AI just got 100-fold more energy efficient
2023-10-12
AI is so energy hungry that most data analysis must be performed in the cloud
New energy-efficient device enables AI tasks to be performed within wearables
This allows real-time analysis and diagnostics for faster medical interventions
Researchers tested the device by classifying 10,000 electrocardiogram samples
The device successfully identified six types of heart beats with 95% accuracy
EVANSTON, Ill. — Forget the cloud.
Northwestern University engineers have developed a new nanoelectronic device that can perform accurate machine-learning classification tasks in the most energy-efficient ...
Around the globe, climate adaptation lacks coordination
2023-10-12
Viewed globally, it is above all individuals and households that are pursuing adaptation to the impacts of climate change; systematic networking of the various groups affected is lacking. This is the conclusion reached by an international team of experts from Universität Hamburg’s Cluster of Excellence for climate research (CLICCS) and Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München (LMU). Their meta-study was just released in the journal Nature Climate Change.
For their meta-study, the 30 authors analyzed more than 1,400 academic studies on climate change adaptation. By doing so, they offer the first global overview of which groups of actors are pursuing adaptation – and ...
Red blood cell transfusion in the ICU
2023-10-12
About The Study: Red blood cell (RBC) transfusion was common in patients admitted to 233 intensive care units in 30 countries between 2019 and 2022, with high variability across centers in transfusion practices. Although many different clinical reasons and triggers were stated for RBC transfusion, the three most common reasons (low hemoglobin level, active bleeding, hemodynamic instability) and triggers (hypotension, tachycardia, no physiological trigger affected the decision to transfuse) were largely overlapping in all regions.
Authors: Alexander P. J. Vlaar, M.D., Ph.D., M.B.A., of Amsterdam University Medical ...
Small-volume blood collection tubes to reduce transfusions in intensive care
2023-10-12
About The Study: This randomized trial in 25 adult medical-surgical intensive care units (ICUs) in Canada found that the transition from standard-volume to small-volume tubes for blood collection in the ICU may reduce red blood cell transfusion without impacting biospecimen sufficiency for laboratory analysis.
Authors: Deborah M. Siegal, M.D., M.Sc., of McMaster University in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.20820)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for ...
The burden of lung cancer in women compared with men in the US
2023-10-12
About The Study: Based on high-quality population-based data, this study found that the higher lung cancer incidence in women than in men has not only continued in individuals younger than 50 years but also now extends to middle-aged adults as younger women with a high risk of the disease enter older age. Reasons for this shift are unclear because the prevalence and intensity of smoking are not higher in younger women compared with men except for a slightly elevated prevalence among those born in the 1960s.
Authors: Ahmedin Jemal, D.V.M., Ph.D., of the American Cancer Society in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Race and ethnicity and primary language in emergency department triage
2023-10-12
About The Study: In this study of 249,000 visits to seven academic and community hospital emergency departments, patients who identified as Black, Hispanic, and Other race and ethnicity were assigned less acute Emergency Severity Index scores than their white peers despite having received more involved physician workups, suggesting some degree of mistriage. Clinical decision support systems might reduce these disparities but would require careful calibration to avoid replicating bias.
Authors: Joshua W. Joseph, M.D., M.S., ...
Big blood savings: large trial in JAMA shows taking less blood for lab testing reduces transfusions in intensive care
2023-10-12
A world-first clinical trial published in JAMA could provide an easy way to save tens of thousands of units of blood every year in Canada and much more worldwide. The trial, which involved more than 27,000 patients in 25 adult intensive care units (ICUs) across Canada, showed that taking less blood for lab tests using “small-volume” tubes reduced the need for almost one blood transfusion for every 10 patients.
Most hospitals use standard tubes that automatically draw four to six milliliters (ml) of blood, but a typical laboratory test requires less than 0.5 ml of blood, meaning the rest (more ...
We can respond to verbal stimuli while sleeping
2023-10-12
Sleep is generally defined as a period during which the body and mind are at rest—as if disconnected from the world. However, a new study led by Delphine Oudiette, Isabelle Arnulf, and Lionel Naccache at Paris Brain Institute shows that the frontier between wakefulness and sleep is much more porous than it seems.
The researchers have shown that ordinary sleepers can pick up verbal information transmitted by a human voice and respond to it by contracting their facial muscles. This astonishing ability occurs intermittently during almost all stages of sleep—like windows of connection with the outside world were temporarily opened on this occasion.
These new findings ...
Flagship individuals can boost conservation
2023-10-12
“Flagship” individual animals like Cecil the lion or Freya the walrus can boost conservation, new research suggests.
Much-loved species like pandas and polar bears are widely used in conservation campaigns.
