Physicists describe sun's electric field
2021-07-14
As the Parker Solar Probe ventures closer to the sun, we are learning new things about our home star.
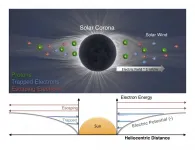
In a new study, physicists led by the University of Iowa report the first definitive measurements of the sun's electric field, and how the electric field interacts with the solar wind, the fast-flowing current of charged particles that can affect activities on Earth, from satellites to telecommunications.
The physicists calculated the distribution of electrons within the sun's electric field, a feat made possible by the fact that the Parker Solar Probe jetted within 0.1 astronomical units (AU), or a mere 9 million miles, from the sun--closer than any spacecraft has approached. From the electrons' distribution, the physicists ...
Hard to swallow: Coral cells seen engulfing algae for first time
2021-07-14
For the first time, scientists have seen stony coral cells engulf dinoflagellates - single-celled, photosynthetic algae that are crucial for keeping coral alive
The researchers used a cell line called IVB5, which contains endoderm-like cells cultured from the stony coral, Acropora tenuis
Around 40% of coral cells incorporated the algae in around 30 minutes and remained healthy for one month
The research is a step towards understanding the partnership between coral and dinoflagellates and could shed light on how coral bleaching occurs
In a world-first, scientists in Japan have observed individual stony coral cells engulfing single-celled, photosynthetic algae.
The microscopic algae, known as dinoflagellates, were ...
COVID precautions may result in more breast cancer deaths
2021-07-14
A new paper in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, published by Oxford University Press, indicates that disruptions in health care due to the COVID 19 pandemic may increase breast cancer deaths.
In March 2020 public health measures prohibited most elective procedures, including mammography, due to hospital capacity and limited personal protective equipment. This reduced mammograms up to 80%. Breast cancer patients also experienced treatment delays and reductions in planned or expected chemotherapy treatments.
Researchers here used three independently-developed breast cancer simulation models from the National Cancer Institute's Cancer Intervention and Surveillance Modeling Network to ...
Study finds "thriving gap" between students who attend high school remotely vs. in person
2021-07-14
Washington/Philadelphia, July 14, 2021--New research finds that high school students who attended school remotely during the COVID-19 pandemic suffered socially, emotionally, and academically compared with those who attended in person.
The study was published today in Educational Researcher (ER) by researchers Angela L. Duckworth, Tim Kautz, Amy Defnet, Emma Satlof-Bedrick, Sean Talamas, Benjamin Lira, and Laurence Steinberg. ER is a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association.
"Many news stories have reported on individual stories of teenagers who have suffered from anxiety, depression, and other mental health challenges during the pandemic," said lead author Duckworth, ...
Oncotarget: CEA as a blood-based biomarker in anal cancer
2021-07-14
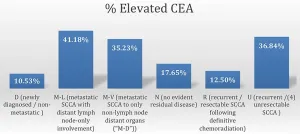
Oncotarget published "CEA as a blood-based biomarker in anal cancer" which reported that the mean Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) among subgroups by clinical status at the time of presentation to our institution was highest among those patients with metastatic Squamous cell carcinoma of the anal canal (SCCA) to visceral organs, however this finding was not statistically significant by ANOVA .
By clinical subgroup, the percentage of patients with an abnormally elevated CEA was highest in those patients with metastatic disease to lymph nodes followed by recurrent/unresectable SCCA , and metastatic SCCA ...
A history of drug dependence is associated with negative mental health outcomes
2021-07-14
New research published online in the International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction found that Canadians with a history of drug dependence are much less likely to have flourishing mental health and are more likely to have mental illness.
Researchers compared a nationally representative sample of 460 Canadians with a history of illicit drug dependence (excluding cannabis) to 20,305 Canadians with no history of illicit drug dependence using data drawn from Statistic Canada's Canadian Community Health Survey-Mental Health.
While 80% of those with a history of drug dependence were in remission, more than half (52.1%) were still experiencing mental illness. Further, only 37.9% were in excellent mental health, which is markedly lower than the 74.1% of ...
