Significant development in mild cognitive impairment treatment revealed in Australia
2023-10-11
AUSTRALIA, Sydney – October 11, 2023 – Western Sydney University’s NICM Health Research Institute has led a world-first clinical trial in Australia that offers new hope in the treatment of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) among older people. The trial’s results, published in Alzheimer's and Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment and Disease Monitoring, a journal of the Alzheimer’s Association, signal the efficacy and safety of Sailuotong (SLT), a novel herbal extract, as a potential treatment for MCI.
Trial ...
Rivers may not recover from drought for years
2023-10-11
Lack of rainfall is not the only measure of drought. New UC Riverside research shows that despite a series of storms, the impact of drought can persist in streams and rivers for up to 3.5 years.
There are two measures of drought in streams. One measure is the total water level, which is impacted by snowmelt and rainfall. Many researchers examine this measurement. Another measure is baseflow, which is the portion of streamflow fed by groundwater.
Fewer researchers examine baseflow droughts, and there was not previously an accurate way to measure them. Because baseflow is strongly tied to groundwater, and because the ...
Chronic kidney disease may be linked to sudden cardiac arrest in Hispanic/Latino adults
2023-10-11
Research Highlights:
Chronic kidney disease was strongly associated with an increased risk of sudden cardiac arrest among Hispanic/Latino adults, in a new study.
Early identification and management of kidney disease may reduce risk of sudden cardiac arrest among Hispanic/Latino people, researchers suggest.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, Oct. 11, 2023
DALLAS, October 11, 2023 — Chronic kidney disease may increase risk and predict sudden cardiac arrest among Hispanic/Latino adults, according to new research published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an open access, peer-reviewed journal of the American ...
Cardiac arrest: Hispanics, Latinos with kidney disease at high risk
2023-10-11
Hispanics and Latinos with chronic kidney disease are at significant risk for suffering from sudden cardiac arrest, according to a new study from the Smidt Heart Institute at Cedars-Sinai.
During sudden cardiac arrest, the heart unexpectedly stops beating.
“Because people who experience sudden cardiac arrest have a survival rate of less than 10%, prevention is extremely important,” said Kyndaron Reinier, Ph.D., associate director of Epidemiology in the Center for Cardiac Arrest Prevention at the Smidt Heart Institute and lead author of the study published in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
“This study highlights the importance for Hispanic ...
Tens of thousands of endangered sharks and rays caught off Congo
2023-10-11
Tens of thousands of endangered sharks and rays are caught by small-scale fisheries off the Republic of the Congo each year, new research shows.
Scientists surveyed fish brought ashore at Songolo, which is home to more than 60% of the country's “artisanal” fishers (small boats, small engines, hand-hauled lines and nets).
In three years, the team – led by the University of Exeter in partnership with the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) Congo Program and the Republic of the Congo’s fisheries department – recorded more than 73,000 sharks and rays landed.
Most were juveniles, and 98% of individuals were of species listed as vulnerable, ...
Bouldering in south-central Madagascar: a new “rock-climbing” gecko species of the genus Paroedura
2023-10-11
Named after its habitat preference, Paroedura manongavato, from the Malagasy words “manonga” (to climb) and “vato” (rock), is a bouldering expert. Part of its “home range” is also very well-known to rock climbers for its massive granitic domes. “Its description represents another step into the crux (in climbing jargon, the most difficult section of a bouldering problem) of resolving the taxonomy of the recently revised P. bastardi group, where the new species belongs, and reaching a total of 25 described species in this genus, ...
Peregrine falcons set off false alarms to make prey easier to catch
2023-10-11
Predators must eat to survive — and to survive, prey must avoid being eaten. One theory, the Wolf-Mangel model, suggests predators could use false attacks to tire prey out or force them to take bigger risks, but this has been hard to show in practice. Now, scientists observing peregrine falcons have found evidence that they deliberately exhaust their prey to improve later hunting success.
“Although predators are imagined as clever in novels and movies, like the velociraptors in Jurassic Park, empirical biologists are generally not inclined to give much credence to such ideas,” ...
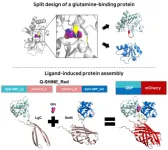
Make diagnosing serious geriatric diseases as easy as measuring blood sugar
2023-10-11
In 2023, life expectancy in Korea will be 83.6 years, the third highest among OECD countries, and it is steadily increasing every year. As the proportion of the elderly population increases, the social cost of treating various geriatric diseases is also increasing rapidly, and there is a growing interest in early diagnosis of diseases. Among the various diagnostic methods, researchers are actively conducting research on measuring glutamine as an indicator of geriatric diseases by finding that the concentration of glutamine in the cells and blood of patients with serious diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and dementia is significantly changed compared to normal people.
Dr. Seo, Moon-Hyeong ...