However, a new study argues that individual animals or plants can also be used as flagships, with enormous potential to raise awareness and mobilise public support.
The recent outcry over the felling of the “Sycamore Gap” tree in the UK demonstrates the power of individual plants or animals in public opinion.
“Flagship individuals typically share some common characteristics,” ...
Letting go of an extra weight to control sleeping sickness
2023-10-12
Letting go of an extra weight to control sleeping sickness
A new study led by Luísa Figueiredo, group leader at the Instituto de Medicina Molecular João Lobo Antunes (iMM; Portugal), and published today in the scientific journal Nature Microbiology* found a new strategy by the host to cope with Trypanosoma brucei infection. Trypanosoma brucei is the parasite that causes sleeping sickness in humans, and nagana in cattle, which remain a public health ...
Simulations of ‘backwards time travel’ can improve scientific experiments
2023-10-12
Physicists have shown that simulating models of hypothetical time travel can solve experimental problems that appear impossible to solve using standard physics.
If gamblers, investors and quantum experimentalists could bend the arrow of time, their advantage would be significantly higher, leading to significantly better outcomes.
Researchers at the University of Cambridge have shown that by manipulating entanglement – a feature of quantum theory that causes particles to be intrinsically linked – they can simulate what could happen if one could travel backwards in time. So that gamblers, investors and ...
Extraordinary fossil find reveals details about the weight and diet of extinct saber-toothed marsupial
2023-10-12
Recent paleontological explorations in the Tatacoa Desert in Colombia led to the recovery of the most complete skeleton of a "saber-toothed marsupial” discovered in northern South America. The specimen belongs to the species Anachlysictis gracilis, which is part of a group of extinct predatory mammals known as sparassodonts, that lived in South America during the Cenozoic, after the extinction of the dinosaurs.
This species lived approximately 13 million years ago in the area known among paleontologists as ‘La Venta’, in the current La Tatacoa desert, a tropical dry forest that “at that time was a tropical rainforest, similar to the current Amazon,” said ...
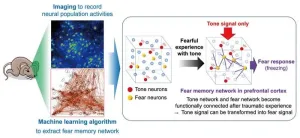
Traumatic memories can rewire the brain
2023-10-12
Okazaki, Japan – Scientists have long speculated about the physical changes that occur in the brain when a new memory is formed. Now, research from the National Institute for Physiological Sciences (NIPS) has shed light on this intriguing neurological mystery.
In a study recently published in Nature Communications, The research team has succeeded in detecting the brain neuronal networks involved in trauma memory by using a novel method that combines optical and machine-learning-based approaches, capturing the complex changes that occur during memory formation and uncovering the mechanisms by which trauma memories ...
Could you correctly identify someone wearing sunglasses from a distance of 20 meters?
2023-10-12
This comprehensive study focused on three key factors: distance, lighting and facial masking, and their impact on the ability of eyewitnesses to later correctly identify individuals they have seen. In the study, eyewitnesses were asked to identify perpetrators they had seen from various distances (5, 12.5 or 20 metres) and in different lighting conditions (daylight or deep twilight). The perpetrators were shown both with and without facial masking (sunglasses, hood, or both sunglasses and hood).
The key finding of the study is that distance plays a crucial role – the longer the distance, the harder it is ...
Children with prediabetes and obesity may be more likely to progress to diabetes
2023-10-12
A new Journal of the Endocrine Society study highlights how to identify children at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes and strategies for prevention, such as anti-obesity or anti-diabetes medication and lifestyle changes.
Prediabetes is a health condition in which blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not yet high enough to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. Prediabetes increases the risk of developing chronic kidney disease, heart disease and stroke. Around 5%-10% of adults with prediabetes develop diabetes each year.
Over the past three decades, there has been a sharp increase in the incidence and prevalence ...
Hostile sexism linked to less responsive parenting
2023-10-12
Fathers and mothers who believe that men should hold the power and authority in the family exhibit less responsive parenting behavior, according to a new article in Social Psychological and Personality Science. This research provides the first behavioral evidence demonstrating that hostile sexism is linked to less responsive parenting by both fathers and mothers.
Hostile sexism is characterized by beliefs that men should hold power and authority in society. Its harmful effects are well-established, especially in predicting harmful behavior toward women. However, this new research highlights its impact on parenting ...
Study: Struggling students who repeat third grade see improved achievement
2023-10-12
Washington, October 12, 2023—Third-grade retention can increase the reading and math scores of struggling students, with positive effects lasting into middle school, according to new research released today. The study, by NaYoung Hwang at the University of New Hampshire and Cory Koedel at the University of Missouri, was published today in Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association.
