Information about abortion care largely omitted or buried on 80% of health systems’ patient-facing websites
2023-10-16
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 16 October 2023
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. Information ...
Andrea Califano receives Alfred G. Knudson award from NCI
2023-10-16
Andrea Califano, Dr, has been honored with the 26th Alfred G. Knudson Award in Cancer Genetics by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) for his exceptional contributions to the field of cancer research. Califano, a pioneer in the field of cancer genetics, is the Clyde and Helen Wu Professor of Chemical and Systems Biology at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons and a member of the Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center.
The award is named in honor of geneticist and cancer researcher Alfred G. Knudson, MD, a 1947 graduate of the Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, who helped uncover several major genetic mysteries behind ...
Learning more about how cancer affects stroke risk
2023-10-16
Patients with a previous or current cancer diagnosis are more likely to have a stroke than the general population, but how are specific cancers and treatments associated with stroke risk?
A collaborative team led by University of Cincinnati, University of North Carolina (UNC) and Duke University researchers is seeking to answer that question.
Soma Sengupta, MD, PhD, now division chief of neuro-oncology at UNC, had the idea to study the prevalence of stroke in patients with different cancer types while a faculty member at UC. She recruited a team that included stroke experts Stacie Demel, DO, PhD, of UC and Wuwei Feng of Duke to put together a retrospective pilot study.
“This ...
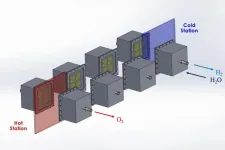
MIT design would harness 40% of the sun’s heat to produce clean hydrogen fuel
2023-10-16
MIT engineers aim to produce totally green, carbon-free hydrogen fuel with a new, train-like system of reactors that is driven solely by the sun.
In a study appearing today in Solar Energy Journal, the engineers lay out the conceptual design for a system that can efficiently produce “solar thermochemical hydrogen.” The system harnesses the sun’s heat to directly split water and generate hydrogen — a clean fuel that can power long-distance trucks, ships, and planes, while in the process emitting no greenhouse gas emissions.
Today, hydrogen is largely produced through processes that involve natural gas and other fossil fuels, ...
Fungal infection in the brain produces changes like those seen in Alzheimer’s disease
2023-10-16
Previous research has implicated fungi in chronic neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, but there is limited understanding of how these common microbes could be involved in the development of these conditions.
Working with animal models, researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions discovered how the fungus Candida albicans enters the brain, activates two separate mechanisms in brain cells that promote its clearance, and, important for the understanding of Alzheimer’s disease development, generates amyloid beta (Ab)-like peptides, toxic protein ...
Jefferson Lab to lead $300+ million high performance data facility hub
2023-10-16
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – The U.S. Department of Energy has just announced the selection of Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility as the lead for its new High Performance Data Facility Hub. Jefferson Lab will partner with DOE’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory to form a joint project team led by Jefferson Lab. The HPDF will be a $300-500 million computing and data infrastructure resource that will provide transformational capabilities for data analysis, networking and storage for the nation’s research enterprise. ...
VA study provides new insights into COVID-19 pandemic death rates
2023-10-16
A multi-institutional team of researchers led by the White River Junction VA, and including the West Haven and Palo Alto VA, analyzed electronic health record data from more than 5.9 million Veterans―spanning both pre-pandemic (March 2018 - February 2020) and pandemic (March 2020 - February 2022) periods―to discover nuanced insights from COVID-19’s impact on mortality rates.
While former studies have primarily relied on aggregate data, this research―published in the October 2023 issue of the International Journal of Epidemiology―offered a unique perspective ...
Leading scientists, philosophers identify nature’s missing evolutionary law
2023-10-16
A paper in the prestigious Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences today describes “a missing law of nature,” recognizing for the first time an important norm within the natural world’s workings.
In essence, the new law states that complex natural systems evolve to states of greater patterning, diversity, and complexity. In other words, evolution is not limited to life on Earth, it also occurs in other massively complex systems, from planets and stars to atoms, minerals, and more.
Authored by a nine-member team — leading scientists from the Carnegie Institution for ...
Study shows long-term health impacts after exposure to environmental disaster
2023-10-16
Exposure to a large-scale disaster, such as a tsunami, impacts population health over a decade later. A new study by an inter-disciplinary team of researchers in the United States and Indonesia has found that women who lived along the coast of Aceh, Indonesia when it was hit by waves from the 2004 tsunami have lower cortisol levels 14 years later than women who lived in other, nearby coastal communities that were not directly affected.