Commonly used herbicide is harmful to adolescent brain function
2023-10-11
Herbicides are the most used class of pesticides worldwide, with uses in agriculture, homes and industry. Exposures to two of the most popular herbicides were associated with worse brain function among adolescents, according to a study led by researchers at the Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human Longevity Science at University of California San Diego.
In the Oct. 11, 2023 online issue of Environmental Health Perspectives, the researchers reported measuring metabolite concentrations of two commonly used herbicides — glyphosate and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) — and the insect repellent DEET in urine samples ...
New antibiotic drug developed by HKU Chemistry research team approved for clinical trials in humans
2023-10-11
A new antibiotic drug developed by a research team led by Professor Li Xuechen from the Department of Chemistry at The University of Hong Kong (HKU) has recently gained approval from the authorities to undergo clinical trials in the Mainland.
The new drug, which has taken the research team ten years to develop and is named Kynomycin, received the "Notice of Approval for Drug Clinical Trials" from the National Medical Products Administration of China to be tested in human subjects.
The new antibiotic drug targets complex skin and soft tissue infections (cSSTI) caused by bacteria. It ...
Scientists discover ‘flipping’ layers in heterostructures to cause changes in their properties
2023-10-11
Transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD) semiconductors are special materials that have long fascinated researchers with their unique properties. For one, they are flat, one-atom-thick two-dimensional (2D) materials similar to that of graphene. They are compounds that contain different combinations of the transition metal group (e.g., molybdenum, tungsten) and chalcogen elements (e.g., sulfur, selenium, tellurium).
What's even more fascinating is that assembling different TMD layers into vertical stacks creates a new artificial material called a van der Waals (vdW) heterostructure. By incorporating different materials, it becomes possible to ...
USC researchers develop blood test for early-stage ovarian cancer
2023-10-11
High-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HGSOC) is the most common type of ovarian cancer. It is also the most lethal form, in part because clinicians do not have effective ways to screen women for it during the cancer's early stages, when it's easiest to treat.
For patients with a pelvic mass (an abnormal lump or growth in the lower abdomen), it is difficult to detect whether the growth is benign or cancerous ahead of surgery. Unlike many other cancers, biopsies are typically not an option. That makes it hard for doctors to choose the best course of treatment.
Now, a new blood test ...
Killing remains a threat to Bornean orangutans
2023-10-11
University of Queensland research has found despite considerable conservation efforts, the illegal killing of critically endangered orangutans on Borneo may be an ongoing threat to the species.
PhD candidate Emily Massingham from UQ’s Faculty of Science managed a team of researchers which visited 79 villages across the Bornean orangutan range in Kalimantan, conducting face to face interviews with 431 people.
“Our study builds on previous research which indicated killing was one of the key reasons for orangutan population decline, alongside habitat loss,” Ms Massingham said.
“The ...
Lundquist Investigator Dr. Loren Miller is the lead author of the “universal decolonization” study published in the New English Journal of Medicine
2023-10-11
Nursing homes that use a chlorhexidine bathing routine to clean the skin, and an over-the-counter antiseptic to clean the nose, prevent serious infections and reduce the amount of antibiotic-resistant organisms in the nursing home setting, according to the findings of researchers at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center, the University of California, Irvine, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The findings were published today in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“The ...
Renting rather than owning a private sector home linked to faster ‘biological ageing’
2023-10-11
The biological impact of renting, as opposed to owner occupancy, is nearly double that of being out of work vs having paid employment, the findings suggest.
Fortunately, these effects are reversible, emphasising the importance of housing policy in health improvement, say the researchers.
Numerous aspects of housing are associated with physical and mental health, including cold, mould, crowding, injury hazards, stress, and stigma. But exactly how they might exert their effects isn’t entirely clear, say the researchers.
To explore this further, they drew on epigenetic ...
Genes may be responsible for third of complex regional pain syndrome cases
2023-10-11
But the condition is less common in men, even though they are more likely to have the 4 genetic variations implicated in heightened risk, suggesting that there may be sex specific causes, say the researchers.
Most cases of CRPS are usually triggered by an injury, with the skin of the affected body part hypersensitive to the slightest touch or temperature change. CRPS is difficult to treat, and while it often improves with time, some people experience intense pain for many years.
But why some people develop CRPS yet others don’t after the same injury, isn’t clear. ...
Singapore’s smoke-free law may have warded off 20,000 heart attacks in over 65s
2023-10-11
The extension was associated with a monthly fall in the rate of heart attacks, with older people and men benefitting the most from the move.
Second-hand smoke exposure is responsible for 1.3 million annual deaths around the globe, many of which are caused by heart attacks, note the researchers.
But the existing evidence on the health benefits of comprehensive smoke-free laws, which many countries (67 since 2003) have implemented, is largely confined to indoor smoking bans rather than those for housing estates and outdoor spaces, they say.
In 2013 Singapore extended smoke-free legislation ...