Unlike other global crises, COVID-19 pandemic did not spark more smoking in its initial stage
2021-07-14
Unlike other population-level stressful events such as natural disasters, COVID-19 has not resulted in a net increase in smoking, according to a new study from the International Tobacco Control (ITC) Project, at the University of Waterloo.
The researchers also found that although nearly half of smokers reported that COVID-19 made them think about quitting, the vast majority of smokers did not change their smoking habits during the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Led by Shannon Gravely, research assistant professor with the ITC Project, the study ...
How does the world use emojis?
2021-07-14
Before Millennials were over laugh-cry emojis, they were the most used emojis across the world, according to researchers at USC. The emoji was more popular than smiley faces say researchers who categorized millions of tweets across 30 countries and evaluated over 1700 emojis. Their study, "An empirical study of emoji usage on Twitter in linguistic and national contexts" was published in Online Social Networks and Media.
Mayank Kejriwal, a research assistant professor in the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering, and a research lead at the USC Information Sciences Institute who is the lead author on the paper, says approximately 100 emojis are used most often.
The most important take away? Emojis represent ...
Lateral flow tests are 95% effective at detecting Covid-19 when used at the onset of symptoms
2021-07-14
A new study by researchers at Queen Mary University of London, University of Oxford, Institute for Advanced Studies, Vienna, and the Medical University of Graz, has found that lateral flow tests detect Covid-19 with similar accuracy to laboratory-based PCR tests, providing they are used at the onset of infection and soon after symptoms start.
Lateral flow tests are cheaper and produce a result in just 30 minutes - much faster than the time it takes to receive a PCR test result, which can take 1-3 days. The finding could be pivotal to national strategies ...
DNA from 1,600-year-old Iranian sheep mummy brings history to life
2021-07-14
A team of geneticists and archaeologists from Ireland, France, Iran, Germany, and Austria has sequenced the DNA from a 1,600-year-old sheep mummy from an ancient Iranian salt mine, Chehrābād. This remarkable specimen has revealed sheep husbandry practices of the ancient Near East, as well as underlining how natural mummification can affect DNA degradation.
The incredible findings have just been published in the international, peer-reviewed journal Biology Letters.
The salt mine of Chehrābād is known to preserve biological material. Indeed, it is in this mine that human remains of the famed "Salt Men" were recovered, dessicated by the salt-rich environment. The ...
Survival for babies born with a birth defect - a "post-code lottery"
2021-07-14
Survival for a baby born with a birth defect - otherwise known as a congenital anomaly - is a "post-code lottery", according to scientists from 74 countries.
A study published today in The Lancet, led by researchers from King's College London, examined the risk of mortality for nearly 4000 babies born with birth defects in 264 hospitals around the world. The study found babies born with birth defects involving the intestinal tract have a two in five chance of dying in a low-income country compared to one in five in a middle-income country and one in twenty in a high-income country.
Gastroschisis, a birth defect where the baby is born with ...
The Lancet Onc.: Alcohol consumption linked to more than 740,000 new cancer cases in 2020
2021-07-14
A global study provides up-to-date estimates for the effect of alcohol consumption on cancers worldwide. It suggests that 4% of all newly diagnosed cancers in 2020 may be associated with drinking alcohol, with men accounting for more than three quarters of those cases.
Risky and heavy drinking was estimated to contribute the highest number of cancer cases, but moderate drinking - the equivalent of around two daily drinks - was estimated to lead to more than 103,000 cases in 2020, almost 1 in 7 of all alcohol-associated cases.
The proportion of new cancer cases associated with alcohol varied widely between world regions, with the lowest found in Northern Africa and Western Asia, and the highest in ...
Early anticoagulant treatment shown to reduce death in moderately ill COVID-19 patients
2021-07-14
COVID-19 is marked by heightened inflammation and abnormal clotting in the blood vessels, particularly in the lungs, and is believed to contribute to progression to severe disease and death. New trial results show that administering a full dose of a standard blood thinner early to moderately ill hospitalized patients with COVID-19 could halt the thrombo-inflammation process and reduce the risk of severe disease and death.
