DNA from 1,600-year-old Iranian sheep mummy brings history to life
2021-07-14
A team of geneticists and archaeologists from Ireland, France, Iran, Germany, and Austria has sequenced the DNA from a 1,600-year-old sheep mummy from an ancient Iranian salt mine, Chehrābād. This remarkable specimen has revealed sheep husbandry practices of the ancient Near East, as well as underlining how natural mummification can affect DNA degradation.
The incredible findings have just been published in the international, peer-reviewed journal Biology Letters.
The salt mine of Chehrābād is known to preserve biological material. Indeed, it is in this mine that human remains of the famed "Salt Men" were recovered, dessicated by the salt-rich environment. The ...
Survival for babies born with a birth defect - a "post-code lottery"
2021-07-14
Survival for a baby born with a birth defect - otherwise known as a congenital anomaly - is a "post-code lottery", according to scientists from 74 countries.
A study published today in The Lancet, led by researchers from King's College London, examined the risk of mortality for nearly 4000 babies born with birth defects in 264 hospitals around the world. The study found babies born with birth defects involving the intestinal tract have a two in five chance of dying in a low-income country compared to one in five in a middle-income country and one in twenty in a high-income country.
Gastroschisis, a birth defect where the baby is born with ...
The Lancet Onc.: Alcohol consumption linked to more than 740,000 new cancer cases in 2020
2021-07-14
A global study provides up-to-date estimates for the effect of alcohol consumption on cancers worldwide. It suggests that 4% of all newly diagnosed cancers in 2020 may be associated with drinking alcohol, with men accounting for more than three quarters of those cases.
Risky and heavy drinking was estimated to contribute the highest number of cancer cases, but moderate drinking - the equivalent of around two daily drinks - was estimated to lead to more than 103,000 cases in 2020, almost 1 in 7 of all alcohol-associated cases.
The proportion of new cancer cases associated with alcohol varied widely between world regions, with the lowest found in Northern Africa and Western Asia, and the highest in ...
Early anticoagulant treatment shown to reduce death in moderately ill COVID-19 patients
2021-07-14
COVID-19 is marked by heightened inflammation and abnormal clotting in the blood vessels, particularly in the lungs, and is believed to contribute to progression to severe disease and death. New trial results show that administering a full dose of a standard blood thinner early to moderately ill hospitalized patients with COVID-19 could halt the thrombo-inflammation process and reduce the risk of severe disease and death.
The study, led by investigators at St. Michael's Hospital, a site of Unity Health Toronto, and the University of Vermont Larner College of Medicine, is available as ...
Impairments found in neurons derived from people with schizophrenia and genetic mutation
2021-07-14
A scientific team has shown that the release of neurotransmitters in the brain is impaired in patients with schizophrenia who have a rare, single-gene mutation known to predispose people to a range of neurodevelopmental disorders.
Significantly, the results from the research with human-derived neurons validated previous and new experiments that found the same major decrease in neurotransmitter release and synaptic signaling in genetically engineered human neurons with the same genetic variant - the deletion of neurexin 1 (NRXN1). NRXN1 is a protein-coding gene at the synapse, a cellular junction that ...
Baylor study evaluates biodiversity impacts of alternative energy strategies
2021-07-14
WACO, Texas (July 13, 2021) - Climate change mitigation efforts have led to shifts from fossil-fuel dependence to large-scale renewable energy. However, renewable energy sources require significant land and could come at a cost to ecosystems. A new study led by Ryan McManamay, Ph.D., assistant professor of environmental science at Baylor University, evaluates potential conflicts between alternative energy strategies and biodiversity conservation.
The study, published in Biological Conservation, evaluates potential tradeoffs between climate benefits ...
Financial barriers fell for some cancer survivors after Affordable Care Act
2021-07-13
Cancer survivors ages 18 to 64 faced fewer financial barriers to health care after the Affordable Care Act was implemented than they did before the landmark law took effect, University of Michigan researchers found.
