Giving a "tandem" boost to solar-powered water splitting
2021-07-12
Turning away from fossil fuels is necessary if we are to avert an environmental crisis due to global warming. Both industry and academia have been focusing heavily on hydrogen as a feasible clean alternative. Hydrogen is practically inexhaustible and when used to generate energy, only produces water vapor. However, to realize a truly eco-friendly hydrogen society, we need to be able to mass-produce hydrogen cleanly in the first place.
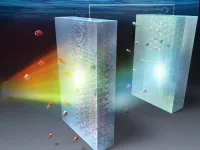
One way to do that is by splitting water via "artificial photosynthesis," a process in which materials called "photocatalysts" leverage solar energy to produce oxygen and hydrogen from water. However, the available photocatalysts are not yet where they need to be to make solar-powered water splitting economically feasible and scalable. ...
Theoretical model able to reliably predict low-temperature properties of compounds
2021-07-12
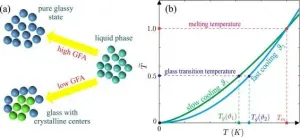
Co-authors Bulat Galimzyanov and Anatolii Mokshin (Department of Computational Physics) have developed a unique model that allows for a universal interpretation of experimental data on viscosity for systems of different types, while also proposing an alternative method for classifying materials based on a unified temperature scale.
The publication was funded by Russian Science Foundation's grant 'Theoretical, simulation and experimental studies of physical and mechanical features of amorphous systems with inhomogeneous local viscoelastic properties', guided by Professor Mokshin.
Using the developed viscosity model, scientists processed experimental data obtained for thirty different ...
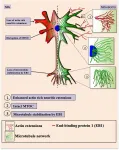
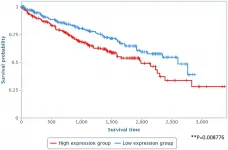
Study sheds light on precise personalized hepatocellular carcinoma medicine
2021-07-12
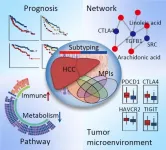
A research group led by Prof. PIAO Hailong from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) identified hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) subtypes with distinctive metabolic phenotypes through bioinformatics and machine learning methods, and elucidated the potential mechanisms based on a metabolite-protein interaction network and multi-omics data.
The study, published in Advanced Science on July 11, provides insights guiding precise personalized HCC medicine.
Metabolic reprogramming, which can promote rapid cell proliferation by regulating energy and nutrient metabolism, is considered to be one hallmark of cancer. It can impact other biological processes through complex metabolite-protein ...
Want to avoid running overuse injuries? Don't lean forward so much, says CU Denver study
2021-07-12
The ubiquitous overuse injuries that nag runners may stem from an unlikely culprit: how far you lean forward.
Trunk flexion, the angle at which a runner bends forward from the hip, can range wildly--runners have self-reported angles of approximately -2 degrees to upward of 25. A new study from the END ...
Heart risk 'calculators' overlook increased risk for people of South Asian ancestry
2021-07-12
DALLAS, July 12, 2021 -- People of South Asian ancestry have more than double the risk of developing heart disease compared to people of European ancestry, yet clinical risk assessment calculators used to guide decisions about preventing or treating heart disease may fail to account for the increased risk, according to new research published today in the American Heart Association's flagship journal Circulation.
About a quarter of the world's population (1.8 billion people) are of South Asian descent, and prior research has shown South Asians experience higher rates of heart disease compared to people of most other ethnicities.
To better understand the variables surrounding the heart disease risk for people of South Asian ancestry, researchers evaluated ...
Innovative gene therapy 'reprograms' cells to reverse neurological deficiencies
2021-07-12
A novel method of gene therapy is helping children born with a rare genetic disorder called AADC deficiency that causes severe physical and developmental disabilities. The study, led by researchers at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and The Ohio State University College of Medicine, offers new hope to those living with incurable genetic and neurodegenerative diseases.
Research findings are published online in the journal Nature Communications.
This study describes the findings from the targeted delivery of gene therapy to midbrain to treat a rare ...