Cortisol is a stress hormone produced by the adrenal glands. Cortisol levels rise in response to stress as part of the fight or flight response, but consistently elevated ...
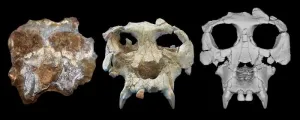
Extinct ape gets a facelift, 12 million years later
2023-10-16
A new study led by scientists at the American Museum of Natural History, Brooklyn College, and the Catalan Institute of Paleontology Miquel Crusafont has reconstructed the well-preserved but damaged skull of a great ape species that lived about 12 million years ago. The species, Pierolapithecus catalaunicus, may be crucial to understanding great ape and human evolution. The researchers describe their findings today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Pierolapithecus catalaunicus, a species from northeastern Spain first described in 2004, was one of a diverse group of now-extinct ...
Signatures of the Space Age: Spacecraft metals left in the wake of humanity’s path to the stars
2023-10-16
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – The Space Age is leaving fingerprints on one of the most remote parts of the planet — the stratosphere — which has potential implications for climate, the ozone layer and the continued habitability of Earth.
Using tools hitched to the nose cone of their research planes and sampling more than 11 miles above the planet’s surface, researchers have discovered significant amounts of metals in aerosols in the atmosphere, likely from increasingly frequent launches and returns of spacecraft and satellites. That mass of metal is changing atmospheric chemistry in ways that ...
Stress levels worse in women who have heart attacks with blockages, study finds
2023-10-16
Stress and depression are known to increase risk of heart attack, especially among women. They’ve also been linked to worse recovery. But does stress and depression contribute more to women with heart attacks with open arteries or blocked arteries? That’s what a new study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology aimed to find out.
Researchers found stress and depression were indeed common among women at the time of heart attack and for two months after. But they also found that women with heart attacks due to blockages (MI-CAD) in their coronary arteries had higher ...
The new robot is taking its first intuitive steps
2023-10-16
When walking on the sidewalk, a person is able to avoid puddles, other walkers, and cracks in the pavement. It may seem intuitive – and that's because it is.
There’s actually a biological component that allows humans and other mammals to navigate our complex environments. Central Pattern Generators (CPG) are neural networks that produce rhythmic patterns of control signals for limbs using simple environmental cues. When we quickly step away to avoid something blocking our path, that’s ...
Neutrons see stress in 3D-printed parts, advancing additive manufacturing
2023-10-16
Using neutrons to see the additive manufacturing process at the atomic level, scientists have shown that they can measure strain in a material as it evolves and track how atoms move in response to stress.
The automotive, aerospace, clean energy and tool-and-die industries — any industry that needs complex and high-performance parts — could use additive manufacturing,” said Alex Plotkowski, materials scientist in ORNL’s Materials Science and Technology Division and the lead scientist of the experiment. Plotkowski and his ...
How to tell if your boss is a ‘corporate psychopath’
2023-10-16
Findings from research to help the business world identify destructive ‘corporate psychopaths’ will be presented at the Chelmsford Science Festival on Monday, 23 October.
Dr Clive Boddy of Anglia Ruskin University, a pioneer in the field of corporate psychopathy, will discuss his research, published in the International Journal of Market Research, looking at how the financial industry can identify, manage and, if necessary, remove these individuals.
Around 1% of the adult population are ...
Ochsner Health Recipient of the 2023-24 WebMD Choice Awards
2023-10-16
NEW ORLEANS, La. - Ochsner Health was named among the “Best Hospitals According to Patients & Health Care Providers” by WebMD, an online publication for health news and information.
The 2023 WebMD Choice Awards recognized a select group of 167 health systems with Elite Choice Awards, WebMD Patient Choice Awards, and Medscape Physician Choice Awards. Results were gathered via a survey of a national audience encompassing thousands of patients and healthcare clinicians to determine which hospitals they believe deliver the best quality and treatments. The awards program identifies the “best in class” ...
Carnegie Mellon University's Synergy Lab releases three papers on ubiquitous sensing
2023-10-16
Researchers from Carnegie Mellon's Systems, Networking, and Energy Efficiency (Synergy) Lab will present several multi-year studies on their work around ubiquitous sensing at this week's ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (UbiComp).
The works unveil several innovative systems and explain how the collected data can be converted to offer useful insights, all while ensuring the privacy of the individuals being monitored.
Led by School of Computer Science Associate Professor Yuvraj Agarwal, ...