In fact, they believe the ACA helped the financial burden (problems related to the cost of medical care) for younger cancer survivors fall to its lowest estimated levels in 20 years.
"There has been a lot of talk about the ACA affecting people who don't have the Medicare safety net," said Christopher Su, M.D., a clinical fellow in the division of hematology and oncology at Michigan Medicine and the first author of the paper. "We were able to drill down to that and show that it did make a difference to younger cancer ...
Study assesses the prevalence of mental illness during the pandemic among folks aged 50-80
2021-07-13
The COVID-19 pandemic and the situations of stress and sadness associated with it have not significantly increased the prevalence of depression and anxiety among participants in the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brazil) who live in the city of São Paulo.
ELSA-Brazil has been monitoring the overall health of 15,000 civil servants at six public universities and research centers in Brazil since 2008. The survey on mental health during the pandemic was conducted in São Paulo and involved 2,117 members of the staff of the University of São Paulo (USP) - in active service or retired - who are participants in the nationwide study and aged 50-80.
The survey is supported by São Paulo Research Foundation ...
From 'distress' to 'unscathed' -- mental health of UW students during spring 2020
2021-07-13
In early March 2020, the University of Washington became the first four-year U.S. university to transition to online-only classes due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Many researchers predicted severe consequences of these physical distancing measures. To understand how this change affected college students' mental health, UW researchers surveyed 147 UW students over the 2020 spring quarter, which began shortly after the university transitioned to online-only classes. The team compared the students' responses to a previous survey of 253 students in spring quarter 2019.
The researchers didn't see much change in average levels of students' depressive symptoms, anxiety, stress or loneliness between 2019 and 2020 or between the beginning and the end of spring quarter ...
Galactic gamma ray bursts predicted last year show up right on schedule
2021-07-13
Magnetars are bizarre objects -- massive, spinning neutron stars with magnetic fields among the most powerful known, capable of shooting off brief bursts of radio waves so bright they're visible across the universe.
A team of astrophysicists has now found another peculiarity of magnetars: They can emit bursts of low energy gamma rays in a pattern never before seen in any other astronomical object.
It's unclear why this should be, but magnetars themselves are poorly understood, with dozens of theories about how they produce radio and gamma ray bursts. The recognition of this unusual pattern of gamma ray activity ...
Bacteria are key to vaginal health, UArizona health sciences researchers say
2021-07-13
Bacterial vaginosis is the most common and recurrent gynecological condition affecting nearly 30% of women between the ages of 15 and 44, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. A University of Arizona Health Sciences-led study recently identified a specific bacteria family and uncovered how it contributes to bacterial vaginosis, paving the way for new insights into disease prevention and treatment.
Led by Melissa Herbst-Kralovetz, PhD, a member of the BIO5 Institute and associate professor of basic medical sciences at the College of Medicine - Phoenix, researchers found that members of the Veillonellaceae bacteria family contribute to an increase in inflammation and cell death, and alter the acidity of the cervical microenvironment. These changes support bacterial ...
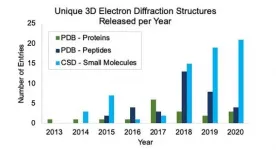
Microcrystal electron diffraction supports a new drug development pipeline
2021-07-13
CAMBRIDGE July 13, 2021 - To date, solving structures of potential therapeutics using X-ray diffraction (XRD) has been an assumed, pivotal step in the drug development process. But a recent paper by a team of researchers led by NanoImaging Services shows how microcrystal electron diffraction (MicroED) is growing to obtain the structures of potential pharmaceuticals.
Three-dimensional crystal structures that show the relative positions of atoms, bonds and intramolecular interactions are needed to understand stability, reactivity, solubility and, ultimately, suitability ...
COVID-19 hospitalization and mortality: Sex differences
2021-07-13
New Rochelle, NY, July 13, 2021--Males with COVID-19 had significantly higher rates of hospitalization and of transfer to the intensive care unit (ICU) according to a new study. A higher percentage of males died of COVID-19 compared to females, as reported in the study published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Women's Health. Click here to read the article now.