USC researchers discover better way to identify DNA variants
2021-07-12
USC researchers have achieved a better way to identify elusive DNA variants responsible for genetic changes affecting cell functions and diseases.
Using computational biology tools, scientists at the university's Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences studied "variable-number tandem repeats" (VNTR) in DNA. VNTRs are stretches of DNA made of a short pattern of nucleotides repeated over and over, like a plaid pattern shirt. Though they comprise but 3% of the human genome, the repetitive DNA governs how some genes are encoded and levels of proteins are produced in a cell, and account for most of the structural variation.
Current methods do not accurately detect the variations in genes in some repetitive ...
Scientists blueprint bacterial enzyme believed to "stealthily" suppress immune response
2021-07-12
Scientists have produced the first fine-detail molecular blueprints of a bacterial enzyme known as Lit, which is suspected to play a "stealthy" role in the progression of infection by reducing the immune response.
Blueprints such as these allow drug designers to uncover potential weaknesses in bacterial arsenals as they seek to develop new therapeutics that may help us win the war against antibiotic resistance.
The study, led by scientists from the School of Biochemistry and Immunology and the Trinity Biomedical Sciences Institute (TBSI) at Trinity College Dublin, has just been published by leading international journal Nature Communications.
Lipoproteins and their role in ...
A Trojan horse could help get drugs past our brain's tough border patrol
2021-07-12
Sclerosis, Parkinson's Disease, Alzheimer's and epilepsy are but a few of the central nervous system disorders. They are also very difficult to treat, since the brain is protected by the blood-brain barrier.
The blood-brain barrier works as a border wall between the blood and the brain, allowing just certain molecules to enter the brain. And whereas water and oxygen can get through, as can other substances such as alcohol and coffee. But it does block more than 99 percent of potentially neuroprotective compounds from reaching their targets in the brain.
Now, ...
Just 25 mega-cities produce 52% of the world's urban greenhouse gas emissions
2021-07-12
In 2015, 170 countries worldwide adopted the Paris Agreement, with the goal limiting the average global temperature increase to 1.5°C. Following the agreement, many countries and cities proposed targets for greenhouse gas mitigation. However, the UNEP Emissions Gap Report 2020 shows that, without drastic and strict actions to mitigate the climate crisis, we are still heading for a temperature increase of more than 3°C by the end of the 21st century.
A new study published in the journal Frontiers in Sustainable Cities presents the first global balance sheet of greenhouse gasses (GHGs) emitted by major cities around the world. The aim was to research and monitor the effectiveness of historical GHG reduction ...
Addressing social needs may help mitigate distress and improve the health of women with cancer
2021-07-12
A new study published by Wiley early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society, has identified unmet social needs in women with gynecologic cancer that could be addressed to improve care for patients and lessen disparities. For example, identifying patients who reported needing help with reading hospital materials resulted in the use of a cancer care navigator who provided patient education and support, facilitating physician-patient communication and adherence to care recommendations.
The prospective survey-based ...
Oncotarget: Inhibitory effects of Tomivosertib in acute myeloid leukemia
2021-07-12
Oncotarget published "Inhibitory effects of Tomivosertib in acute myeloid leukemia" which reported that the authors evaluated the therapeutic potential of the highly-selective MNK1/2 inhibitor Tomivosertib on AML cells.
Tomivosertib was highly effective at blocking eIF4E phosphorylation on serine 209 in AML cells.
Moreover, combination of Tomivosertib and Venetoclax resulted in synergistic anti-leukemic responses in AML cell lines.
Mass spectrometry studies identified novel putative MNK1/2 interactors, while in parallel studies we demonstrated that MNK2 - RAPTOR - mTOR complexes are not disrupted by Tomivosertib.
Overall, these Oncotarget findings demonstrate that Tomivosertib exhibits potent ...
Oncotarget: Modulating Tau Post-translational modifications and cytoskeletal network
2021-07-12
Oncotarget published "Epigallocatechin-3-gallate modulates Tau Post-translational modifications and cytoskeletal network" which reported that the chemical modulators of Tau PTMs, such as kinase inhibitors and antibody-based therapeutics, have been developed, but natural compounds, as modulators of Tau PTMs are not much explored.
