Learning aids: Skoltech method helps train computer vision algorithms on limited data
2021-07-15
Researchers from Skoltech have found a way to help computer vision algorithms process satellite images of the Earth more accurately even with very limited data for training. This will make various remote sensing tasks easier for machines and ultimately the people who use their data. The paper outlining the new results was published in the journal Remote Sensing.
Researchers have been using computer vision and machine learning techniques to help with environmental monitoring for a while now. Tasks that may seem tedious and prone to human error are normally a piece of cake for algorithms. But before a neural network can successfully, say, discriminate between the kinds of trees in a forested area, it needs to be trained, ...
High daily screen time linked to cognitive, behavioral problems in children born extremely preterm
2021-07-15
WHAT:
Among 6- and 7-year-olds who were born extremely preterm--before the 28th week of pregnancy--those who had more than two hours of screen time a day were more likely to have deficits in overall IQ, executive functioning (problem solving skills), impulse control and attention, according to a study funded by the National Institutes of Health. Similarly, those who had a television or computer in their bedrooms were more likely to have problems with impulse control and paying attention. The findings suggest that high amounts of screen time may ...
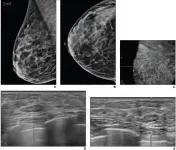
Routine screening for BI-RADS lesions on automated whole-breast ultrasound
2021-07-15
Leesburg, VA, July 15, 2021--According to ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), return to routine screening for BI-RADS 3 lesions on supplemental automated whole-breast US (ABUS) substantially reduces the recall rate, while being unlikely to result in adverse outcome.
"This prospective study supports a recommendation for routine annual follow-up for BI-RADS 3 lesions at supplemental ABUS," wrote lead author Richard G. Barr of Northeastern Ohio Medical University in Rootstown.
From August 2013 to December 2016, Barr and colleagues' prospective study (NCT02650778) ...
"Get out of the water!" Monster shark movies massacre shark conservation
2021-07-15
Undeniably the shark movie to end all shark movies, the 1975 blockbuster, Jaws, not only smashed box office expectations, but forever changed the way we felt about going into the water - and how we think about sharks.
Now, more than 40 years (and 100+ shark movies) on, people's fear of sharks persists, with researchers at the University of South Australia concerned about the negative impact that shark movies are having on conservation efforts of this often-endangered animal.
In a world-first study, conservation psychology researchers, UniSA's Dr Briana Le Busque and Associate Professor Carla Litchfield ...
Modified yeast inhibits fungal growth in plants
2021-07-15
About 70-80% of crop losses due to microbial diseases are caused by fungi. Fungicides are key weapons in agriculture's arsenal, but they pose environmental risks. Over time, fungi also develop a resistance to fungicides, leading growers on an endless quest for new and improved ways to combat fungal diseases.
The latest development takes advantage of a natural plant defense against fungus. In a paper published in Biotechnology and Bioengineering, engineers and plant pathologists at UC Riverside describe a way to engineer a protein that blocks fungi from breaking down cell walls, as well as a way to produce this protein in quantity for external application as a natural fungicide. The work could lead to a new way of controlling plant disease that reduces reliance on conventional ...
Emotion, cooperation and locomotion crucial from an early age
2021-07-15
What are the fundamental skills that young children need to develop at the start of school for future academic success? While a large body of research shows strong links between cognitive skills (attention, memory, etc.) and academic skills on the one hand, and emotional skills on the other, in students from primary school to university, few studies have explored these links in children aged 3 to 6 in a school context. Researchers from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and Valais University of Teacher Education, Switzerland (HEP-VS), in collaboration with teachers from Savoie in France and their pedagogical advisor, examined the links between emotion knowledge, cooperation, locomotor activity and numerical skills in 706 pupils aged 3 to 6. The results, to be read in the journal ...
Human waste contaminating urban water leads to 'superbug' spread -- study
2021-07-15
Contamination of urban lakes, rivers and surface water by human waste is creating pools of 'superbugs' in Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMIC) - but improving access to clean water, sanitation and sewerage infrastructure could help to protect people's health, a new study reveals.
