Wearable device makes memories and powers up with the flex of a finger
2023-10-18
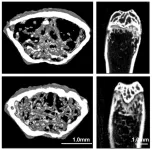
Researchers have invented an experimental wearable device that generates power from a user’s bending finger and can create and store memories, in a promising step towards health monitoring and other technologies.
The innovation features a single nanomaterial incorporated into a stretchable casing fitted to a person’s finger. The nanomaterial enabled the device to generate power with the user bending their finger.
The super-thin material also allows the device to perform memory tasks, as outlined below.
Multifunctional devices normally require several materials in layers, which involves the time-consuming challenge of stacking nanomaterials with high precision.
The team, led ...
AI and 10 seconds of voice can screen for diabetes, new study reveals
2023-10-18
Determining whether a person is diabetic could be as easy as having them speak a few sentences into their smartphone, according to a groundbreaking study from Klick Labs that combines voice technology with artificial intelligence in a major step forward in diabetes detection.
The new study, published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Digital Health, outlines how scientists used six to 10 seconds of people’s voice, along with basic health data, including age, sex, height, and weight, to create an AI model ...
AI identifies antimalarial drug as possible osteoporosis treatment
2023-10-18
Correction (Oct. 17, 2023): The paper’s title has been corrected to “Deep Learning-Predicted Dihydroartemisinin Rescues Osteoporosis by Maintaining Mesenchymal Stem Cell Stemness through Activating Histone 3 Lys 9 Acetylation
Artificial intelligence has exploded in popularity and is being harnessed by some scientists to predict which molecules could treat illnesses, or to quickly screen existing medicines for new applications. Researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have used one such deep learning algorithm, and found that dihydroartemisinin ...
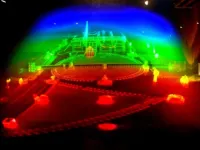
Simplifying the generation of three-dimensional holographic displays
2023-10-18
Holograms that offer a three-dimensional (3D) view of objects provide a level of detail that is unattainable by regular two-dimensional (2D) images. Due to their ability to offer a realistic and immersive experience of 3D objects, holograms hold enormous potential for use in various fields, including medical imaging, manufacturing, and virtual reality. Holograms are traditionally constructed by recording the three-dimensional data of an object and the interactions of light with the object. However, this technique is computationally highly intensive as it requires ...
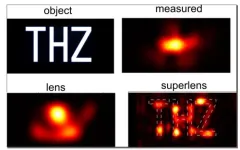
Superlensing without a super lens: physicists boost microscopes beyond limits
2023-10-18
Ever since Antonie van Leeuwenhoek discovered the world of bacteria through a microscope in the late seventeenth century, humans have tried to look deeper into the world of the infinitesimally small.
There are, however, physical limits to how closely we can examine an object using traditional optical methods. This is known as the ‘diffraction limit’ and is determined by the fact that light manifests as a wave. It means a focused image can never be smaller than half the wavelength of light used to observe an object.
Attempts to break this limit with “super lenses” have all hit the hurdle of extreme visual losses, making the lenses opaque. ...
Collaborative study focuses on using computer algorithms to find molecular adaptations to improve COVID-19 drugs
2023-10-18
As the COVID-19 pandemic scattered and isolated people, researchers across Virginia Tech connected for a data-driven collaboration seeking improved drugs to fight the disease and potentially many other illnesses.
A multidisciplinary collaboration spanning several colleges at Virginia Tech resulted in a newly published study, “Data Driven Computational Design and Experimental Validation of Drugs for Accelerated Mitigation of Pandemic-like Scenarios,” in the Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters.
The study focuses on using computer algorithms to generate adaptations to ...
Study predicts potential for 110% electricity increases in U.S. urban buildings
2023-10-18
A research study led by University of Oklahoma assistant professor Chenghao Wang and recently published in the journal Nature Communications tackled the critical issue of how city-scale building energy consumption in urban environments will evolve under the influence of climate change.
Fossil fuels account for approximately 40% of all building energy use in urban city centers in the United States, and the U.S. Energy Information Administration reports that residential and commercial buildings in U.S. cities are one of the major energy ...
Open access: Need to move away from transformative agreements
2023-10-18
Sweden is far ahead when it comes to promoting open access to scholarly publications. But there is risk of getting stuck in a permanent transformation that favours large commercial publishers. A new report from the Association of Swedish Higher Education Institutions develops a strategy on how to work in negotiations with the publishers.
In 2021, the Association of Swedish Higher Education Institutions (Sveriges universitets- och högskoleförbund, SUHF) convened a “Beyond transformative agreements” working group (the BTA group) to lay the foundation for further advancing the transition to open access. Now, the group ...