Death is only the beginning: Birds disperse eaten insects’ eggs
2023-10-11
Relationship patterns among flightless stick insects suggest that birds disperse the eggs after eating gravid females. Lab experiments previously suggested the possibility, but a new genetic analysis of natural populations in Japan by Kobe University researchers now supports the idea.
Most species of stick insects are flightless, yet they are distributed over wide distances and across geographical features that would impede the expansion of flightless animals. This has caused researchers to speculate that their eggs might be dispersed by birds feeding on gravid females, much in the same way as many plant species rely on birds eating their seeds together ...
Early Cambrian microfossils preserve introvert musculature of cycloneuralians
2023-10-11
An international research team led by Prof. ZHANG Huaqiao from the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (NIGPAS) has reported the discovery of extraordinary early Cambrian (ca. 535 million years ago, or Ma) microfossils preserving the introvert musculature of cycloneuralians, a group of animals that include roundworms, horsehair worms, mud dragons, and many other creatures.
The discovery added fleshy insights into early Cambrian cycloneuralians, which are closely related to arthropods, the most successful animals on Earth.
The ...
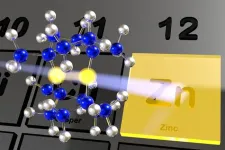
Bringing out the color in zinc
2023-10-11
Zinc is an important element that is found widely in biological systems, is cheap to manufacture relative to other metals, and has low toxicity. However, unlike other similar metals that exhibit a variety of vibrant colors in metal complexes, seeing different colors for zinc materials was not thought possible.
In a study published recently in Angewandte Chemie International Edition, researchers from the Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo, have synthesized a complex with two zinc ions that does exhibit color—greatly expanding the ...
Non-melanoma skin cancer killing more people than melanoma, new study finds
2023-10-11
(Wednesday, 11 October 2023, Berlin, Germany) Non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC) is causing a greater number of global deaths than melanoma, the more serious form of skin cancer, a new study presented today at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venerology (EADV) Congress 2023 has found.1,2
Researchers also believe that NMSC is underreported and that the true impact of this disease may be even higher than estimated.3
Professor Thierry Passeron, lead author of the study, explains, “Although NMSC is less likely to be fatal than melanoma skin cancer, its prevalence is strikingly higher. In 2020, NMSC accounted for 78% of ...
Obesity leads to a complex inflammatory response inside fat tissue
2023-10-10
Fat tissue, for as much as it’s been vilified, is an incredibly complex and essential bodily organ involved in energy storage and hormone production, among other functions. Yet, modern lifestyles have led to a worldwide epidemic of obesity, and a corresponding increase in related conditions like type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Researchers are attempting to uncover the basics of how fat tissue is structured and, specifically, inflammation associated with obesity, in the hopes of unlocking the connection between the accumulation of fat and poor health outcomes.
A new study from Lindsey Muir, Ph.D., Ph.D.-candidate Cooper Stansbury, and their colleagues ...
STARTUP Central project will educate and support biomedical researchers turning innovations into new companies
2023-10-10
LAWRENCE — Bringing an idea from a lab to patients and consumers can be a complicated and intimidating process involving patents, governmental regulations, product development, business structuring, hiring issues and many more complex considerations.
Now, a $3 million initiative based at the University of Kansas will empower biomedical researchers in public universities and colleges across several Plains states to carry their innovations to the marketplace.
The effort involves both a private firm based at KU Innovation Park, Continuum Educational Technologies PBC, and KU researchers working under a new $3 million grant from ...
Protein key to placental heath could be target for reproductive conditions
2023-10-10
New Haven, Conn. — Immune cells play a key role during pregnancy, adjusting immune system response in a way that enables the fetus to develop while also protecting the parent and fetus from outside assaults like viruses. In a new study, Yale researchers found that a particular protein found throughout the body plays a major role in this important immune system modulation, affecting placental health early in pregnancy.
The findings, they say, could lead to new treatments for reproductive conditions in the future.
The study, led by Yale School of Medicine’s Reshef Tal, was published Oct. 10 in the journal JCI Insight. A human fetus contains ...
OmniMotion allows for better video motion estimation
2023-10-10
ITHACA, N.Y. -- Cornell researchers have developed a new optimization tool to estimate motion throughout an input video, which has potential applications in video editing and generative AI video creation.
The tool, called OmniMotion, is described in a paper, “Tracking Everything, Everywhere, All at Once,” presented at the International Conference on Computer Vision, Oct. 2-6 in Paris.
“There are these two dominant paradigms in motion estimation – optical flow, which is dense but short range, and feature tracking, which is sparse but long range,” said Noah ...
[1] ... [1633]
[1634]
[1635]
[1636]
[1637]
[1638]
[1639]
[1640]
1641
[1642]
[1643]
[1644]
[1645]
[1646]
[1647]
[1648]
[1649]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.