Researchers studied bodies of water in urban and rural sites in three areas of Bangladesh - Mymensingh, Shariatpur and Dhaka. They found more antibiotic resistant faecal coliforms in urban surface water compared to rural settings, consistent with reports of such bacteria in rivers across Asia.
Publishing their findings in mSystems today, researchers from the University of Birmingham and the International Centre for Diarrhoeal Disease Research, Bangladesh call for further research to quantify the drivers ...
Hopkins Med news update
2021-07-15
COVID-19 NEWS: CAN DIETARY SUPPLEMENTS HELP THE IMMUNE SYSTEM FIGHT CORONAVIRUS INFECTION?
Media Contact: Patrick Smith, pjsmith88@jhmi.edu
Johns Hopkins Medicine gastroenterologist Gerard Mullin, M.D., and a team of co-authors published an article May 11, 2021, in Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology that details the scientific rationale and possible benefits -- as well as possible drawbacks -- of several dietary supplements currently in clinical trials related to COVID-19 treatment.
According to business analysts, the U.S. nutritional supplement industry grew as much as 14.5% in 2020, due in large part to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Mullin, associate professor of medicine at the Johns Hopkins University ...
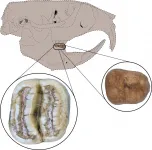
Fossil rodent teeth add North American twist to Caribbean mammals' origin story
2021-07-15
GAINESVILLE, Fla. --- Two fossil teeth from a distant relative of North American gophers have scientists rethinking how some mammals reached the Caribbean Islands.
The teeth, excavated in northwest Puerto Rico, belong to a previously unknown rodent genus and species, now named Caribeomys merzeraudi. About the size of a mouse, C. merzeraudi is the Caribbean's smallest known rodent and one of the region's oldest, dating back about 29 million years.
It also represents the first discovery of a Caribbean rodent from a North American lineage, a finding that complicates an idea ...
Early intervention in schools needed to address Malta's obesity crisis
2021-07-15
A new study by the University of Malta and Staffordshire University highlights an urgent need for change in the curriculum and demonstrates how introducing longer, more frequent and more physically intense PE lessons can significantly improve children's weight and overall health.
Malta currently has one of the highest rates of obesity worldwide with 40% of primary and 42.6% of secondary school children being overweight or obese.
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that children engage in at least 60 minutes of age-appropriate moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) daily, however ...
On the front lines: Correctional nurses and the COVID-19 pandemic
2021-07-15
New Rochelle, NY, July 14, 2021-Firsthand reports from nurses in correctional facilities detail the challenges they faced during the COVID-19 pandemic. These firsthand accounts are reported in a special issue on correctional nursing in the Journal of Correctional Health Care. Click here (https://www.liebertpub.com/toc/jchc/27/2) to read the issue now.
Karen Monsen, PhD, RN, School of Nursing, University of Minnesota, and colleagues present the Omaha System COVID-19 Response Guidelines, which provide evidence-based pandemic response interventions used in correctional ...
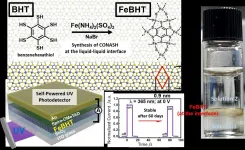
Unlocking efficient light-energy conversion with stable coordination nanosheets
2021-07-15
Converting light to electricity effectively has been one of the persistent goals of scientists in the field of optoelectronics. While improving the conversion efficiency is a challenge, several other requirements also need to be met. For instance, the material must conduct electricity well, have a short response time to changes in input (light intensity), and, most importantly, be stable under long-term exposure.
Lately, scientists have been fascinated with "coordination nanosheets" (CONASHs), that are organic-inorganic hybrid nanomaterials in which organic molecules are bonded to metal atoms in a 2D network. The interest in CONASHs stems mainly from their ability to absorb light at multiple wavelength ranges and convert ...
Life-saving snake venom
2021-07-15
Indiana Jones hates snakes. And he's certainly not alone. The fear of snakes is so common it even has its own name: ophidiophobia.
