New research could help clear backlog of surgery since it shows use of airway device in
2021-07-21
New research published in Anaesthesia (a journal of the Association of Anaesthetists) by researchers from the University of Bristol can help to improve the efficiency of surgery and help tackle the growing backlog of surgery caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. During the pandemic, the number of patients waiting for routine surgery in the UK has almost doubled with more than 5.3 million people awaiting surgery including more than 300,000 waiting more than a year.
A contributory factor is that COVID-19 precautions have led to many operating theatres working at 75-50% of normal working efficiency. Staff working in operating theatres have been required to take special precautions at the start and end of operations to allow viral particles ...
More than 1.5M children lost a primary or secondary caregiver due to the COVID-19 pandemic
2021-07-21
More than 1.5 million children around the world are estimated to have lost at least one parent, custodial grandparent, or grandparent who lived with them due to death related to COVID-19 during the first 14 months of the pandemic, according to a study published today in The Lancet. The study highlights orphanhood as an urgent and overlooked consequence of the pandemic and emphasizes that providing evidence-based psychosocial and economic support to children who have lost a caregiver must be a key part of responding to the pandemic.
The analysis used mortality and fertility data to model rates of COVID-19-associated orphanhood (death of one or both parents) and deaths of custodial and co-residing grandparents (ages 60-84) from March 1, 2020 to April 30, 2021, across 21 countries. This study ...
A substance from Saussurea controversa will help bone tissue regeneration
2021-07-21
Metabolic bone diseases, including osteoporosis, when bones lose their mass and become so fragile that they could be damaged while sneezing or under little stress, are called the silent epidemic of the 21st century. A person does not even know about his illness before the first symptom - it can be a fracture of the spine or the neck of the hip. According to statistics, every third woman and every fifth man after 50 have osteoporosis. Thus, it is promising to search for and obtain substances and materials for implants that have osteoinductive properties and are capable of initiating the processes of transformation of stem cells into bone.
Certain trace elements, such as calcium and magnesium, influence the processes of bone regeneration ...
Virginia Tech's COVID-19 testing demonstrates power, versatility of academic labs
2021-07-21
In the early days of the pandemic, scientists at Virginia Tech created a COVID-19 testing laboratory and novel test for the virus from scratch.
They not only developed a test in-house that avoided the reagent supply shortages that hampered testing efforts nationwide, but also used 3D-engineered supplies and stable storage media, enabling samples to be transported to rural sites in Virginia without the need for constant refrigeration.
This novel protocol for transforming a research laboratory into a testing operation capable of processing more than 130,000 ...
Microbially produced fibers: Stronger than steel, tougher than Kevlar
2021-07-21
Spider silk is said to be one of the strongest, toughest materials on the Earth. Now engineers at Washington University in St. Louis have designed amyloid silk hybrid proteins and produced them in engineered bacteria. The resulting fibers are stronger and tougher than some natural spider silks.
Their research was published in the journal ACS Nano.
To be precise, the artificial silk -- dubbed "polymeric amyloid" fiber -- was not technically produced by researchers, but by bacteria that were genetically engineered in the lab of Fuzhong Zhang, a professor ...
Small-scale worker resistance impacts food delivery economy in China
2021-07-21
ITHACA, N.Y. - Small-scale. Short-lived. All digital. Out of public view. That's how a new form of collective worker resistance is unfolding in China's app-based food delivery economy, new Cornell University research finds.
Though highly fragmented and not always successful, "mini-strikes" by small groups of food couriers - conducted via WeChat - reflect a new form of leverage, suggest Chuxuan "Victoria" Liu and Eli Friedman, associate professor in the ILR School.
Food couriers are able to maintain complete physical invisibility, and each individual worker can 'strike' from anywhere, they write.
The scholars interviewed couriers, in-person and online, who delivered food for Ele.me, an Alibaba-owned company that controlled ...
Research shows employer-based weight management program with access to anti-obesity medications results in greater weight loss
2021-07-20
Tuesday, July 20, 2021, CLEVELAND: A Cleveland Clinic study demonstrates that adults with obesity lost significantly more weight when they had access to medications for chronic weight management in conjunction with their employer-based weight management program, compared to adults who did not have access to the medications. The study was published in JAMA Network Open.
Obesity is a complex disease that is caused by multiple factors, including genetic, environmental, and biological. A lifestyle intervention with a focus on nutrition and exercise is often not enough to treat obesity, which is a chronic disease that requires long-term therapy. The U.S. Food and Drug ...
Study: Wireless radiation exposure for children is set too high
2021-07-20
WASHINGTON - A peer-reviewed study by the Environmental Working Group recommends stringent health-based exposure standards for both children and adults for radiofrequency radiation emitted from wireless devices. EWG's children's guideline is the first of its kind and fills a gap left by federal regulators.
The study, published in the journal Environmental Health, relies on the methodology developed by the Environmental Protection Agency to assess human health risks arising from toxic chemical exposures. EWG scientists have applied the same methods to radiofrequency radiation from wireless devices, ...