Video: Co-author NaYoung Hwang discusses findings and implications of the study
Despite mixed reviews among policymakers, researchers, ...
New center addresses global climate change impacts on water, other resources
2023-10-12
Jordan ranks second among countries with the lowest access to water and is expected to reach water insecurity by 2030. Within the country, the most water deprived communities live in the Northeast region of Mafraq’s Azraq Basin which is also home to approximately 120,000 resettled Syrian refugees who are dependent on water resources.
A new three-year program called the Global Center on Climate Change, Water, Energy, Food, and Health Systems, led by the University of California San Diego Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human ...
NIH research program All of Us establishes CU Anschutz-led Center aimed at better utilizing data
2023-10-12
AURORA, Colo. (October 12, 2023) – The National Institutes of Health’s All of Us Research Program has awarded $30 million to the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus and its partners to establish the Center for Linkage and Acquisition of Data (CLAD). The All of Us Research Program is a historic effort to enroll at least 1 million people who reflect the diversity of the United States. Providing researchers with the data will help drive new discoveries and advance precision medicine.
“This is ...
Team develops HydroBIM platform for design of hydropower hub buildings
2023-10-12
A research team has developed a platform based on building information modeling (BIM) technology for use in the design of hydropower hub buildings. The platform, called HydroBIM, combines BIM technology with geographic information systems, computer-aided engineering, internet of things, artificial intelligence, and other technologies. The HydroBIM platform provides a comprehensive approach to digital design, intelligent construction, and smart operation of hydropower engineering projects.
The work ...
Stronger lithium batteries may need ‘weaker’ solvation structure, researchers report
2023-10-12
Lithium batteries power our phones, computers, many of our cars and so much more — even the drill and weedwhacker. But as technology advances, can they keep up in their current format? No, but there is a way forward, according to a new review paper from researchers at Hong Kong Polytechnic University, by further developing the electrolytes that allow for energy storage and discharge.
The team published their work in Energy Materials and Devices on September 18, 2023.
“Lithium batteries ...
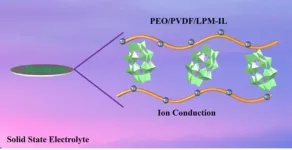
Polyoxometalates and ionic liquid enhance solid-state lithium-ion electrolyte performance
2023-10-12
Polyoxometalates (POMs) containing charged lithium ions combined with ionic liquids, increase the ion conductivity of a solid-state electrolyte membrane.
Solid-state lithium-ion batteries depend on the movement of ions (charged atoms) in the solid, rather than liquid, state to either charge or discharge the battery. These solid-state electrolytes are safer, more cost efficient and capable of higher energy densities than batteries that rely on liquid electrolyte solutions, but suffer from low ionic conductivity, or movement of ions, and poor thermal stability. A new composite ...
New study unveils stretchable high-resolution user-interactive synesthesia displays for visual–acoustic encryption
2023-10-12
The future of human-machine interfaces is on the cusp of a revolution with the unveiling of a groundbreaking technology - a stretchable high-resolution multicolor synesthesia display that generates synchronized sound and light as input/output sources. A research team, led by Professor Moon Kee Choi in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at UNIST, has succeeded in developing this cutting-edge display using transfer-printing techniques, propelling the field of multifunctional displays into new realms of possibility.
Traditionally, multifunctional ...
The advantage of digital-native brands setting up physical brand stores—and the challenge of preventing sales losses in existing channels
2023-10-12
Researchers from Erasmus School of Economics at Erasmus University Rotterdam, KU Leuven, Universität zu Lübeck, Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel, and FoodLabs published a new Journal of Marketing article that investigates the multichannel impact of brand stores by digital-native FMCG brands.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Assessing the Multichannel Impact of Brand Store Entry by a Digital-Native Grocery Brand” and is authored ...
Extreme habitats: Microbial life in Old Faithful Geyser
2023-10-12
Contributed by Arianna Soldati, GSA Science Communication Fellow
Pittsburgh, Pa., USA: An eruption of Old Faithful Geyser in Yellowstone National Park is a sight to behold. Indeed, millions of tourists flock to the park each year to see it. Hot water and steam are ejected in the air to a height of 100–180 feet approximately every 90 minutes. Many adjectives come to mind to describe it: powerful, mesmerizing, unique, otherworldly . . . homey? Not so much. Yet new research by Lisa M. Keller, published on PNAS Nexus earlier this year and to be presented on Sunday at the Geological Society of America’s GSA Connects 2023 meeting, shows that for ...
[1] ... [1616]
[1617]
[1618]
[1619]
[1620]
[1621]
[1622]
[1623]
1624
[1625]
[1626]
[1627]
[1628]
[1629]
[1630]
[1631]
[1632]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.