Kibret Mequanint doesn't particularly like the slithery reptiles either (he actually hates them too) but the Western University bioengineer and his international collaborators have found a novel use for snake venom: a body tissue 'super glue' that can stop life-threatening bleeding in seconds.
Over the past 20 years, Mequanint has developed a number of biomaterials-based medical devices and therapeutic technologies - some of which are either licensed to medical companies or are in the advanced stage of preclinical testing.
His latest collaborative research discovery ...
Engineers find imaging technique could become treatment for deep vein thrombosis
2021-07-15
Penn State College of Engineering researchers set out to develop technology capable of localizing and imaging blood clots in deep veins. Turns out their work may not only identify blood clots, but it may also be able to treat them.
The team, led by Scott Medina, assistant professor of biomedical engineering, published its results in Advance Healthcare Materials.
"Deep vein thrombosis is the formation of blood clots in deep veins, typically in a person's legs," said Medina. "It's a life-threatening blood clotting condition that, if left unaddressed, can cause deadly pulmonary embolisms -- when the clot travels to the lungs and blocks an artery. To manage DVT, and prevent these life-threating complications, it's critical to be able to rapidly detect, monitor and treat it."
The ...
New research at ESMT Berlin shows potential variance in academic research
2021-07-15
The research seeks to understand what drives decisions in data analyses and the process through which academics test a hypothesis by comparing the analyses of different researchers who tested the same hypotheses on the same dataset. Analysts reported radically different analyses and dispersed empirical outcomes, including, in some cases, significant effects in opposite directions from each other. Decisions about variable operationalizations explained the lack of consistency in results beyond statistical choices (i.e., which analysis or covariates to use).
"Our findings illustrate the importance of analytical choices and how different statistical methods can lead to different conclusions," says Martin Schweinsberg. ...
New guidance on how to diagnosis and manage osteoporosis in chronic kidney disease
2021-07-15
Patients with advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD) typically suffer from impaired bone quality and quantity, with a non-vertebral fracture risk which is 4-to 6-fold higher than the fracture risk of matched controls. However, despite their high risk of fragility fractures, the vast majority of patients with chronic CKD stages 4 to 5D, are not receiving osteoporosis therapy.
A newly published review by the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) and European Renal Association-European Dialysis and Transplant Association (ERA-EDTA) CKD-MBD working group now provides concise recommendations, with a clear management algorithm, to support clinicians' knowledge and confidence in managing ...
Antihypertension drug may help patients with noncancerous brain tumors affecting hearing
2021-07-15
BOSTON - New research led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and Massachusetts Eye and Ear indicates that the blood pressure drug losartan may benefit patients with neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2), a hereditary condition associated with vestibular schwannomas, or noncancerous tumors along the nerves in the brain that are involved with hearing and balance. The findings, which are published in Science Translational Medicine, are especially important because vestibular schwannomas are currently treated with surgery and radiation therapy (which carry risks of nerve damage), and no drug is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat these tumors or their associated hearing ...
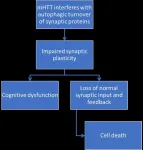
Autophagy may be the key to finding treatments for early Huntington's disease
2021-07-15
Amsterdam, July 15, 2021 - Huntington's Disease (HD) is a progressive neurodegenerative condition characterized by motor, cognitive, and psychiatric symptoms, and motor symptoms are often preceded by cognitive changes. Recent evidence indicates that autophagy plays a central role in synaptic maintenance, and the disruption in autophagy may be at the root of these early cognitive changes. Understanding this mechanism better may help researchers develop treatments for patients with HD early in their disease progression, report scientists in a review article published in the Journal of Huntington's Disease.
In this review, experts describe how autophagy, the cellular process responsible ...
What does the sleeping brain think about?
2021-07-15
We sleep on average one third of our time. But what does the brain do during these long hours? Using an artificial intelligence approach capable of decoding brain activity during sleep, scientists at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, were able to glimpse what we think about when we are asleep. By combining functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electroencephalography (EEG), the Geneva team provides unprecedented evidence that the work of sorting out the thousands of pieces of information processed during the day takes place during ...