Strong immune response underlies acute kidney injury related to COVID-19
2021-07-20
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Mayo Clinic researchers have found that acute kidney injury associated with COVID-19 resembles sepsis-caused kidney injury, and the immune response triggered by the infection plays a pivotal role.
The findings, published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings, also suggest that mitochondrial dysfunction -- a loss of function in cellular energy production -- is commonly found in kidney injury related to COVID-19. More than one-third of hospitalized COVID-19 patients report acute kidney injury, and sudden kidney failure is a risk factor for in-hospital mortality, according to studies published last ...
Muddied waters: Sinking organics alter seafloor records
2021-07-20
The remains of microscopic plankton blooms in near-shore ocean environments slowly sink to the seafloor, setting off processes that forever alter an important record of Earth's history, according to research from geoscientists, including David Fike at Washington University in St. Louis.
Fike is co-author of a new study published July 20 in Nature Communications.
"Our previous work identified the role that changing sedimentation rates had on local versus global controls on geochemical signatures that we use to reconstruct environmental change," said Fike, professor of earth and planetary sciences and director of environmental studies in Arts & Sciences.
"In this study, we investigated organic carbon loading, or how much ...
Patients billed up to $219 million in total for preventive services that should be free
2021-07-20
Experts say these unexpected healthcare costs may discourage people from seeking recommended preventive care.
Despite a sharp reduction in out-of-pocket (OOP) costs for preventive care since the Affordable Care Act was enacted in 2010, patients are still receiving unexpected bills for preventive services that should be free, according to a new study co-authored by a Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) researcher.
Published in the journal Preventive Medicine, study found that total out-of-pocket costs billed for preventive services to Americans with employer-sponsored insurance (ESI) in 2018 ranged from $75.6 million to $219 million, with 1 in 4 patients who used preventive care incurring these charges.
"The ACA enabled great strides in making preventive care free to ...
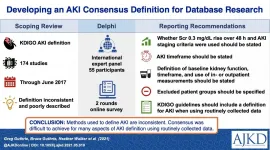
Most studies of acute kidney injury are flawed due to non-use of standard definitions
2021-07-20
In an article published in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases (AJKD), researchers found that among 176 studies on acute kidney injury, the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) definitions of kidney injury were inconsistently applied and 80% of studies did not define recovery of kidney function.
The KDIGO definition of AKI is used in both clinical practice and in research. This scoping review demonstrated that there is a wide variation of practice in how this definition is applied and also a lack of transparency about how researchers applied it. An international panel of experts in AKI was formed in an attempt to achieve consensus on how this definition should be applied. They participated in a Delphi process and while they were able to ...
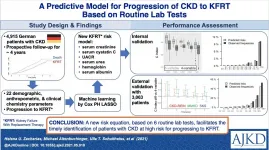
Risk score with 6 routinely available lab tests accurately predicts kidney failure
2021-07-20
Researchers developed a new risk equation, based on six routinely available patient parameters, that yielded improved performance in estimating the risk of a chronic kidney disease (CKD) patient to progress to end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) requiring kidney replacement therapy (KRT).
A novel risk equation for the timely identification of chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients at risk for progressing to kidney failure requiring kidney replacement therapy was developed in 4,915 patients with CKD stage 1-5 with and without albuminuria, from the German Chronic Kidney Disease (GCKD) Study. It includes six laboratory tests: ...
Digital health technologies hold key to new Parkinson's treatments
2021-07-20
TUCSON, Ariz., July 20, 2021 -- The use of digital health technologies across health care and drug development has accelerated. A new paper titled "Digital Progression Biomarkers as Novel Endpoints in Clinical Trials: A Multistakeholder Perspective," co-authored by experts across diverse disciplines, highlights how new remote monitoring technologies present a tremendous opportunity to advance digital medicine in health care even further, specifically in Parkinson's disease. This perspective paper is co-authored by the academic leader of the largest funded project for digital technologies in Europe, Professor Lynn Rochester, University of Newcastle; European Medicines Agency (EMA) ...
New discoveries reveal how acute myeloid leukemia walks line between growth and cell death
2021-07-20
Researchers revealed new insights into how acute myeloid leukemia (AML) develops and progresses, according to a study published in END ...
Researchers develop novel method for glucagon delivery
2021-07-20
For children with Type 1 diabetes, the risk of experiencing a severe hypoglycemic episode is especially common -- and for parents, the threat of that happening in the middle of the night is especially frightening. Sudden and critical drops in blood sugar can go undetected overnight when the child is asleep, resulting in coma and death -- an event known as "dead in bed syndrome."
"A parent can check their child's glucose levels right before they go to bed and everything looks fine, then around 2 a.m. their blood sugar is dangerously low -- near comatose level," said Matthew Webber, associate professor of chemical and ...
COVID-19 shutdowns reveal racial disparities in exposure to air pollution
2021-07-20
WASHINGTON (July 20, 2021)--A new study of COVID-19 shutdowns in the United States reveals pronounced disparities in air pollution -- with disenfranchised, minority neighborhoods still experiencing more exposure to a harmful air pollutant compared to wealthier, white communities. This first-of-a-kind study published today by researchers at the George Washington University looks at how air pollution changed after schools and businesses shut down in March 2020 in attempts to curb the spread of COVID-19.