Graz University of Technology study on e-scooter accidents: more helmets and less speed reduce the injury risk
2023-10-18
The use of e-scooters has increased significantly in recent years, but so has the number of accidents involving this relatively new form of transport. At the same time, knowledge about injury mechanisms in this area was still very limited. In the project SURF, funded by Zukunftsfonds Steiermark, the Vehicle Safety Institute at Graz University of Technology (TU Graz) investigated this topic using Human Body Models and derived recommendations to reduce the injury risk in e-scooter accidents.
Put on a helmet, decrease speed and get off the pavement
As ...
Reef-devouring predator survives coral bleaching and feasts on the survivors
2023-10-18
Research conducted by marine biologists from the University of Sydney has found juvenile crown-of-thorns starfish can withstand tremendous heatwaves well above levels that kill coral. These starfish then develop into carnivorous predators that devour reefs just as they begin to regrow.
Crown-of-thorns starfish are native to the Great Barrier Reef and found in the Indo-Pacific region, but they are classified as a species of concern because the damage large populations cause to coral is more significant than any other species. ...
Does SARS-CoV-2 infection have urological effects?
2023-10-18
Research published in the Journal of Internal Medicine indicates that SARS-CoV-2 infection may worsen lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) in men.
The study included 17,986 men receiving medication for LUTS within the public healthcare system of Hong Kong in 2021–2022, half of whom had SARS-CoV-2 infection. The group with SARS-CoV-2 had significantly higher rates of retention of urine (4.55% versus 0.86%); blood in the urine (1.36% versus 0.41%); clinical urinary tract infection (4.31% versus 1.49%); bacteria in the urine (9.02% versus 1.97%); and addition of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, which are drugs prescribed for enlarged prostate. (0.50% versus 0.02%). These urological ...
How did the initial COVID-19 wave affect mental health in the UK?
2023-10-18
New research published in Economic Inquiry reports substantial increases in psychological distress in the UK during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Mental health effects were more pronounced for females; younger individuals; Black, Asian, and minority ethnic communities; and migrants. Also, people who had financial worries, loneliness, or were living in overcrowded dwellings experienced significantly worse mental health deterioration during the first wave.
The study used data from the UKHLS, also known as Understanding Society, which is a household panel dataset that captures, among other things, information from adults about their economic and social circumstances, ...
Heat-tolerant predatory sea stars will likely be a threat to coral during climate change
2023-10-18
Population outbreaks of the crown-of-thorns sea star (COTS), a predator of coral, can cause widespread coral mortality. COTS are herbivorous as juveniles but then switch to coral consumption as they grow to adulthood. When researchers exposed juvenile COTS to heat stress scenarios at time and temperature durations designed to reflect conditions that cause coral bleaching and mortality, juveniles exhibited tolerance to heatwave conditions well above levels that kill coral.
The findings, which are published in Global Change Biology, indicate that juvenile COTS are likely to persist as major coral predators in reefs already vulnerable to the effects of climate change.
“This ...
Does COVID-19 affect Alzheimer’s disease risk?
2023-10-18
The various neurological symptoms that patients with COVID-19 have experienced suggest that viral infections may increase the risk of neurodegeneration, which could in turn contribute to the development of conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD). A review in the Journal of Neurochemistry highlights the potential mechanistic links between COVID-19 and AD.
The authors note that age is the largest contributing factor to AD and COVID-19, and both appear to enhance the effects of the other, with potentially synergistic effects on neurodegeneration.
“I believe over the next several ...
Can planting multiple crops in the same plot improve agricultural production and sustainability?
2023-10-18
Agricultural management has typically focused on increasing yields, but there is an increasing need for sustainable food production that limits negative impacts on the environment. A new study published in Grassland Research provides insights into the potential benefits of diversifying agricultural practices, revealing how different mixtures of plant species can improve production, quality, and conservation.
For the study, investigators planted multiple species in different grassland plots, manipulating plant species richness from one to six species spanning three functional groups ...
New method may accurately identify body fluids at crime scenes
2023-10-18
Identifying different types of body fluids can help forensic experts reconstruct a crime scene, but it’s difficult to do so. In a study published in Electrophoresis, researchers developed a method using two different types of RNA—called microRNA (miRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA)—to determine five common body fluids.
Compared with previously reported single mRNA or miRNA assays, the combination of several mRNAs and miRNAs showed significant advantages for labeling human body fluids.
“Our findings indicate that this combined mRNA and miRNA system may provide a scientific ...
You don’t lose if you snooze
2023-10-18
It is often claimed that using the snooze button can have negative effects on sleep and cognitive processes, but there has been no direct evidence to this effect. New research from the Department of Psychology at Stockholm University shows that snoozing may actually support the waking process for regular snoozers.