The study, led by investigators at St. Michael's Hospital, a site of Unity Health Toronto, and the University of Vermont Larner College of Medicine, is available as ...
Impairments found in neurons derived from people with schizophrenia and genetic mutation
2021-07-14
A scientific team has shown that the release of neurotransmitters in the brain is impaired in patients with schizophrenia who have a rare, single-gene mutation known to predispose people to a range of neurodevelopmental disorders.
Significantly, the results from the research with human-derived neurons validated previous and new experiments that found the same major decrease in neurotransmitter release and synaptic signaling in genetically engineered human neurons with the same genetic variant - the deletion of neurexin 1 (NRXN1). NRXN1 is a protein-coding gene at the synapse, a cellular junction that ...
Baylor study evaluates biodiversity impacts of alternative energy strategies
2021-07-14
WACO, Texas (July 13, 2021) - Climate change mitigation efforts have led to shifts from fossil-fuel dependence to large-scale renewable energy. However, renewable energy sources require significant land and could come at a cost to ecosystems. A new study led by Ryan McManamay, Ph.D., assistant professor of environmental science at Baylor University, evaluates potential conflicts between alternative energy strategies and biodiversity conservation.
The study, published in Biological Conservation, evaluates potential tradeoffs between climate benefits ...
Financial barriers fell for some cancer survivors after Affordable Care Act
2021-07-13
Cancer survivors ages 18 to 64 faced fewer financial barriers to health care after the Affordable Care Act was implemented than they did before the landmark law took effect, University of Michigan researchers found.
In fact, they believe the ACA helped the financial burden (problems related to the cost of medical care) for younger cancer survivors fall to its lowest estimated levels in 20 years.
"There has been a lot of talk about the ACA affecting people who don't have the Medicare safety net," said Christopher Su, M.D., a clinical fellow in the division of hematology and oncology at Michigan Medicine and the first author of the paper. "We were able to drill down to that and show that it did make a difference to younger cancer ...
Study assesses the prevalence of mental illness during the pandemic among folks aged 50-80
2021-07-13
The COVID-19 pandemic and the situations of stress and sadness associated with it have not significantly increased the prevalence of depression and anxiety among participants in the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brazil) who live in the city of São Paulo.
ELSA-Brazil has been monitoring the overall health of 15,000 civil servants at six public universities and research centers in Brazil since 2008. The survey on mental health during the pandemic was conducted in São Paulo and involved 2,117 members of the staff of the University of São Paulo (USP) - in active service or retired - who are participants in the nationwide study and aged 50-80.
The survey is supported by São Paulo Research Foundation ...
From 'distress' to 'unscathed' -- mental health of UW students during spring 2020
2021-07-13
In early March 2020, the University of Washington became the first four-year U.S. university to transition to online-only classes due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Many researchers predicted severe consequences of these physical distancing measures. To understand how this change affected college students' mental health, UW researchers surveyed 147 UW students over the 2020 spring quarter, which began shortly after the university transitioned to online-only classes. The team compared the students' responses to a previous survey of 253 students in spring quarter 2019.
The researchers didn't see much change in average levels of students' depressive symptoms, anxiety, stress or loneliness between 2019 and 2020 or between the beginning and the end of spring quarter ...
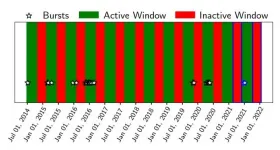
Galactic gamma ray bursts predicted last year show up right on schedule
2021-07-13
Magnetars are bizarre objects -- massive, spinning neutron stars with magnetic fields among the most powerful known, capable of shooting off brief bursts of radio waves so bright they're visible across the universe.
A team of astrophysicists has now found another peculiarity of magnetars: They can emit bursts of low energy gamma rays in a pattern never before seen in any other astronomical object.
It's unclear why this should be, but magnetars themselves are poorly understood, with dozens of theories about how they produce radio and gamma ray bursts. The recognition of this unusual pattern of gamma ray activity ...
