McWilliams School of Biomedical Informatics researchers awarded $6.4M NIH grant to develop deep learning model systems to understand mechanisms of Alzheimer’s disease
2023-10-18
A five-year, $6.4 million grant to develop an integrated, multiscale artificial intelligence (AI) approach to study genetic factors associated with Alzheimer’s disease has been awarded to UTHealth Houston by the National Institute on Aging, part of the National Institutes of Health.
A team led by Zhongming Zhao, PhD, and Xiaoqian Jiang, PhD, principal investigators and professors at McWilliams School of Biomedical Informatics at UTHealth Houston, are developing a deep-learning AI system to link brain imaging with cell-specific ...
SwRI’s Dr. Alan Stern will conduct research and experiment training in space aboard Virgin Galactic’s VSS Unity this November
2023-10-18
SAN ANTONIO — October 18, 2023 —On November 2, Dr. Alan Stern, planetary scientist and associate vice president of Southwest Research Institute’s Space Science Division, will fly aboard the Virgin Galactic commercial spaceship VSS Unity on a suborbital space mission to train for a future NASA-funded Virgin Galactic suborbital flight in which he will perform two NASA experiments in space.
“When I was a kid, human spaceflight was only available to NASA astronauts and Russian cosmonauts. Now that’s changing, and SwRI is pioneering a new era of space research being conducted in space, by space scientists,” Stern ...
More is not better: Trial finds giving more antibiotics to prevent joint replacement infections doesn't help
2023-10-18
Knee and hip replacements are increasing globally due to an ageing population. In the United States, the number of patients needing a joint replacement will exceed 2.7 million in the next 7 years. Post-surgery infections, while rare at 1-5% of patients, result in high patient morbidity and mortality.
In the United States the annual national hospital costs for treating infection are projected to exceed $1.85 billion.
We currently use an antibiotic, cefazolin, at the time of surgery to prevent infection. But with the rise of antibiotic resistant bacteria, experts ...
Promising new options for treating aggressive prostate cancer
2023-10-18
Cedars-Sinai Cancer investigators have identified two promising new treatment options for men with recurrent prostate cancer—both of which helped patients live longer without their disease progressing than the current standard treatment. The results of their international Phase III clinical trial were published today in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“If these treatments are approved by the Food and Drug Administration, our results will be practice changing,” said Stephen Freedland, MD, associate director for Training and Education and the Warschaw, Robertson, ...
Liverpool chemist presented with 2023 Eni Energy Frontiers Award by President of Italy
2023-10-18
Professor Matt Rosseinsky, from the University of Liverpool’s Department of Chemistry and Materials Innovation Factory, was presented with the 2023 Eni Energy Frontiers Award by Sergio Mattarella, the President of the Republic of Italy, at a ceremony in Rome this week.
Professor Rosseinsky received the prestigious Eni Award for the digital design and discovery of next-generation energy materials.
The presentation ceremony took place at the Palazzo del Quirinale in Rome which was also attended by Giuseppe Zafarana, Chairman of Eni and Claudio Descalzi, CEO of Eni.
Professor Rosseinsky said: “It was a great honour to be presented with this award by the President ...
Study focusing on Black cancer survivors documents how exposure to racial discrimination impacts care
2023-10-18
The medical community has understood for some time that experiences with discrimination are bad for the health of people from underserved racial or ethnic groups — populations burdened with worse health outcomes than white patients for conditions including many cancers. The effects of chronic stress on the body have been considered one chief culprit.
Now, a research team from the Keck School of Medicine of USC and USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, supported in part by the National Institutes of Health, has added new knowledge about how Black patients in particular are impacted by exposure to discrimination in the course of cancer care. Through interviews ...
Choosing exoskeleton settings like a Pandora radio station
2023-10-18
Images // Video
Taking inspiration from music streaming services, a team of engineers at the University of Michigan, Google and Georgia Tech has designed the simplest way for users to program their own exoskeleton assistance settings.
Of course, what's simple for the users is more complex underneath, as a machine learning algorithm repeatedly offers pairs of assistance profiles that are most likely to be comfortable for the wearer. The user then selects one of these two, and the predictor offers another ...
School discipline referrals for substance use increased in Oregon middle schools after legalization of recreational marijuana
2023-10-18
School Discipline Referrals for Substance Use Increased in Oregon Middle Schools after Legalization of Recreational Marijuana
A recent study found that Oregon middle school students received office discipline referrals (ODRs) for substance use offenses 30% more often after legalization of recreational marijuana relative to comparison schools in other states over the same period (school years 2012/2013 – 2018/2019). There were no statistically discernable changes in high school ODRs. Recreational use by adults was legalized in Oregon in 2015.
