradicated by blue light
2023-10-17
Washington, D.C. – Blue light kills both dried cells and biofilms of the pathogen Listeria monocytogenes, a frequent contaminant of food processing facilities. Demise of L. monocytogenes occurred quickest when cells or biofilms were placed on polystyrene, a widely used, transparent form of plastic. The research is published in Applied and Environmental Microbiology, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
“These results contribute to advancing our understanding of the potential of blue light to treat inert surfaces contaminated with L. monocytogenes,” said corresponding author ...
Public health interventions prevented transmission within BU most SARS-CoV-2 cases
2023-10-17
(Boston)— SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of COVID-19, began impacting the U.S. in March 2020 with many schools and universities shifting to remote education by early April 2020 in response to the public health emergency. Despite public health interventions (increased ventilation, masking policies, surveillance testing, contact tracing of confirmed cases and quarantine procedures for infected students, faculty and staff) there were still concerns that institutes of higher education would be a hotbed of transmission, including transmission from students into surrounding communities.
But, were these fears warranted?
A ...
CastleVax Inc. receives BARDA project NextGen award valued at up to $338 million to advance intranasal NDV-based COVID-19 booster vaccine into phase 2b clinical efficacy testing
2023-10-17
CastleVax, a clinical stage vaccine platform company, has received a Project NexGen award valued at up to $338 million from the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA), part of the Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response (ASPR) in the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), to support the development of a next-generation, booster vaccine to protect against COVID-19 for years to come. The initial phase of the award provides approximately $8.5 million to plan a Phase 2b clinical trial that would compare CastleVax’s vaccine to currently ...
New cancer therapy target stops tumor cells from sharing resources
2023-10-17
Researchers at University of California San Diego have discovered a process in which liver cells share molecules via vesicle exchange in order to multiply under conditions that would ordinarily suppress cell proliferation. They also found evidence that this process occurs in various types of cancer cells, paving the way for a new approach to tackling treatment resistance in cancer. The findings were published on October 17, 2023 in eLife.
“Understanding cell proliferation is a fundamental issue in both cancer research and biomedical science as a whole,” said Gen-Sheng Feng, PhD, a professor of pathology at UC San Diego School of Medicine and of molecular biology ...
International team reveals source of largest ever Mars quake
2023-10-17
A global team of scientists have announced the results of an unprecedented collaboration to search for the source of the largest ever seismic event recorded on Mars. The study, led by the University of Oxford, rules out a meteorite impact, suggesting instead that the quake was the result of enormous tectonic forces within Mars’ crust.
The quake, which had a magnitude of 4.7 and caused vibrations to reverberate through the planet for at least six hours, was recorded by NASA’s InSight lander on May 4 2022. ...
The dark side of the American lawn
2023-10-17
The American residential lawn is, for many, an iconic landscape and about half of homeowners in the US use fertilizer to keep their yards green and lush. Some proportion of the nitrogen in this fertilizer enters the broader environment, with negative consequences including algal blooms and deoxygenated waters. Peter Groffman and colleagues studied residential landscapes in the Baltimore, Maryland metropolitan area, which drains to the Chesapeake Bay, seeking to identify locations (hotspots) or times (hot moments) with disproportionately high rates of nitrogen export. The authors went to lawns in exurban, ...
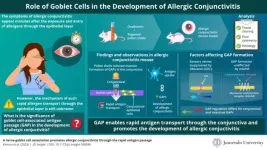
New study sheds light on the developmental mechanism of allergic conjunctivitis
2023-10-17
When it comes to eye allergies, the transition from allergen contact to bothersome symptoms has always been quick, appearing within a span of a few minutes. The initial stage of allergic conjunctivitis involves the penetration of allergen through the epithelial cell layer (cells covering the outer surface of the body). However, the exact mechanism underlying the rapid allergen transfer has remained a mystery so far.
Fortunately, in a new ground-breaking study published in the journal JCI Insight on October 11, 2023, researchers from Juntendo ...
Western University researchers reveal link between Alzheimer’s and sex hormones
2023-10-17
LONDON, ON., CA:
Alzheimer’s disease disproportionately affects women, who represent about two-thirds of those diagnosed with the late-onset type of the disease.
Previous research has shown Alzheimer’s is also more severe and progresses more rapidly in women, and women with Alzheimer’s experience a steeper cognitive decline – loss of memory, attention, and the ability to communicate and make decisions – compared to men with the disease.
The biological bases for these differences between men and women with Alzheimer’s disease are not well understood. ...
How to help save plants from extinction
2023-10-17
Now is the time to identify the conditions that cause plants to die. Doing so will allow us to better protect plants by choosing conservation targets more strategically, UC Riverside botanists argue in a new paper.
Published in the Oxford Academic journal Conservation Physiology, the paper demonstrates how scientists can learn the limits past which plants’ vital functions shut down, and makes the case that not doing so is a mistake in this era of increasing drought and wildfires.
“We can measure the amount of water loss plants ...
Kennedy Krieger receives $5 million grant to expand reach of its pediatric post-COVID-19 clinic and support school students
2023-10-17
BALTIMORE, October 17, 2023—Researchers at Kennedy Krieger Institute have received a $5 million grant from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), through the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), to expand access to comprehensive care for children and adolescents with long COVID-19, particularly among underserved populations.
During the five-year project, researchers at the Pediatric Post-COVID-19 Rehabilitation Clinic will receive up to $1 million annually to expand and strengthen its integrative services in Baltimore and the overall mid-Atlantic ...
Can lifestyle interventions benefit patients with advanced breast cancer?
2023-10-17
MIAMI, FLORIDA (Oct. 17, 2023) – Can lifestyle interventions such as exercise and intermittent fasting help patients with advanced breast cancer better tolerate side effects from treatment?
That is the question Tracy Crane, PhD, RDN, and Carmen Calfa, MD, at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine and their collaborators will strive to answer with a $4-million, five-year grant from the National Cancer Institute (NCI).
Crane, co-lead of Cancer Control and director of Lifestyle Medicine, Prevention and ...
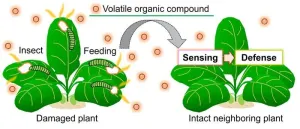
Unlocking nature's silent conversations: Real-time visualization of plant-plant communications through airborne volatiles
2023-10-17
Saitama, Japan: Plants emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere upon mechanical damages or insect attacks. Undamaged neighboring plants sense the released VOCs as danger cues to activate defense responses against upcoming threats (Figure 1). This phenomenon of airborne communication among plants through VOCs was first documented in 1983 and has since been observed in more than 30 different plant species. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying VOC perception to defense induction remain unclear.
Unveiling the Invisible Conversation
The ...
Critical step made for managing brushtail possums
2023-10-17
Researchers say mapping the genetic code of the brushtail possum will benefit those working to both conserve and control the animal.
In a five-year long study, just published in Nature Communications, an international group of researchers led by the University of Otago, has assembled the entire genetic code of the marsupial mammal.
The work also uncovered where and when their genes are expressed, and revealed surprising details about their population diversity, reproduction, and origins.
Study lead Associate Professor Tim Hore, of Otago’s Department of Anatomy, describes possums as “a fascinating animal that is loved ...
[1] ... [1620]
[1621]
[1622]
[1623]
[1624]
[1625]
[1626]
[1627]
1628
[1629]
[1630]
[1631]
[1632]
[1633]
[1634]
[1635]
[1636]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.