Joanne Michelle Gomez, MD, Rush University Medical Center, and coauthors, studied the first 8,108 positive COVID-19 patients that presented to the Rush University System from March 1-June 21, 2020. Nineteen percent of males required hospitalization, compared to 13% of females. ...
"Long COVID": More than a quarter of COVID-19 patients still symptomatic after 6 months
2021-07-13
In a new study of adults from the general population who were infected with COVID-19 in 2020, more than a quarter report not having fully recovered after six to eight months. Those findings are described this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Milo Puhan and colleagues at the University of Zurich, Switzerland.
While initial public health responses to the SARS-CoV-2 virus focused on reducing the acute burden of COVID-19, a growing body of evidence indicates that the infection can also result in longer-term physical and mental health consequences. These long-term consequences, currently referred to as "post-COVID-19 syndrome" or "Long Covid" are ...
Allocating COVID-19 vaccines based on health and socioeconomics could reduce mortality
2021-07-13
COVID-19 vaccination strategies in the United States are informed by individual characteristics such as age and occupation. A study published in the open access journal PLOS Medicine by Sasikiran Kandula and Jeffrey Shaman of Columbia University, New York, United States suggests that including socioeconomic indicators as prioritization criteria for vaccination may help minimize severe outcomes, particularly deaths.
Efforts to reduce COVID-19 mortality rates in the US have focused on prioritizing vaccination initially for those at a higher risk of severe outcomes. The effectiveness of population-level ...
Allocating COVID vaccines based on health and socioeconomic factors could cut mortality
2021-07-13
An estimated 43 percent of the variability in U.S. COVID-19 mortality is linked with county-level socioeconomic indicators and health vulnerabilities, with the strongest association seen in the proportions of people living with chronic kidney disease and living in nursing homes. The study by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health researchers suggests that allocating vaccines based on these factors could help minimize severe outcomes, particularly deaths. Results are published in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine.
"It is well known that COVID-19 deaths are concentrated in communities with underlying ...
Global study reveals effectiveness of protected areas
2021-07-13
Researchers have conducted a global study on the effectiveness of recently established protected areas in preventing forest loss
The study explores protected area performance by countries, with South Africa, Cambodia, Latvia, Guatemala, Uruguay, Brazil and New Zealand leading the way in the effectiveness of their protected areas
The research team estimated that overall, protected areas established between 2000-2012 prevented 86,062 square kilometers of forest loss
If all countries had protected areas that were as effective as their top-performing neighbor, then an additional 33,020 square kilometers of forests would have been saved
Machine learning found that agricultural ...
Species of gut bacteria linked to enhanced cognition and language skills in infant boys
2021-07-13
The University of Alberta-led research followed more than 400 infants from the CHILD Cohort Study (CHILD) at its Edmonton site. Boys with a gut bacterial composition that was high in the bacteria Bacteroidetes at one year of age were found to have more advanced cognition and language skills one year later. The finding was specific to male children.
"It's well known that female children score higher (at early ages), especially in cognition and language," said Anita Kozyrskyj, a professor of pediatrics at the U of A and principal investigator of the SyMBIOTA (Synergy in Microbiota) laboratory. "But when it comes to gut microbial ...
Air pollution exposure linked to poor academics in childhood
2021-07-13
Children exposed to elevated levels of air pollution may be more likely to have poor inhibitory control during late childhood and poor academic skills in early adolescence, including spelling, reading comprehension, and math skills. Difficulty with inhibition in late childhood was found to be a precursor to later air pollution-related academic problems. Interventions that target inhibitory control might improve outcomes.
Results of the study by researchers at the Columbia Center for Children's Environmental Health (CCCEH) at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and Columbia University Irving Medical Center are published in the journal Environmental ...
Lesbian, gay, bisexual smokers are at a higher risk for smoking menthol cigarettes
2021-07-13
Compared with heterosexual smokers, menthol cigarette smoking is higher among lesbian, gay and bisexual cigarette smokers, according to a Rutgers-led study, especially among bisexual and lesbian/gay female cigarette smokers.
