Living near woodlands is good for children and young people's mental health
2021-07-19
Analysis of children and young people's proximity to woodlands has shown links with better cognitive development and a lower risk of emotional and behavioural problems, in research led by UCL and Imperial College London scientists that could influence planning decisions in urban areas.
In what is believed to be one of the largest studies of its kind, researchers used longitudinal data relating to 3,568 children and teenagers, aged nine to 15 years, from 31 schools across London. This period is a key time in the development of adolescents' thinking, reasoning and understanding of the world.
The study, published in Nature Sustainability, looked at the links between different types of natural urban environments and ...
Renewable energy OK, but not too close to home
2021-07-19
When it comes to transitioning from carbon-based to renewable source energy systems, Americans are on board. They're less keen, however, having these new energy infrastructures--wind turbines or solar farms--built close to their homes, which creates hurdles for policymakers. That's according to a study from University of Georgia researcher Thomas Lawrence.
Lawrence and an international team conducted surveys in the United States, Germany and Ireland to assess people's attitudes about renewable energy technologies and their willingness to have the necessary infrastructures built nearby.
"People in Germany and Ireland were more open to having renewable ...
Tail without a comet: the dusty remains of Comet ATLAS
2021-07-19
A serendipitous flythrough of the tail of a disintegrated comet has offered scientists a unique opportunity to study these remarkable structures, in new research presented today at the National Astronomy Meeting 2021.
Comet ATLAS fragmented just before its closest approach to the Sun last year, leaving its former tail trailing through space in the form of wispy clouds of dust and charged particles. The disintegration was observed by the Hubble Space Telescope in April 2020, but more recently the ESA spacecraft Solar Orbiter has flown close to the tail remnants in the course of its ongoing mission.
This lucky ...
New material could mean lightweight armor, protective coatings
2021-07-19
RESEARCH TRIANGLE PARK, N.C. -- Army-funded research identified a new material that may lead to lightweight armor, protective coatings, blast shields and other impact-resistant structures.
Researchers at the U.S. Army's Institute for Soldier Nanotechnologies at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Caltech and ETH Zürich found that materials formed from precisely patterned nanoscale trusses are tougher than Kevlar and steel.
In experiments, the ultralight structures, called nanoarchitectured materials, absorbed the impact of microscopic projectiles accelerated to supersonic speeds.
"Increasing protection while simultaneously decreasing the weight that ...
Cannabis: sexually diverse youths with depression use more
2021-07-19
It's no secret that studies show that sexually diverse youth - in particular, lesbian, gay and bisexual (LGB) youth - use more cannabis and experience more mental health challenges than their heterosexual peers.
But what about the changes that occur in the rates of cannabis use: do they precede those related to mental health or is it the other way around? A new study from Université de Montréal offers some answers.
In the Journal of Abnormal Psychology, Kira London-Nadeau, a doctoral student and CIHR Vanier Scholar in the Department of Psychology at UdeM and the CHU Sainte-Justine Research ...
Inadequate protection for women and girls seeking refuge in Germany
2021-07-19
Germany is not meeting its legal obligations to protect refugee women and girls from discrimination. This is the conclusion of a "shadow report" by the University of Göttingen, the association Pro Asyl and the refugee councils of Bavaria, Hesse, Lower Saxony and Saxony-Anhalt. Shadow reports are a useful tool to present important information in parallel with official government reports. Based on current research results and a survey of 65 women's counselling centres, psychosocial counselling centres and institutions working with refugees from all 16 federal states, the study finds that Germany does not adequately protect refugee women and girls and does not meet the requirements of the Istanbul Convention.
"The Istanbul Convention - also known as the Council of Europe convention ...
Novel coronavirus discovered in British bats
2021-07-19
A coronavirus related to the virus that causes Covid-19 in humans has been found in UK horseshoe bats - according to new collaborative research from the University of East Anglia, ZSL (Zoological Society of London), and Public Health England (PHE).
However, there is no evidence that this novel virus has been transmitted to humans, or that it could in future, unless it mutates.