Insilico Medicine presents data on AI-designed cancer drugs at 3 major cancer conferences
2023-10-16
Clinical stage artificial intelligence (AI) drug discovery company Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”) has been invited to present scientific data on its novel anti-cancer assets at three major upcoming cancer conferences -- the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) conference in Madrid Oct. 20-24, 2023; the Society of Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) conference Nov. 1-5, 2023 in San Diego; and the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS) Dec. 5-9, 2023.
Small molecule oncology ...
American Society of Anesthesiologists recognizes Philip G. Morgan, M.D., and Margaret M. Sedensky, M.D., with its Excellence in Research Award
2023-10-16
SAN FRANCISCO — The American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) today presented Philip G. Morgan, M.D., and Margaret M. Sedensky, M.D., with its 2023 Excellence in Research Award in recognition of their extensive research focused on understanding how anesthetics work and whether certain anesthetics are safe for children with mitochondrial disease. The award is presented annually for outstanding achievement in research that has had, or is likely to have, an important impact on the practice of anesthesiology.
Drs. Morgan and Sedensky are professors in the Department of Anesthesiology ...
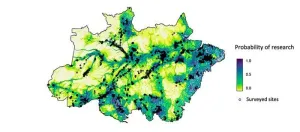
Study reveals areas of Brazilian Amazon where no ecological research has been done
2023-10-16
Many parts of the Brazilian Amazon are neglected in ecological research, for several reasons, according to an article published in the journal Current Biology. Authored by Joice Ferreira of the Federal University of Pará (UFP) and colleagues from many countries who also belong to the Synergize Consortium, the article identifies the areas missing from ecological research and the factors that have determined these gaps, pinpointing opportunities for the planning of new investments in research ...
New polymer membranes, AI predictions could dramatically reduce energy, water use in oil refining
2023-10-16
A new kind of polymer membrane created by researchers at Georgia Tech could reshape how refineries process crude oil, dramatically reducing the energy and water required while extracting even more useful materials.
The so-called DUCKY polymers — more on the unusual name in a minute — are reported Oct. 16 in Nature Materials. And they’re just the beginning for the team of Georgia Tech chemists, chemical engineers, and materials scientists. They also have created artificial intelligence tools to predict the performance of these kinds of polymer membranes, which could accelerate development of new ones.
The implications are stark: ...
Firearm exposure associated with poorer health in communities around the U.S.
2023-10-16
Gun violence is tied to poverty, unemployment, broken families, disengaged youth and racial segregation, according to a study by the New Jersey Gun Violence Research Center at Rutgers.
Published in the Journal of Urban Health, the study found that people living in disadvantaged communities face gun violence at higher levels that are harmful to the health and well-being of whole neighborhoods.
“Many of America’s most disadvantaged neighborhoods are stuck in a vicious cycle of violence and collateral damage that is almost impossible to escape,” ...
Transforming wastewater into valuable chemicals with sunlight
2023-10-16
Researchers led by Prof. GAO Xiang from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Prof. LU Lu from the Harbin Institute of Technology have proposed a novel method to transform wastewater contaminants into valuable chemicals using sunlight, thus paving the way for sustainable and eco-friendly chemical manufacturing.
The study was published in Nature Sustainability on Oct. 16.
Conventional chemical manufacturing relies on energy-intensive processes. Semiconductor biohybrids, integrating efficient light-harvesting materials with superior living cells, have emerged as an exciting advancement ...
Viral persistence and serotonin reduction can cause long COVID symptoms, Penn Medicine research finds
2023-10-16
PHILADELPHIA—Patients with long COVID – the long-term symptoms like brain fog, fatigue, or memory loss in the months or years following COVID-19 – can exhibit a reduction in circulating levels of the neurotransmitter serotonin, according to new research published today in Cell. The study, led by researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, sheds new light on the mechanisms of how persistent inflammation after contracting the SARS-CoV-2 virus can cause long-term neurological symptoms.
According to the CDC, nearly one in five American adults who had COVID-19 experience symptoms of long ...
Can ChatGPT diagnose your condition? Not yet
2023-10-16
A research group led by Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) finds that when common orthopedic symptoms are given, ChatGPT’s diagnosis and recommendations are inconsistent
Tokyo, Japan – ChatGPT, a sophisticated chatbot driven by artificial intelligence (AI) technology, has been increasingly used in health care contexts, one of which is assisting patients in self-diagnosing before seeking medical help. Although it seems very useful at first glance, AI may cause more harm than good to the patient if it is not accurate in its diagnosis and recommendations. A research team from Japan and ...
[1] ... [1622]
[1623]
[1624]
[1625]
[1626]
[1627]
[1628]
[1629]
1630
[1631]
[1632]
[1633]
[1634]
[1635]
[1636]
[1637]
[1638]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.