"New York and other major urban areas had cleaner air as many commuters and others stayed off the roads," Gaige Kerr, the lead researcher on the study and a research scientist at the GW Milken ...
75% of sexual assault survivors have PTSD one month later
2021-07-20
Researchers want sexual assault survivors to know that it's normal to feel awful right after the assault, but that many will feel better within three months.
In a meta-analysis published in Trauma, Violence & Abuse, researchers found that 81% of sexual assault survivors had significant symptoms of post-traumatic stress (PTSD) one week after the assault. One month afterward - the first point in time that PTSD can be diagnosed - 75% of sexual assault survivors met criteria for the disorder. That figure dropped to 54% after three months and 41% after one year.
"One of the main takeaways is that the majority of recovery from post-traumatic stress happens in first three months," ...
Research shows microbes play critical role boosting vigor of hybrid corn
2021-07-20
LAWRENCE -- A new paper appearing the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences gives new detail and understanding to the cultivation of corn, one of the United States' biggest cash crops.
The research by a team at the University of Kansas centers on "hybrid vigor," also known as "heterosis," a well-known phenomenon where crosses between inbred lines of corn and other crops produce offspring that outperform their parents in yield, drought resistance and other desirable qualities. Yet, the mechanisms underpinning heterosis are little understood despite over a century of intensive research.
The new PNAS research examines the relationship between heterosis and soil microbes, showing, ...
Using snakes to monitor Fukushima radiation
2021-07-20
Ten years after one of the largest nuclear accidents in history spewed radioactive contamination over the landscape in Fukushima, Japan, a University of Georgia study has shown that radioactive contamination in the Fukushima Exclusion Zone can be measured through its resident snakes.
The team's findings, published in the recent journal of Ichthyology & Herpetology, report that rat snakes are an effective bioindicator of residual radioactivity. Like canaries in a coal mine, bioindicators are organisms that can signal an ecosystem's health.
An abundant species in Japan, rat snakes travel short distances and can accumulate high levels of radionuclides. According ...
Elite runners spend more time in air, less on ground, than highly trained but nonelite peers
2021-07-20
A recent study led by Geoff Burns, an elite runner and postdoctoral researcher at the University of Michigan Exercise & Sport Science Initiative, compared the "bouncing behavior"--the underlying spring-like physics of running--in elite-level male runners (sub-four-minute milers) vs. highly trained but not elite runners.
Subjects ran on a treadmill instrumented with a pressure plate beneath the belt, so Burns and colleagues could see how much time they spent in the air and in contact with the ground. When running, muscles and limbs coordinate to act like a giant pogo stick, and those muscles, tendons and ligaments interact to recycle energy from step to step, Burns says.
The researchers looked at the basic physics of the runners ...
Health care providers missing opportunities to talk about sexual health with young people
2021-07-20
Routine adolescent preventive visits provide important opportunities for promoting sexual and reproductive health and for preventing unintended pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections.
A new study END ...
Mind and matter: Modeling the human brain with machine learning
2021-07-20
We all like to think that we know ourselves best, but, given that our brain activity is largely governed by our subconscious mind, it is probably our brain that knows us better! While this is only a hypothesis, researchers from Japan have already proposed a content recommendation system that assumes this to be true. Essentially, such a system makes use of its user's brain signals (acquired using, say, an MRI scan) when exposed to a particular content and eventually, by exploring various users and contents, builds up a general model of brain activity.
"Once we obtain the 'ultimate' brain model, we should be able to perfectly estimate the brain activity of ...
American Board of Urology outlines processes to ensure diversity in leadership
2021-07-20
July 19, 2021 - At the organization responsible for certifying the training and skills of US urologists, achieving and maintaining diversity, equity and inclusion is more than just a "numbers game," according to a special article in Urology Practice®, an Official Journal of the American Urological Association (AUA). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
In the new article, the American Board of Urology (ABU) points out that the practice of diversity and inclusion has been a cornerstone of its values for years. However, the Board acknowledges that while progress has been made, ...
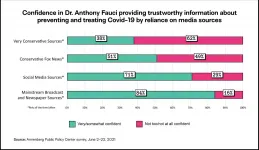
Public trust in CDC, FDA, and Fauci holds steady, survey shows
2021-07-20
With more than two-thirds of American adults vaccinated with at least one dose of an authorized Covid-19 vaccine, the top U.S. health agencies retain the trust of the vast majority of the American public, as does Dr. Anthony Fauci, the public face of U.S. efforts to combat the virus, according to a new survey from the Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC) of the University of Pennsylvania.
The survey revealed growing public confidence in both the safety and effectiveness of vaccines to prevent Covid-19.
But after months of attacks on Fauci in conservative and social media, the survey found that people who said they rely on conservative and very conservative media rather than other sources ...
[1] ... [2116]
[2117]
[2118]
[2119]
[2120]
[2121]
[2122]
[2123]
2124
[2125]
[2126]
[2127]
[2128]
[2129]
[2130]
[2131]
[2132]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.