UEA researchers collected faecal samples from more than 50 lesser horseshoe bats in Somerset, Gloucestershire and Wales and sent them for viral analysis at Public Health England.
Genome sequencing found a novel coronavirus in one of the bat samples, which the team have named 'RhGB01'.
It is the first time that a sarbecovirus ...
New Zealand drug agency provides model to insulate NICE from impacts of trade deals
2021-07-19
UK policymakers preparing trade deals post-Brexit can learn important lessons from New Zealand's 'unique drug agency' the Pharmaceutical Management Agency (PHARMAC), if prices for therapies and access to key drugs are to be protected, say researchers behind a new study.
Over two decades, New Zealand has managed to reduce spending on drugs significantly and consistently despite maintaining access for its population to key treatments. As such, it is an outlier among the world's richest nations: no other OECD country has managed to achieve this.
The investigation from researchers at the universities of Bath and Durham suggest New Zealand's ...
Survey shows rise in vaccine hesitancy in Ghana
2021-07-19
Research led by the University of Southampton into the uptake of the COVID-19 vaccine in Ghana, West Africa has concluded that vaccine hesitancy has seen a small, but significant increase over the last three months. This research is in collaboration with youth-led not-for-profit organisation PACKS Africa.
In the latest survey of 1,295 unvaccinated people, in May/June 2021, willingness to be vaccinated remained relatively high at just over 71.4 percent. However, this figure is down 11 percent on results from March 2021 when an earlier version of the same survey was conducted.
The latest findings show 28.6 percent of respondents are still either undecided or unwilling to get the jab. Among this 28.6 percent group, a little over half said ...
Championing chrononutrition with protein, the morning elixir for muscle growth
2021-07-19
Proteins constitute an essential dietary component that help in the growth and repair of the body. Composed of long chains of amino acids, proteins promote the growth of skeletal muscles, the group of muscles that help us move. Humans have been aware of the benefits of proteins for long. However, recent studies have shown that having the right amount of protein at the right time of the day is essential for proper growth. This is called 'Chrononutrition,' in which when you eat is as important as what and how you eat.
The reason behind this is the body's internal biological clock, called the 'circadian rhythm.' This rhythm is followed by all cells and controls life functions like metabolism and growth. Interestingly, protein digestion and absorption have been ...
Mechanisms to separately regulate synaptic vesicle release and recycling
2021-07-19
Chemical synapses transmit information within the nervous system. When a presynaptic cell is electrically excited, synaptic vesicles fuse with the presynaptic membrane causing messenger substances within the vesicles to be released into the synaptic cleft. These then bind to receptors in the postsynaptic cell where they trigger an electrical signal once again. The temporal and spatial sequence of the incoming signals determines how information is processed and transmitted in the brain. In order to sustain their function in the long term, chemical synapses need to recycle synaptic vesicles to make them available for renewed signal transmission. Professor Carsten Duch and Professor Martin Heine and their respective ...
An automated flight control system for drone swarms has been developed
2021-07-19
"The project's main objective is to integrate a certain degree of automation, so that an operator can control a small fleet of up to 10 drones from a single ground station," says Luis E. Moreno, LABYRINTH's coordinator and researcher at the UC3M's Robotics Lab. "The idea is that the operator indicates the mission to be undertaken (for example, monitoring traffic in a particular area) and the system automatically converts this mission into a set of routes that each drone has to follow, automatically calculating alternative routes when necessary," he explains. In addition ...
Unsustainable Arctic shipping risks accelerating damage to the Arctic environment
2021-07-19
The economic and environmental pros and cons of melting Arctic ice creating shorter shipping routes through the polar region are weighed up in ground-breaking research from UCL experts in energy and transport.
They conclude that policy makers must properly assess the environmental trade-offs and costs in addition to the commercial benefits and opportunities in Arctic shipping. The authors also want to see more incentives to drive technological developments that will accelerate the uptake of green fuels and technologies.
The Arctic is the fastest-warming region on the planet.
Shorter Arctic shipping routes, which mean less fuel used are already used by a handful of ships, when areas of the Arctic ice melt ...
