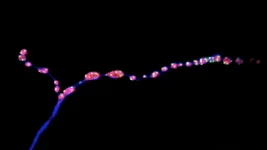
New insight into "training" highly reactive chemical compounds
2021-07-20
Led by Dr Jonas Warneke, researchers at the Wilhelm Ostwald Institute of Physical and Theoretical Chemistry at Leipzig University have made a decisive advance in the study of one type of highly reactive particles. Based on their research, they now understand the "binding preferences" of these particles.
Their research serves as the basis for the targeted use of these highly reactive molecules, for example, to generate new molecular structures or to bind hazardous chemical "waste" and in this way dispose of it. The researchers have now published their findings in the journal Chemistry - A European Journal, and their research was featured on the cover thanks to the excellent review they received.
What molecules and people have in common
Molecules and people actually have a lot in ...
15,000-year-old viruses discovered in Tibetan glacier ice
2021-07-20
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Scientists who study glacier ice have found viruses nearly 15,000 years old in two ice samples taken from the Tibetan Plateau in China. Most of those viruses, which survived because they had remained frozen, are unlike any viruses that have been cataloged to date.
The findings, published today in the journal Microbiome, could help scientists understand how viruses have evolved over centuries. For this study, the scientists also created a new, ultra-clean method of analyzing microbes and viruses in ice without contaminating it.
"These glaciers were formed gradually, and along with dust and ...
Automobile class society
2021-07-20
In order to correctly separate vehicles into classes, for instance for mobility pricing, one must be able to clearly distinguish mid-sized cars from upper class cars or small cars from compact cars. But this is becoming increasingly difficult: On photos, an Audi A4 looks almost the same as an Audi A6, a Mini One looks similar to a Mini Countryman. To date, there is no independent procedure for doing this.
Thus far, the classes in each country have been determined by experts - to a large extend at their own discretion. Empa researcher Naghmeh Niroomand has now developed a system that can classify cars worldwide based on their dimensions. Purely mathematical and fair. Thanks to it, the current classification ...
Fish friends help in a crisis
2021-07-20
FORT LAUDERDALE/DAVIE, Fla. - It's good to have friends.
Most humans have experienced social anxiety on some level during their lives. We all know the feeling - we show up to a party thinking it is going to be chock full of friends, only to find nearly all total strangers. While we typically attribute the long-lasting bonds of social familiarity to complex thinkers like humans, growing evidence indicates that we underestimate the importance of friendship networks in seemingly "simple" animals, like fish, and its importance for survival in the wild. To better understand how familiarity impacts social fishes, a group of research scientists studied this idea using schooling coral reef fish.
"We studied how the presence of ...
SARS-CoV-2: Achilles' heel of viral RNA
2021-07-20
FRANKFURT, GERMANY. When SARS-CoV-2 infects a cell, it introduces its RNA into it and re-programmes it in such a way that the cell first produces viral proteins and then whole viral particles. In the search for active substances against SARS-CoV-2, researchers have so far mostly concentrated on the viral proteins and on blocking them, since this promises to prevent, or at least slow down, replication. But attacking the viral genome, a long RNA molecule, might also stop or slow down viral replication.
The scientists in the COVID-19-NMR consortium, which is coordinated by Professor Harald Schwalbe from the Institute of Organic Chemistry and Chemical Biology at Goethe University, have now completed an important ...
The environmental toll of disposable masks
2021-07-20
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Since the Covid-19 pandemic began last year, face masks and other personal protective equipment have become essential for health care workers. Disposable N95 masks have been in especially high demand to help prevent the spread of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes Covid-19.
All of those masks carry both financial and environmental costs. The Covid-19 pandemic is estimated to generate up to 7,200 tons of medical waste every day, much of which is disposable masks. And even as the pandemic slows down in some parts of the world, health care workers are expected to continue wearing masks most of the time.
That toll could be dramatically cut by adopting reusable masks, according to a new study from MIT that has calculated the financial ...
