Employed individuals more likely to contract the flu, study shows
2021-06-30
A University of Arkansas researcher and international colleagues found that employed individuals, on average, are 35.3% more likely to be infected with the flu virus.
The findings confirm a long-held assumption about one prevalent way illness spreads and could influence government policy on public health and several issues for private companies, from optimal design and management of physical work spaces to policy decisions about sick leave and remote work.
To track influenza incidence, Dongya "Don" Koh, assistant professor of economics in the Sam M. Walton College of Business, and colleagues relied on nationally representative data from the Medical ...
College students experience significant grief reactions during global pandemic
2021-06-30
A new study shows that colleges students are experiencing significant grief reactions in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. The paper, "College Student Experiences of Grief and Loss Amid the COVID-19 Global Pandemic," was recently published in OMEGA - Journal of Death and Dying.
"This study aimed to identify the most common non-death losses and grief reactions experienced by undergraduate and graduate college students amid the pandemic," said author Erica H. Sirrine, Ph.D., director of Social Work at St. Jude Children's Research Hospital. "What we found is that students ...
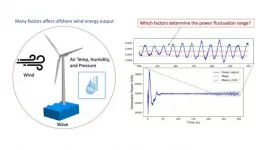
Researchers create better method to predict offshore wind power
2021-06-30
New Brunswick, N.J. (June 28, 2021) - Rutgers researchers have developed a machine learning model using a physics-based simulator and real-world meteorological data to better predict offshore wind power.
The findings appear in the journal Applied Energy.
Offshore wind is rapidly maturing into a major source of renewable energy worldwide and is projected to grow by 13% in the next two decades and 15-fold by 2040 to become a $1 trillion industry, matching capital spending on gas- and coal-fired power generation. In the United States, for instance, New York and New Jersey recently awarded two offshore ...
Rattlesnakes may like climate change
2021-06-30
When it comes to climate change, not all organisms will lose out. A new Cal Poly study finds that rattlesnakes are likely to benefit from a warming climate.
A combination of factors makes a warming climate beneficial to rattlesnakes that are found in almost every part of the continental United States but are especially common in the Southwest.
Rattlers are experts at thermoregulation. Researchers found that, when given a choice, the snakes prefer a body temperature of 86-89 degrees Fahrenheit, a much warmer temperature than they generally experience in nature. The average ...
Reducing need for blood transfusion during heart surgery is focus of new practice guideline
2021-06-30
CHICAGO (June 30, 2021) -- Four leading medical specialty societies released a new clinical practice guideline today that includes recommendations for reducing blood loss during heart surgery and improving patient outcomes. The document, a multidisciplinary collaboration among The Society of Thoracic Surgeons, the Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists, the American Society of ExtraCorporeal Technology, and the Society for the Advancement of Patient Blood Management, is available online in The Annals of Thoracic Surgery and two other journals.
"As medicine evolves and we learn more, it always is important to review past ...
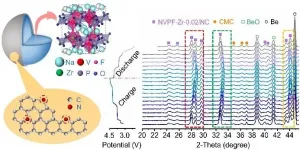
In-situ structural evolution of Zr-doped Na<sub>3</sub>V<sub>2</sub>(PO<sub>4</sub>)<sub>2</sub>F<sub>3</sub> coated by N-doped carbon for SIB
2021-06-30
Na3V2(PO4)2F3(NVPF), a cathode material used in sodium-ion batteries (SIB), features ultrafast Na+ migration and high structural stability because of its three-dimensional open framework. However, the poor intrinsic electronic conductivity of NVPF often leads to high polarization, low Coulombic efficiency, and unsatisfactory rate performance, which hinder its commercial application.
Recently, a group led by Prof. Shuangqiang Chen and Prof. Yong Wang from Shanghai University synthesized zirconium-doped NVPF nanoparticles coated with a nitrogen-doped ...
Breakthrough for tracking RNA with fluorescence
2021-06-30
Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, have succeeded in developing a method to label mRNA molecules, and thereby follow, in real time, their path through cells, using a microscope - without affecting their properties or subsequent activity. The breakthrough could be of great importance in facilitating the development of new RNA-based medicines.
RNA-based therapeutics offer a range of new opportunities to prevent, treat and potentially cure diseases. But currently, the delivery of RNA therapeutics into the cell is inefficient. For new therapeutics to fulfil ...
Slowing down grape ripening can improve berry quality for winemaking
2021-06-30
Wine grapes are particularly finicky when it comes to their environment. For instance, heatwaves and droughts lead to earlier berry ripening and lackluster wine. And these types of episodes are expected to intensify as Earth's climate changes. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry have tweaked growing conditions for Cabernet Sauvignon grapes to slow down their ripening, which increased the levels of compounds associated with wine's characteristic floral and fruity notes.
As grapes ripen and change color from light green to deep red, sugars and aroma compounds accumulate in the berries. But, when they ripen quickly because of heat or water stress, the resulting fruits produce ...
Discovery of the role of a key gene in the development of ALS
2021-06-30
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS, attacks nerve cells known as motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord, gradually leading to paralysis. The loss of function of an important gene, C9orf72, may affect communication between motor neurons and muscles in people with this disease. These findings were revealed by the team of Dr Kessen Patten of the Institut national de la recherche scientifique (INRS) in the prestigious journal Communications Biology.