No stone unturned: An extensive search for cation substitution in lithium-ion batteries
2021-07-19
Ishikawa, Japan - Powering everything from smartphones to electric cars, lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have evolved markedly with advances in technology and revolutionized our world. The next step in the progress of technology is developing even better batteries to power electronic devices for longer durations. One promising technique for increasing battery performance involves the atomic substitution of positively charged ions or "cations" in the cathode material. However, doing so systematically for different substituent cations to determine the ideal ones experimentally is complex and expensive, leaving us with simulations as the only viable option for narrowing down the choices.
Several studies have reported an improved battery life and ...
uOttawa study first to investigate newly introduced butterfly which could become widespread in Canada
2021-07-19
This summer, if you see a butterfly with wings that are blue on top with orange spots underneath, you may have crossed paths with a male European Common Blue (or Polyommatus icarus), a newly introduced species in Canada.
Could it be a fluke? Probably not, according to a group of researchers from the University of Ottawa who have taken a close look at this captivating blue creature. They are in fact the first to study its ecology.
"The results of our study suggest that the Polyommatus icarus (P. icarus) could become widespread in the future since it prefers urban areas," said uOttawa PhD student Stephanie Rivest, who is the first ...
Cosmic rays help supernovae explosions pack a bigger punch
2021-07-19
The final stage of cataclysmic explosions of dying massive stars, called supernovae, could pack an up to six times bigger punch on the surrounding interstellar gas with the help of cosmic rays, according to a new study led by researchers at the University of Oxford. The work will be presented by PhD student Francisco Rodríguez Montero today (19 July) at the virtual National Astronomy Meeting (NAM 2021).
When supernovae explode, they emit light and billions of particles into space. While the light can freely reach us, particles become trapped in spiral loops by magnetic shockwaves generated during the explosions. Crossing back and forth through shock fronts, these particles are accelerated almost to the speed of light and, on escaping the supernovae, are thought ...
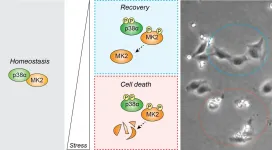
To die or not to die in response to stress, a decision regulated by MK2 protein levels
2021-07-19
Living organisms are often exposed to stress stimuli generated either by external or internal factors, and they need to respond accordingly. At a cellular level, stress usually triggers the activation of survival pathways that contribute to the recovery of cell homeostasis. However, when stress is too high, a process of cell death is initiated that eliminates the damaged cell.
Scientists led by ICREA researcher Dr. Angel Nebreda, head of the Signalling and Cell Cycle laboratory at IRB Barcelona, have identified an important role of the p38-MK2 pathway in determining cell fate in response to stress.
"Our ...
Novel techniques extract more accurate data from images degraded by environmental factors
2021-07-19
Computer vision technology is increasingly used in areas such as automatic surveillance systems, self-driving cars, facial recognition, healthcare and social distancing tools. Users require accurate and reliable visual information to fully harness the benefits of video analytics applications but the quality of the video data is often affected by environmental factors such as rain, night-time conditions or crowds (where there are multiple images of people overlapping with each other in a scene). Using computer vision and deep learning, a team of researchers led by Yale-NUS College Associate Professor of Science (Computer Science) Robby Tan, who is also from the National University of Singapore's (NUS) Faculty of Engineering, ...
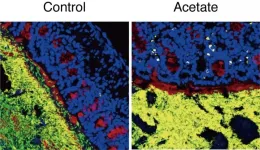
A simple compound to control complex gut microbes
2021-07-19
Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences (IMS) have discovered that acetate, a major metabolite produced by some intestinal bacteria, is involved in regulating other intestinal bacteria. Specifically, experiments showed that acetate could trigger an immune response against potentially harmful bacteria. The findings, published in the scientific journal Nature, will lead to the development of new ways to regulate the balance of intestinal bacteria.
You may be surprised to know that 40 trillion important bacteria live in our intestines. They help keep us healthy by producing essential nutrients and eliminating foreign pathogens. On the other ...