Machine learning models to help photovoltaic systems find their place in the sun
2021-07-20
With the looming threat of climate change, it is high time we embrace renewable energy sources on a larger scale. Photovoltaic systems, which generate electricity from the nearly limitless supply of sunlight energy, are one of the most promising ways of generating clean energy. However, integrating photovoltaic systems into existing power grids is not a straightforward process. Because the power output of photovoltaic systems depends heavily on environmental conditions, power plant and grid managers need estimations of how much power will be injected by photovoltaic systems so as to plan optimal generation and maintenance schedules, among other important operational aspects.
In line with modern trends, if something needs predicting, you can safely ...
Enzyme-based plastics recycling is more energy efficient, better for environment
2021-07-20
Researchers in the BOTTLE Consortium, including from the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE's) National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and the University of Portsmouth, have identified using enzymes as a more sustainable approach for recycling polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a common plastic in single-use beverage bottles, clothing, and food packaging that are becoming increasingly relevant in addressing the environmental challenge of plastic pollution. An analysis shows enzyme-recycled PET has potential improvement over conventional, fossil-based methods of PET production across a broad spectrum of energy, carbon, and socioeconomic impacts.
The concept, if further developed and implemented at scale, could lead to ...
Brain 'noise' keeps nerve connections young
2021-07-20
Neurons communicate through rapid electrical signals that regulate the release of neurotransmitters, the brain's chemical messengers. Once transmitted across a neuron, electrical signals cause the juncture with another neuron, known as a synapse, to release droplets filled with neurotransmitters that pass the information on to the next neuron. This type of neuron-to-neuron communication is known as evoked neurotransmission.
However, some neurotransmitter-packed droplets are released at the synapse even in the absence of electrical impulses. These miniature release events -- or ...
"Springing forward" affects early birds less than night owls, study finds
2021-07-20
Every spring, the Daylight Saving Time shift robs people of an hour of sleep - and a new study shows that DNA plays a role in how much the "spring forward" time change affects individuals.
People whose genetic profile makes them more likely to be "early birds" the rest of the year can adjust to the time change in a few days, the study shows. But those who tend to be "night owls" could take more than a week to get back on track with sleep schedule, according to new data published in Scientific Reports by a team from the University of Michigan.
The study uses data from continuous sleep tracking ...
DNA assay aids in identifying and protecting North American wolves, coyotes
2021-07-20
Forensics specialists can use a commercial assay targeting mitochondrial DNA to accurately discriminate between wolf, coyote and dog species, according to a new study from North Carolina State University. The genetic information can be obtained from smaller or more degraded samples, and could aid authorities in prosecuting hunting jurisdiction violations and preserving protected species.
In the U.S., certain wolf subspecies or species are endangered and restricted in terms of hunting status. It is also illegal to deliberately breed wolves or coyotes with domesticated dogs.
"If ...
Child with rare genetic syndrome successfully treated in less than two years
2021-07-20
EAST LANSING, Mich. - Diagnosing a rare medical condition is difficult. Identifying a treatment for it can take years of trial and error. In a serendipitous intersection of research expertise, an ill patient in this case a child and innovative technology, Bachmann-Bupp Syndrome has gone from a list of symptoms to a successful treatment in just 16 months.
The paper chronicling this lightning-fast scientific response to the Bachmann-Bupp Syndrome was published in the open-access journal, eLife.
For more than 25 years, André Bachmann, professor of pediatrics in Michigan State University College ...
Study: Long-term prognosis for some patients with severe brain injury better than expected
2021-07-20
New research adds to a body of evidence indicating decisions about withdrawing life-sustaining treatment for patients with moderate-to-severe traumatic brain injury (TBI) should not be made in the early days following injury.
In a July 6, 2021, study published in JAMA Neurology, researchers led by UC San Francisco, Medical College of Wisconsin and Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital followed 484 patients with moderate-to-severe TBI. They found that among the patients in a vegetative state, 1 in 4 "regained orientation" - meaning they knew who they were, their ...