Researchers examined the extent to which legalization of recreational marijuana ...
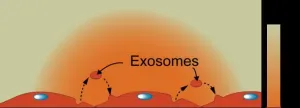
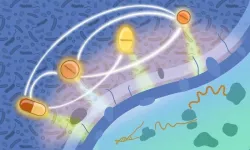
UMass Amherst engineering professor is awarded $1.9 million to push the bounds of cancer, heart disease research
2023-10-18
UMass Amherst Engineering Professor Is Awarded $1.9 Million to Push the Bounds of Cancer, Heart Disease Research
Jinglei Ping will explore a new method of controlling cell communication by electronically regulating exosome traffic through the National Institutes of Health grant
AMHERST, Mass. — The human body is a sophisticated organism that has complex internal communication systems down to a cellular level. However, these systems transmit more than just messages about healthy human functions; they can also influence disease.
Consider cancer. Jinglei Ping poses the question: “How do unhealthy cells transport their own cancer ...
American Society of Anesthesiologists names Ronald L. Harter, M.D., FASA, new president
2023-10-18
SAN FRANCISCO — Ronald L. Harter, M.D., FASA, professor of anesthesiology in the Department of Anesthesiology at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center in Columbus, was today named president of the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA), the nation’s largest organization of physician anesthesiologists. Dr. Harter assumed office at the ANESTHESIOLOGY® 2023 annual meeting and will serve for one year.
“ASA is the premier educational, research and scientific organization representing anesthesiology in the U.S., and I’m honored to have this opportunity to advance ...
Study finds increased risk of Guillain-Barré after COVID-19 infection
2023-10-18
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, OCTOBER 18, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – Having a COVID-19 infection is associated with an increased risk of developing the rare disorder called Guillain-Barré syndrome within the next six weeks, according to a study published in the October 18, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study also found that people who received the mRNA vaccine from Pfizer-BioNTech were less likely to develop the ...
Protecting polar bears aim of new and improved radar technology
2023-10-18
Research testing new technology to more effectively locate polar bear dens across the Arctic is showing promising results. Researchers from Simon Fraser University and Brigham Young University (BYU), collaborating with Polar Bears International, hope that improving detection tools to locate dens—which are nearly invisible and buried under snow—will help efforts to protect mother polar bears and their cubs.
Results of a pilot study aimed at improving den location in Churchill, Manitoba—using ARTEMIS Inc., an imaging system that relies on Synthetic Aperture Radar, or SAR—are published this week ...
From one nightmare to another. Anthony Fauci’s new concern
2023-10-18
(WASHINGTON) -- “What keeps you up at night?”
It’s a question Anthony Fauci, MD, heard repeatedly over the course of his nearly four decades as director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases at the National Institutes of Health.
Now a Distinguished University Professor at Georgetown University School of Medicine and the McCourt School of Public Policy, Fauci says he realized his worst nightmare -- a twist on the usual question -- in January 2020 when the type of virus he most feared triggered a worldwide pandemic.
Today, as the COVID-19 pandemic wanes, Fauci describes a new nemesis ...
Robotic prosthetic ankles improve ‘natural’ movement, stability
2023-10-18
Robotic prosthetic ankles that are controlled by nerve impulses allow amputees to move more “naturally,” improving their stability, according to a new study from North Carolina State University and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
“This work focused on ‘postural control,’ which is surprisingly complicated,” says Helen Huang, corresponding author of the study and the Jackson Family Distinguished Professor in the Joint Department of Biomedical Engineering at NC State and UNC.
“Basically, when we are standing still, ...
New study suggests promising approach for treating pancreatic cancer
2023-10-18
A new study carried out in mice, led by Queen Mary University of London, has identified cells that drive the spread of pancreatic cancer and discovered a weakness in these cells that could be targeted using existing drugs. This offers a promising new approach for treating pancreatic cancer.
The research, published in Science Advances and funded by Barts Charity and Cancer Research UK, found that many patients' pancreatic cancer contains cells called amoeboid cells. These are aggressive, invasive ...
The encounter between Neanderthals and Sapiens as told by their genomes
2023-10-18
About 40,000 years ago, Neanderthals, who had lived for hundreds of thousands of years in the western part of the Eurasian continent, gave way to Homo sapiens, who had arrived from Africa. This replacement was not sudden, and the two species coexisted for a few millennia, resulting in the integration of Neanderthal DNA into the genome of Sapiens. Researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE) have analyzed the distribution of the portion of DNA inherited from Neanderthals in the genomes of humans (Homo sapiens) ...