These authors applied biophysical and biochemical techniques like fluorescence kinetics, oligomerization analysis and transmission electron microscopy to investigate the impact of EGCG on Tau glycation in vitro.
EGCG inhibited methyl glyoxal -induced Tau glycation in vitro.
EGCG potently inhibited MG-induced advanced glycation endproducts formation in neuroblastoma cells as well modulated the localization ...
Oncotarget: LAPAS1 is required for S phase progression and cell proliferation
2021-07-12
Oncotarget published "A novel E2F1-regulated lncRNA, LAPAS1, is required for S phase progression and cell proliferation" which reported that long non-coding RNAs are major regulators of many cellular processes, including cell cycle progression and cell proliferation.
Inhibition of LAPAS1 expression increases the percentage of S phase cells, and its silencing in synchronized cells delays their progression through S phase.
In agreement with its suggested role in cell cycle progression, prolonged inhibition of LAPAS1 attenuates proliferation of human cancer cells.
Importantly, knockdown of SPNS2 rescues the effect of LAPAS1 silencing on cell cycle ...
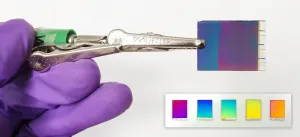
New electronic paper displays brilliant colours
2021-07-12
Imagine sitting out in the sun, reading a digital screen as thin as paper, but seeing the same image quality as if you were indoors. Thanks to research from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, it could soon be a reality. A new type of reflective screen - sometimes described as 'electronic paper' - offers optimal colour display, while using ambient light to keep energy consumption to a minimum.
Traditional digital screens use a backlight to illuminate the text or images displayed upon them. This is fine indoors, but we've all experienced the difficulties of viewing such screens in bright sunshine. Reflective screens, however, attempt to use the ambient light, mimicking the way our eyes ...
Protein appears to prevent tumor cells from spreading via blood vessels
2021-07-12
Researchers have identified a specialized protein that appears to help prevent tumor cells from entering the bloodstream and spreading to other parts of the body.
"We have discovered that this protein, TRPM7, senses the pressure of fluid flowing in the circulation and stops the cells from spreading through the vascular system," said Kaustav Bera, a Johns Hopkins University PhD candidate in chemical and biomolecular engineering and a lead author of the study, which was done with colleagues at the University of Alberta and Universitat Pompeu Fabra.
"We found that metastatic tumor cells have markedly reduced levels of this sensor protein, and that is why they ...
Monitoring proves better than active treatment for low-risk prostate cancer
2021-07-12
Men over 60 with low-risk prostate cancer could spend ten years with no active treatment, have a better sex life as a result, yet still be very unlikely to die from the disease, new research has found.
The findings come from two new studies looking at 'active surveillance' of prostate cancer - when the disease is closely monitored but not treated - presented at the European Association of Urology congress, EAU21, today.
The first uses data from Sweden's National Prostate Cancer Register, which has information on virtually every man diagnosed with the disease in that country since 1998 - 23,649 of whom went on active surveillance. ...
Care home residents are at risk of COVID-19 even after being fully vaccinated
2021-07-12
Care homes need to be vigilant for outbreaks of COVID-19, even after residents have received two doses of the vaccine, according to new research being presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) held online this year.
Long-term care facilities, such as care homes with elderly residents with multiple underlying conditions, are at high risk of COVID-19 outbreaks and many vaccination campaigns have initially focused on care home residents and the staff looking after them. An outbreak in a French care home, however, raises questions about how effective the vaccine is in the elderly.
Martin Martinot, of ...
Outbreaks of COVID-19 in French nursing homes traced back to staff
2021-07-12
COVID-19 outbreaks in French nursing homes almost certainly started in staff - and none of measures put in place stopped the virus from taking hold, new research being presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID), held online this year, shows.
Residents of long-term care facilities represent a small fraction of the general population but account for a disproportionate number of SARS-CoV-2-related deaths in many countries.