Wolf pups born on Isle Royale, moose poised for decline
2021-07-15
The COVID-19 pandemic halted the in-person wintertime survey of wolves and moose on the island for the first time in 63 years. Consequently, there are no estimates of wolf or moose abundance for 2021, and the next estimates are scheduled in February 2022. But though the Isle Royale Winter Study didn't happen quite as planned, researchers were still able to visit the remote national park in the spring.
Now, fieldwork has resumed and Michigan Technological University researchers have already uncovered new information about these two iconic wildlife populations. In particular, wolves produced at least two litters of pups, and moose appear poised for decline.
In the Isle Royale Winter Study, Michigan ...
A genome of photosynthetic animals decoded
2021-07-15
Plants, algae and some bacteria are able to perform photosynthesis, which is the process of transforming sunlight energy into sugar. Animals are generally unable to use this process to acquire energy, but there are a few known exceptions to this. Some sea slugs take up chloroplasts from the algae that they consume into their cells. These chloroplasts retain their ability to perform photosynthetic activity within the animal cells for several months, and thus provide them with photosynthesis-derived nutrition. This process is called "kleptoplasty", and it has attracted much attention due to its amazing uniqueness in making animals photosynthetic for over 50 years.
A pressing question is how these sequestered chloroplasts retains their photosynthetic capability without algal nuclei. ...
Visibly transparent radiative cooler under direct sunlight
2021-07-15
Since the Paris Climate Agreement that took effect in 2016, 121 countries have pledged to become carbon neutral by 2050 as the world tries to reduce its fuel consumption. The Korean government also unveiled its 2050 Carbon Neutral Strategy on December 7, 2020 and declared Carbon Zero, making transition to new and renewable energy a topic of conversation. Recently, a joint research team from POSTECH and Korea University has developed a radiative cooling material that can reduce energy consumption by selectively reflecting or transmitting sunlight.
A research team led by Professor Junsuk Rho, Ph.D. candidate Minkyung Kim, and Dr. Dasol Lee of POSTECH's departments of mechanical engineering and chemical engineering, and a team led by Professor Heon Lee and Soomin of the Department of Materials ...
Study shows strong association between perceived risk, availability and past-year cannabis use
2021-07-15
Combined perceptions of the risk and availability of cannabis influence the risk of cannabis use more than perceived risk and perceived availability alone, according to a new study at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. Researchers observed that those who perceived cannabis as low-risk and available were more likely to report using the drug in the past year and almost daily compared to those individuals who perceived cannabis as high-risk and unavailable. This is the first study to consider the joint effects of perceived risk and perceived availability. The results are published in the journal Drug and Alcohol Dependence.
"Our study described the evolution of joint perceptions of cannabis risk and availability from 2002-2018 and estimated the relationship between combined ...
Study finds adolescent girls and young women in Africa will use HIV prevention products
2021-07-15
Adolescent girls and young women can and will use HIV prevention products with consistency, according to interim results of a study of two different methods: daily use of the antiretroviral (ARV) tablet Truvada® as oral pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and the monthly END ...
UBCO researchers light the way to cleaner water
2021-07-15
Shining a beam of light into potentially contaminated water samples may hold the key to real-time detection of hydrocarbons and pesticides in water.
UBC Okanagan researchers are testing the use of fluorescence to monitor water quality. The results, they say, show great promise.
When a beam of light is shone into the water, it excites the electrons in molecules of certain compounds and causes them to emit light. The characteristics of the emitted light are like a fingerprint and can be used to identify certain contaminants, explains Nicolas Peleato, an assistant professor at UBCO's School of Engineering.
"The challenge with using this fluorescence approach is that ...
[1] ... [2128]
[2129]
[2130]
[2131]
[2132]
[2133]
[2134]
[2135]
2136
[2137]
[2138]
[2139]
[2140]
[2141]
[2142]
[2143]
[2144]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.