The study, published in the journal Nicotine & Tobacco Research, examined national data from 2015 to 2019 of individuals ages 18 years and older by sex and sexual identity and found that among smokers, 54 and 50 percent of bisexual and lesbian/gay females smokers preferred menthol cigarettes, respectively, compared with 39 percent of smokers overall.
This study comes in the wake of plans by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to ban menthol cigarettes; a move that researchers say is ...
5D imaging of ultrafast phenomena
2021-07-13
Information-rich optical imaging can provide multidimensional information to enable observation and analysis of a detected target, contributing insights into mysterious and unknown worlds. With its ability to capture dynamic scenes on picosecond—and even femtosecond—timescales, ultrafast multidimensional optical imaging has important applications in the detection of the ultrafast phenomena in physics, chemistry, and biology.
While pump-probe-based ultrafast imaging can acquire high-resolution multidimensional information, it cannot adequately capture unstable or irreversible transient scenes. Fortunately, compressed ultrafast photography (CUP), based ...
Rats prefer to help their own kind; humans may be similarly wired
2021-07-13
A decade after scientists discovered that lab rats will rescue a fellow rat in distress, but not a rat they consider an outsider, new research from the University of California, Berkeley, pinpoints the brain regions that drive rats to prioritize their nearest and dearest in times of crisis. It also suggests humans may share the same neural bias.
The findings, published today, Tuesday, July 13, in the journal eLife, suggest that altruism, whether in rodents or humans, is motivated by social bonding and familiarity rather than sympathy or guilt.
"We have found that the group identity ...
Long-term memory setup requires a reliable delivery crew
2021-07-13
JUPITER, FL - The brain is wired for learning. With each experience, our neurons branch out to make new connections, laying down the circuitry of our long-term memories. Scientists call this trait plasticity, referring to an ability to adapt and change with experience.
For plasticity to happen, our neurons' synapses, or connection points, must constantly remodel and adapt, too. The mechanics underlying neurons' synaptic plasticity have become clearer, thanks to new research from the lab of Scripps Research neuroscientist Sathya Puthanveettil, PhD.
Scientists have learned that synaptic plasticity requires a complex relay from the neuron's cell body to its dendrite arms and its synapse junctions. Like a 24-hour port and highway network, an internal ...
Farm marketing success linked to natural, cultural assets
2021-07-13
ITHACA, N.Y. - Direct farm marketing efforts, such as farmers markets and roadside stands, are more successful in communities with more nonprofits, social enterprises and creative industries, according to a team including Cornell University researchers, who created a nationwide database of assets to help municipalities craft community-specific development plans.
While many municipalities seek to encourage direct-to-consumer (DTC) marketing - an important factor in farmers' livelihoods - the success of their efforts hinges on a wide array of community resources, or capital assets, with natural and cultural ...
The two-thousand-year-old mystery of the havoc-wreaking worm
2021-07-13
AMHERST, Mass. - Humans have known for over two thousand years that shipworms, a worm-like mollusk, are responsible for damage to wooden boats, docks, dikes and piers. Yet new research from the University of Massachusetts Amherst published in Frontiers in Microbiology reveals that we still don't know the most basic thing about them: how they eat.
"It's unbelievable," says Reuben Shipway, adjunct assistant professor in microbiology at UMass Amherst, research fellow at the Centre for Enzyme Innovation at the University of Portsmouth, UK, and one of the paper's authors. "The ancient Greeks wrote about them, Christopher Columbus lost his fleet due to what he called 'the havoc which the worm had wrought,' and, today, shipworms cause billions of dollars of damage a year."
Shipworms ...
[1] ... [2114]
[2115]
[2116]
[2117]
[2118]
[2119]
[2120]
[2121]
2122
[2123]
[2124]
[2125]
[2126]
[2127]
[2128]
[2129]
[2130]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.