In France, 5,203 outbreaks (of 1 case or more) were reported in nursing homes during the first wave of COVID-19. In the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region, there were 651 outbreaks, 3,885 residents had confirmed COVID-19 infection and 1,772 ...
Flu jab protects against some of the severe effects of COVID-19, including
2021-07-12
The flu vaccine may provide vital protection against COVID-19, new research being presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID), held online this year, concludes.
An analysis of patient data from around the world strongly suggests that the annual flu shot reduces the risk of stroke, sepsis and DVT in patients with COVID-19. Patients with COVID-19 who had been vaccinated against flu were also less likely to visit the emergency department and be admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU).
Immunising the world against COVID-19 is a daunting challenge and, although production and distribution of vaccines increases daily, some countries are not expected to vaccinate large numbers of their population ...
Hepatitis C vaccine could be rolled out within five years, says Nobel Prize winner who discovered virus
2021-07-12
A vaccine to protect against infection with hepatitis C could be in use within 5 years, says Professor Sir Michael Houghton, who won the Nobel Prize for Medicine and Physiology along with three other scientists for discovering the hepatitis C virus (HCV) in 1989. Sir Michael will discuss the development of a vaccine in a special presentation at this year's European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID), held online this year.
Up to 2 million new HCV infections occur every year around the world, with an estimated 70 million carriers of the virus globally, most of whom are not diagnosed. The virus is estimated to cause some 400,000 deaths annually. Many infected with the virus go on to develop liver cirrhosis and liver cancer.
"While the advent of ...
High-tech toilets could spread antibiotic-resistant superbugs in hospitals, Japanese study suggests
2021-07-12
Water-jet nozzles in electric toilets--commonly used in Japan and other parts of Asia--may be reservoirs for multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MDRP) in hospitals, increasing the risk of dangerous germ transmission among patients, according to new research being presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) held online this year.
"This is the first report of hospital transmissions associated with electric toilets and could have major implications for infection control," says Dr Itaru Nakamura from Tokyo Medical University Hospital ...
New study shows that silver foil could reduce the risk of infection in hospitals
2021-07-12
New research presented at this year's European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) taking place online (9-12 July) shows that covering high-touch (the most regularly touched) surfaces in hospitals with silver-impregnated foil could significantly reduce levels of contamination by clinically important bacterial pathogens.
The study by Professor Andreas Widmer and colleagues at the University Hospital Basel, Basel, Switzerland, evaluated the antimicrobial effectiveness of a polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foil containing an integrated silver-based agent containing 2% silver ions.
The hospital environment has increasingly been recognised as having critical importance when formulating infection control measures ...
Obesity increases survival in advanced prostate cancer
2021-07-11
Obese patients with a form of advanced prostate cancer survive longer than overweight and normal weight patients, new research has found.
The study, presented today at the European Association of Urology congress, EAU21, followed more than 1500 patients over three years. Patients classed as obese - with a BMI over 30 - had a ten percent higher survival rate than thinner patients over 36 months.
Although obesity is usually associated with an increased risk of death from many cancers and some other chronic diseases, there is some evidence in a few cancers of a survival advantage for patients with high body mass index. ...
Beautiful VR setting could reduce pain in unpleasant medical procedure
2021-07-11
Being immersed in a stunning 'virtual' Icelandic landscape can reduce the pain caused by uncomfortable medical procedures, new research has found.
The study compared patients with and without virtual reality (VR) headsets having rigid cystoscopies, where a rigid telescope is inserted through the urethra into the bladder. The research is being presented today at the European Association of Urology congress, EAU21.
Diagnosing and treating bladder cancer usually requires checking the bladder through a cystoscopy, which is perceived by patients as unpleasant and painful. Some patients avoid follow-up and as a result suffer uncontrolled and irreversible development of the disease. It is possible to have a flexible cystoscopy, which is less painful, ...
[1] ... [2131]
[2132]
[2133]
[2134]
[2135]
[2136]
[2137]
[2138]
2139
[2140]
[2141]
[2142]
[2143]
[2144]
[2145]
[2146]
[2147]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.