Migrants in Denmark face disparities in care for type 2 diabetes
2023-10-18
A large, population-wide study of Denmark residents with type 2 diabetes shows that migrants typically face a greater risk of inferior care for their disease than native Danes, particularly when it comes to monitoring their disease and controlling biomarkers—managing blood levels of key substances that are associated with diabetes. Anders Aasted Isaksen of Aarhus University and Steno Diabetes Center Aarhus, Denmark, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS Global Public Health.
Prior research ...
Drought conditions expose rivers to hotter water temperatures
2023-10-18
As climate change warms the planet and droughts are anticipated to become more frequent and extreme, a new study reveals how reduced water flows and rising atmospheric temperatures are set to heat our rivers - creating major challenges for aquatic life, ecosystems, and society.
Water temperature is an important control for all the physical, chemical, and biological processes in rivers. It is particularly important for organisms that cannot regulate their own body temperature, such as fish. River temperature is important for human health and industrial, domestic, and recreational ...
The right to be forgotten: ESMO calls on EU countries to ensure equal financial rights for cancer survivors
2023-10-18
ESMO calls on EU member states to adopt a five-year threshold for cancer survivors’ right to be forgotten when transposing the revised EU Consumer Credits Directive to their national legislation
The Society has been selected as one of the key stakeholders involved in the development of the EU Code of Conduct which seekS to ensure that advances in cancer care are reflected in the commercial practices of financial service providers
The ESMO Patient Advocacy Working Group aims to launch a pan-European campaign to illustrate to decision-makers the life-changing impact of a simple ...
Researchers uncover mechanism that links NAD+ to fertility problems
2023-10-18
A woman’s fertility normally decreases by her late 30s with reproductive function eventually ceasing at menopause. It is known that a small molecule called nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) plays a critical role in this decline, and Buck scientists have revealed how this happens and have identified potential new approaches to enhance reproductive longevity.
“Studying ovarian biology and reproductive aging is not just about trying to increase fertility, but really about the overall ...
Study elucidates evolution of mosquitoes and their hosts
2023-10-18
Researchers at North Carolina State University and global collaborators have mapped the mosquito’s tree of life, a major step toward understanding important traits, such as how the insects choose their hosts, feed on blood and spread disease. The findings will help researchers make better predictions to model disease transmission and understand what makes some mosquitoes better disease carriers than others.
The research suggests that mosquito evolution over the past 200 million years mirrors the Earth’s ...
Fighting antimicrobial resistance with new drug combinations
2023-10-18
Antimicrobial resistance – occurring when pathogens can survive antibiotic treatment – is one of the most rapidly emerging global public health threats today. According to a 2022 study, nearly five million deaths were associated with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in 2019, with over a million deaths per year directly attributable to antimicrobial resistance.
In a new study, researchers from the Typas Group at EMBL Heidelberg have systematically profiled over 10,000 drug combinations for their effectiveness against common multidrug-resistant bacteria.
“Previously, ...
New model provides window into Alzheimer’s disease development
2023-10-18
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (Oct. 18, 2023) — A new model developed by Van Andel Institute, Lund University and University of Florence scientists will enable researchers to better understand how Alzheimer’s disease progresses in the brain.
Like other neurodegenerative diseases, Alzheimer’s is challenging to study. It is immensely complex, develops over a long period of time and varies from person to person. Critically, scientists also lack non-invasive techniques to monitor disease progression in the human brain. Instead, they often rely on models that mimic the disease, allowing them to ...
Trends, outcomes of assisted reproductive technology cycles using a gestational carrier
2023-10-18
About The Study: There was an increased likelihood of live birth among assisted reproductive technology cycles with a gestational carrier versus those without a gestational carrier in this analysis of 2014 to 2020 national surveillance data. Gestational carrier use was a risk factor for twins, even after adjusting for the number of embryos transferred. More than one-quarter of embryo transfers to gestational carriers involved two or more embryos despite national recommendations of single embryo transfer.
Authors: Lisa M. Shandley, M.D, M.Sc., of the Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access ...
Over $3.7 million in NIH grants will fund research on impacts of climate change on HIV-related health outcomes
2023-10-18
New York, NY | October 18, 2023 – Two grants from the National Institute of Allergies and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), a four-year $3.2 million award and a 12-month $550,000 administrative supplement, will support innovative research to advance the understanding of how climate change and extreme weather influence HIV-related health outcomes around the world.
A multidisciplinary team of researchers from the CUNY Institute for Implementation Science in Population Health (CUNY ISPH) at the CUNY Graduate School of ...
[1] ... [1615]
[1616]
[1617]
[1618]
[1619]
[1620]
[1621]
[1622]
1623
[1624]
[1625]
[1626]
[1627]
[1628]
[1629]
[1630]
[1631]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.