Study refutes suspicion that dengue increases risk of microcephaly associated with zika
2021-07-20
By Luciana Constantino | Agência FAPESP – A pregnant woman infected by zika virus does not face a greater risk of giving birth to a baby with microcephaly if she has previously been exposed to dengue virus, according to a Brazilian study that compared data for pregnant women in Rio de Janeiro and Manaus.
A zika epidemic broke out in Brazil in 2015-16 in areas where dengue is endemic. Both viruses are transmitted by the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Some of the states affected by the zika epidemic reported a rise in cases of microcephaly, a rare neurological disorder in which the baby’s brain fails to develop completely. Others saw no such rise.
According to this new study by Brazilian researchers, two factors explain the rise in microcephaly in only some areas: the ...
Improving access to mental health services in low-income communities
2021-07-20
When it comes to improving access to mental health services for children and families in low-income communities, a University of Houston researcher found having a warm handoff, which is a transfer of care between a primary care physician and mental health provider, will help build trust with the patient and lead to successful outcomes.
"Underserved populations face certain obstacles such as shortage of providers, family beliefs that cause stigma around mental health care, language barriers, lack of transportation and lack of insurance. A warm handoff, someone who serves as a go-between for experts and patients, can ensure connections are made," said Quenette L. Walton, assistant professor at the ...
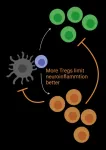
UCI-led study finds unleashing Treg cells may lead to treatments for multiple sclerosis
2021-07-20
Irvine, CA - July 20, 2021 - In a new University of California, Irvine-led study, researchers found that a certain protein prevented regulatory T cells (Tregs) from effectively doing their job in controlling the damaging effects of inflammation in a model of multiple sclerosis (MS), a devastating autoimmune disease of the nervous system.
Published this month in Science Advances, the new study illuminates the important role of Piezo1, a specialized protein called an ion channel, in immunity and T cell function related to autoimmune neuroinflammatory disorders.
"We found that Piezo1 selectively restrains Treg cells, limiting their potential to mitigate ...
Babies at risk for diabetes may have microbiota restored
2021-07-20
Newborns at risk for Type 1 diabetes because they were given antibiotics may have their gut microorganisms restored with a maternal fecal transplant, according to a Rutgers study.
The study, which involved genetic analysis of mice, appears in the journal Cell Host & Microbe.
The findings suggest that newborns at risk for Type 1 diabetes because their microbiome - the trillions of beneficial microorganisms in and on our bodies - were disturbed can have the condition reversed by transplanting fecal microbiota from their mother into their gastrointestinal tract after the antibiotic course has been completed.
Type 1 diabetes is the most ...
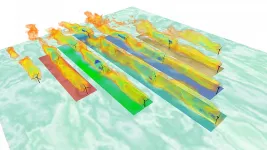
Data identifies turbine wake clustering, improves wind farm productivity via yaw control
2021-07-20
WASHINGTON, July 20, 2021 -- In the wind power industry, optimization of yaw, the alignment of a wind turbine's angle relative to the horizonal plane, has long shown promise for mitigating wake effects that cause a downstream turbine to produce less power than its upstream partner. However, a critical missing puzzle piece in the application of this knowledge has recently been added -- how to automate the identification of which turbines are experiencing wake effects amid changing wind conditions.
In the Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, by AIP Publishing, ...
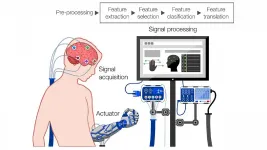
Bleak cyborg future from brain-computer interfaces if we're not careful
2021-07-20
WASHINGTON, July 20, 2021 -- Surpassing the biological limitations of the brain and using one's mind to interact with and control external electronic devices may sound like the distant cyborg future, but it could come sooner than we think.
Researchers from Imperial College London conducted a review of modern commercial brain-computer interface (BCI) devices, and they discuss the primary technological limitations and humanitarian concerns of these devices in APL Bioengineering, from AIP Publishing.