It's common to want to stay in bed, potentially even go back to sleep, when the alarm goes off in the morning. The snooze button has been a function in alarm clocks and cell phones for decades and is ...
Do humans get lazier when robots help with tasks?
2023-10-18
Now that improvements in technology mean that some robots work alongside humans, there is evidence that those humans have learned to see them as team-mates — and teamwork can have negative as well as positive effects on people’s performance. People sometimes relax, letting their colleagues do the work instead. This is called ‘social loafing’, and it’s common where people know their contribution won’t be noticed or they’ve acclimatized to another team member’s high performance. Scientists at the Technical University of Berlin investigated whether humans social loaf when they work with robots.
“Teamwork ...
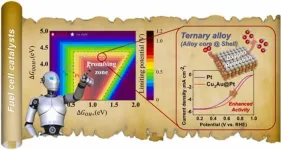
Using AI to develop hydrogen fuel cell catalysts more efficiently and economically
2023-10-18
Proton exchange membrane hydrogen fuel cells (PEMFCs) used in hydrogen vehicles use expensive platinum catalysts to facilitate the oxygen reduction reaction at the anode. There are a vast number of elemental combinations and compositions that need to be explored to develop more efficient and cost-effective catalyst materials than platinum, and researchers are still doing a lot of trial and error in the lab.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, President Seok Jin Yoon) announced that Dr. Donghun ...
Enhancing the safety and efficacy of drone flights in polar regions
2023-10-18
Collecting accurate weather data in remote and challenging environments like the polar regions and mountains can be extremely difficult. These areas often lack the infrastructure and resources needed for traditional weather stations, and the harsh weather conditions can make it dangerous for humans to access and maintain these stations.
Drones can navigate these challenging terrains, gather data, and transmit it to researchers, making them an indispensable tool for addressing these data gaps. Unfortunately, in-cloud flights still pose a challenge, with icing from supercooled cloud droplets that can damage vital drone components, ...
Is it ok to press the snooze button?
2023-10-18
Snoozing, or using intermittent alarms to get in a few more minutes of sleep in the morning, may have benefits for some people, according to research published in the Journal of Sleep Research.
In a study of 1,732 adults who described their waking habits, 69% of participants reported using the snooze function or setting multiple alarms at least “sometimes.” In those who snoozed, the average time spent snoozing per morning was 22 minutes, ranging from 1 to 180 minutes. Snoozers tended to be younger than non-snoozers and were more likely to be evening types. Morning drowsiness and shorter sleep were also more common in those who snoozed.
In a second ...
Prenatal exposure to environmental chemicals linked to childhood growth changes
2023-10-18
A new study led by researchers from the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the ”la Caixa Foundation” has shed light on the influence that Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals (EDCs) can have on children's growth during their early years. The results, published in Environmental Health Perspectives, show that prenatal exposure to some of these environmental chemicals and their mixtures is linked to accelerated Body Mass Index (BMI) gain from birth to nine years ...
Nearly half of oncology drugs approved since 1998 are precision therapies
2023-10-18
Bottom Line: Of the 198 new oncology drugs approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) between 1998 and 2022, approximately 43% were precision oncology therapies, the use of which is guided by biomarker testing.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR).
Authors: Debyani Chakravarty, PhD, assistant attending molecular geneticist in the Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine and lead scientist of the precision oncology knowledge base OncoKB at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK), was the senior author of the study. Sarah P. ...
Ocean Sciences Meeting 2024 press registration now open
2023-10-18
WASHINGTON — Press registration is now open for the 2024 Ocean Sciences Meeting, co-sponsored by the American Geophysical Union (AGU), the Association for the Sciences of Limnology and Oceanography (ASLO), and The Oceanography Society (TOS), in New Orleans, Louisiana 18 to 23 February 2024. The biennial Ocean Sciences Meeting brings together 5,000 scientists, students, policymakers and educators to discuss breaking research across the ocean sciences and critical issues affecting a sustainable future for our oceans.
PRESS: REGISTER and BOOK HOTELS
Staff, freelance and student journalists are eligible to apply for complimentary press registration through the end of the conference. ...
Founder personality could predict start-up success: study
2023-10-18
The stats don’t lie – the overwhelming majority of start-up companies fail. So, what makes the seemingly lucky few not only survive, but thrive?
While good fortune and circumstances can play a part, new research reveals that when it comes to start-up success, a founder’s personality – or the combined personalities of the founding team - is paramount. The study, published today in Scientific Reports, shows founders of successful start-ups have personality traits that differ significantly from the rest of the population – and that these traits are more important for success than many other ...
[1] ... [1617]
[1618]
[1619]
[1620]
[1621]
[1622]
[1623]
[1624]
1625
[1626]
[1627]
[1628]
[1629]
[1630]
[1631]
[1632]
[1633]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.