Bacteria are key to vaginal health, UArizona health sciences researchers say
2021-07-13
Bacterial vaginosis is the most common and recurrent gynecological condition affecting nearly 30% of women between the ages of 15 and 44, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. A University of Arizona Health Sciences-led study recently identified a specific bacteria family and uncovered how it contributes to bacterial vaginosis, paving the way for new insights into disease prevention and treatment.
Led by Melissa Herbst-Kralovetz, PhD, a member of the BIO5 Institute and associate professor of basic medical sciences at the College of Medicine - Phoenix, researchers found that members of the Veillonellaceae bacteria family contribute to an increase in inflammation and cell death, and alter the acidity of the cervical microenvironment. These changes support bacterial ...
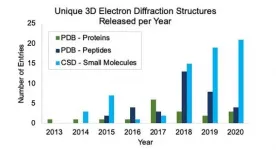
Microcrystal electron diffraction supports a new drug development pipeline
2021-07-13
CAMBRIDGE July 13, 2021 - To date, solving structures of potential therapeutics using X-ray diffraction (XRD) has been an assumed, pivotal step in the drug development process. But a recent paper by a team of researchers led by NanoImaging Services shows how microcrystal electron diffraction (MicroED) is growing to obtain the structures of potential pharmaceuticals.
Three-dimensional crystal structures that show the relative positions of atoms, bonds and intramolecular interactions are needed to understand stability, reactivity, solubility and, ultimately, suitability ...
COVID-19 hospitalization and mortality: Sex differences
2021-07-13
New Rochelle, NY, July 13, 2021--Males with COVID-19 had significantly higher rates of hospitalization and of transfer to the intensive care unit (ICU) according to a new study. A higher percentage of males died of COVID-19 compared to females, as reported in the study published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Women's Health. Click here to read the article now.
Joanne Michelle Gomez, MD, Rush University Medical Center, and coauthors, studied the first 8,108 positive COVID-19 patients that presented to the Rush University System from March 1-June 21, 2020. Nineteen percent of males required hospitalization, compared to 13% of females. ...
"Long COVID": More than a quarter of COVID-19 patients still symptomatic after 6 months
2021-07-13
In a new study of adults from the general population who were infected with COVID-19 in 2020, more than a quarter report not having fully recovered after six to eight months. Those findings are described this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Milo Puhan and colleagues at the University of Zurich, Switzerland.
While initial public health responses to the SARS-CoV-2 virus focused on reducing the acute burden of COVID-19, a growing body of evidence indicates that the infection can also result in longer-term physical and mental health consequences. These long-term consequences, currently referred to as "post-COVID-19 syndrome" or "Long Covid" are ...
Allocating COVID-19 vaccines based on health and socioeconomics could reduce mortality
2021-07-13
COVID-19 vaccination strategies in the United States are informed by individual characteristics such as age and occupation. A study published in the open access journal PLOS Medicine by Sasikiran Kandula and Jeffrey Shaman of Columbia University, New York, United States suggests that including socioeconomic indicators as prioritization criteria for vaccination may help minimize severe outcomes, particularly deaths.
Efforts to reduce COVID-19 mortality rates in the US have focused on prioritizing vaccination initially for those at a higher risk of severe outcomes. The effectiveness of population-level ...
Allocating COVID vaccines based on health and socioeconomic factors could cut mortality
2021-07-13
An estimated 43 percent of the variability in U.S. COVID-19 mortality is linked with county-level socioeconomic indicators and health vulnerabilities, with the strongest association seen in the proportions of people living with chronic kidney disease and living in nursing homes. The study by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health researchers suggests that allocating vaccines based on these factors could help minimize severe outcomes, particularly deaths. Results are published in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine.
"It is well known that COVID-19 deaths are concentrated in communities with underlying ...
[1] ... [2135]
[2136]
[2137]
[2138]
[2139]
[2140]
[2141]
[2142]
2143
[2144]
[2145]
[2146]
[2147]
[2148]
[2149]
[2150]
[2151]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.