The most promising method to achieve real-world BCI applications is through electroencephalography (EEG), a method ...
Climate change threatens food security of many countries dependent on fish
2021-07-20
Millions of people in countries around the world could face an increased risk of malnutrition as climate change threatens their local fisheries.
New projections examining more than 800 fish species in more than 157 countries have revealed how two major, and growing, pressures - climate change and over-fishing - could impact the availability of vital micronutrients from our oceans.
As well as omega-3 fatty acids, fish are an important source of iron, zinc, calcium, and vitamin A. A lack of these vital micronutrients is linked to conditions such as maternal mortality, stunted growth, and pre-eclampsia.
Analyses by an international team from the UK and Canada and led by scientists from Lancaster ...
Gene expression mechanism may have immunity, cancer implications
2021-07-20
PHILADELPHIA -- (July 20, 2021) -- Alternative polyadenylation (APA) is an RNA processing mechanism that regulates gene expression by generating different ends on RNA transcripts of the same gene. Though it affects more than half of human genes, the significance of APA was poorly understood. Now a new study by The Wistar Institute describes an important function of APA in allowing certain mRNAs to reach specific sites of protein synthesis and reveals that length, sequence and structural properties can determine the destination (and fate) of mRNAs within the cell. These findings, published online in the journal Cell Reports, shed light on the consequences of APA that may represent a paradigm shift in the mRNA metabolism field.
The ...
Medical debt in US
2021-07-20
What The Study Did: Credit reports were analyzed to estimate the amount of medical debt in collections nationally and by geographic region and income group and its association with Medicaid expansion under the Affordable Care Act.
Authors: Neale Mahoney, Ph.D., of Stanford University in Stanford, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.8694)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional ...
Recovering DNA from challenging forensic evidence in forensic genomics
2021-07-20
New Rochelle, NY, July 19, 2021--Duct tape and items retrieved from the water are common pieces of evidence in forensic cases. A new study evaluates the recovery of DNA from folded duct tape that has been submerged in ocean water for up to 2 weeks. The study is published in the peer-reviewed journal Forensic Genomics. Click here to read the article now.
Joseph Donfack, PhD, from the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) Laboratory Division, and coauthors showed that it is possible to recover enough DNA to yield a complete short tandem repeat (STR) profile from folded duct tape that has been submerged in ocean water for up to 2 weeks if the initial ...
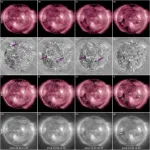
New method predicts 'stealth' solar storms before they wreak geomagnetic havoc on Earth
2021-07-20
On 23 July 2012, humanity escaped technological and economic disaster. A diffuse cloud of magnetized plasma in the shape of a slinky toy tens of thousands of kilometers across was hurled from the Sun at a speed of hundreds of kilometers per second.
This coronal mass ejection (CME) just missed the Earth because its origin on the Sun was facing away from our planet at the time. Had it hit the Earth, satellites might have been disabled, power grids around the globe knocked out, GPS systems, self-driving cars, and electronics jammed, and railway tracks ...
Shoppers' mobility habits: retailers overestimate car use
2021-07-20
Retail traders often fear that reducing the amount of urban space made available for parking private vehicles would have a negative effect on their businesses. A survey conducted by researchers from the Institute for Advanced Sustainability Studies (IASS) on two shopping streets in Berlin shows that traders have a skewed perception of their customers' mobility habits. The findings of this research will facilitate better-informed decision-making around urban land-use planning.
The researchers surveyed around 2,000 customers and 145 retailers on Kottbusser Damm (Friedrichshain-Kreuzberg district) and Hermannstraße (Neukölln district). The vast majority of shoppers - 93 per cent - had not travelled to their ...
[1] ... [2117]
[2118]
[2119]
[2120]
[2121]
[2122]
[2123]
[2124]
2125
[2126]
[2127]
[2128]
[2129]
[2130]
[2131]
[2132]
[2133]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.