High respiratory efforts in COVID-19 patients could result in self-inflicted lung injury
2021-07-19
Some COVID-19 patients who experience acute respiratory failure respond by significantly increasing their respiratory effort - breathing faster and more deeply
There is concern among some doctors that this level of respiratory effort can lead to further damage to these patients' lungs.
Working with an international team of leading intensive care clinicians, engineering researchers at the University of Warwick have used computational modelling to provide new evidence that high respiratory efforts in COVID-19 patients can produce pressures and strains inside the lung that can result in injury.
The impact of high breathing efforts on the lungs of patients suffering with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19 ...
At last: Separated and freshly bound
2021-07-19
The carbon-hydrogen bonds in alkanes--particularly those at the ends of the molecules, where each carbon has three hydrogen atoms bound to it--are very hard to "crack" if you want to replace the hydrogen atoms with other atoms. Methane (CH(4)) and ethane (CH(3)CH(3)) are made up, exclusively, of such tightly bound hydrogen atoms. In the journal Angewandte Chemie, a team of researchers has now described how they break these bonds while forming new carbon-nitrogen bonds (amidation).
If it were possible to easily break the C-H bonds in hydrocarbons, it would be possible to synthesize complex organic ...
Kids' sleep: check in before you switch off
2021-07-19
The struggle to get your child to go to sleep and stay asleep is something most parents can relate to. Once the bedtime battle is over and the kids have finally nodded off, many parents tune out as well.
But University of South Australia researcher Professor Kurt Lushington is calling for parents to check on their small snoozers before switching off.
He says knowing the quality of a child's sleep is important, as it could be an indicator of sleep-disordered breathing - an under-reported medical condition that can affect a child's health and wellbeing.
"During sleep, the muscles keeping the upper airway stiff relax, and as a consequence, the airway narrows, which ...
Scientists adopt deep learning for multi-object tracking
2021-07-19
Computer vision has progressed much over the past decade and made its way into all sorts of relevant applications, both in academia and in our daily lives. There are, however, some tasks in this field that are still extremely difficult for computers to perform with acceptable accuracy and speed. One example is object tracking, which involves recognizing persistent objects in video footage and tracking their movements. While computers can simultaneously track more objects than humans, they usually fail to discriminate the appearance of different objects. This, in turn, can lead to the algorithm to mix up objects in a scene and ultimately produce incorrect tracking results.
At the Gwangju Institute of Science ...
Bats in Tel Aviv enjoy the rich variety and abundance of food the city has to offer
2021-07-19
A new Tel Aviv University study found that, like humans, bats living in Tel Aviv enjoy the wide variety and abundance of food that the city has to offer, in contrast to rural bats living in Beit Guvrin, who are content eating only one type of food. The study was led by research student Katya Egert-Berg, under the guidance of Prof. Yossi Yovel, head of Tel Aviv University's Sagol School of Neuroscience and a faculty member of the School of Zoology in the George S. Wise Faculty of Life Sciences and the Steinhardt Museum of Natural History, as well as a recipient of the 2021 Kadar Family Award for Outstanding ...
July issues of American Psychiatric Association journals
2021-07-19
The July issues of two of the American Psychiatric Association journals, The American Journal of Psychiatry and Psychiatric Services are available online.
The American Journal of Psychiatry is the most widely read psychiatric journal in the world. Its July issue offers a collection of articles discussing the impacts of structural racism, socioeconomic deprivation and stigmatization on mental health. This includes the article From Womb to Neighborhood: A Racial Analysis of Social Determinants of Psychosis in the United States, which was featured at the APA Annual Meeting in May. Among other highlights:
Dismantling Structural Racism in Psychiatry: A Path to Mental Health Equity
Modification of Heritability for Educational Attainment and Fluid Intelligence by Socioeconomic ...
[1] ... [2122]
[2123]
[2124]
[2125]
[2126]
[2127]
[2128]
[2129]
2130
[2131]
[2132]
[2133]
[2134]
[2135]
[2136]
[2137]
[2138]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.