A mutation in the C9orf72 gene is the primary genetic cause of ALS. The mutation in C9orf72 consists of an expansion of a sequence of six DNA bases (GGGGCC) that is very unusual, going from a few copies (less than 20 in a healthy person) to more than 1000 copies. The mutation, in part resulting in a loss of function, ...
The Southern diet - fried foods and sugary drinks - may raise risk of sudden cardiac death
2021-06-30
DALLAS, June 30, 2021 -- Regularly eating a Southern-style diet may increase the risk of sudden cardiac death, while routinely consuming a Mediterranean diet may reduce that risk, according to new research published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an open access journal of the American Heart Association.
The Southern diet is characterized by added fats, fried foods, eggs, organ meats (such as liver or giblets), processed meats (such as deli meat, bacon and hotdogs) and sugar-sweetened beverages. The Mediterranean diet is high in fruits, vegetables, fish, whole grains and legumes and low in meat and dairy.
"While this study was observational in nature, the results suggest that diet may be a modifiable risk factor for sudden cardiac death, and, therefore, diet ...
Diaries of infection preventionists give inside look at the unsung heroes of the pandemic
2021-06-30
Arlington, Va., June 30, 2021 - Much has been rightfully made of the valiant work of doctors and nurses during the coronavirus pandemic. But what of infection preventionists (IP), whose job was to keep those workers and their facilities safe, and who many Americans do not even know exist?
At the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology's (APIC's), 48th Annual Conference, the head of infection prevention at a top New York City hospital presented an iterative diary, kept in real time by infection preventionists during the height of the pandemic, from March-July 2020.
Almost 50 IPs completed more than 150 surveys over 14 survey rounds during those four dark months and told of the fear that frontline medical workers felt.
"Fear ...
Prevalence of COVID-19 among hospitalized infants varies with levels of community transmission
2021-06-30
How common COVID-19 is among infants may depend on the degree of the pandemic virus circulating in a community, a new study finds.
Published online June 30 in the journal Pediatrics, the study found specifically that rates of the infection with the virus that causes COVID-19 were higher among infants hospitalized, not for COVID-19 - but instead because they were being evaluated for a potential serious bacterial infection (SBI) - during periods of high COVID-19 circulation in New York City. The study also found rates of COVID-19 positivity in this age group were lower when infection rates in the city were low.
Led by researchers from NYU Langone Health, the study also examined the clinical course of the infection in young infants and found that the most ...
Postmenopausal bleeding may be a sign of endometrial cancer in obese Asian women
2021-06-30
CLEVELAND, Ohio (June 30, 2021)--The link between obesity and the risk of endometrial cancer has been well documented. A new study, however, shows that an even lower body mass index (BMI) than previously thought can signal an increased risk in Asian women with postmenopausal bleeding. Study results are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
Endometrial cancer is the sixth most common form of cancer in women worldwide and is a leading cause of cancer death. Because there is currently no routine screening for endometrial cancer in asymptomatic women, it is important for healthcare professionals to be aware of added risk factors so that ...
'There may not be a conflict after all' in expanding universe debate
2021-06-30
Our universe is expanding, but our two main ways to measure how fast this expansion is happening have resulted in different answers. For the past decade, astrophysicists have been gradually dividing into two camps: one that believes that the difference is significant, and another that thinks it could be due to errors in measurement.
If it turns out that errors are causing the mismatch, that would confirm our basic model of how the universe works. The other possibility presents a thread that, when pulled, would suggest some fundamental missing new physics is needed to stitch it back together. For several years, each new piece ...
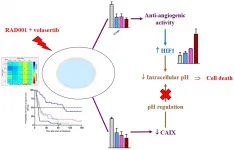
Oncotarget: mTORC1 and PLK1 inhibition in adenocarcinoma NSCLC
2021-06-30
Oncotarget published "High in vitro and in vivo synergistic activity between mTORC1 and PLK1 inhibition in adenocarcinoma NSCLC" which reported that the aim of this study was therefore to define combination of treatment based on the determination of predictive markers of resistance to the mTORC1 inhibitor RAD001/Everolimus.
When looking at biomarkers of resistance by RT-PCR study, three genes were found to be highly expressed in resistant tumors, i.e., PLK1, CXCR4, and AXL.
The authors have then focused this study on the combination of RAD001 Volasertib, a PLK1 inhibitor, and observed a high antitumor activity ...
Scientists intensify electrolysis, utilize carbon dioxide more efficiently with magnets
2021-06-30
For decades, researchers have been working toward mitigating excess atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. One promising approach captures atmospheric CO2 and then, through CO2 electrolysis, converts it into value-added chemicals and intermediates--like ethanol, ethylene, and other useful chemicals. While significant research has been devoted to improving the rate and selectivity of CO2 electrolysis, reducing the energy consumption of this high-power process has been underexplored.
In ACS Energy Letters, researchers from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign report a new opportunity to use magnetism to reduce the energy required for CO2 electrolysis by up to 60% in a flow electrolyzer.
In a ...
Wildfire changes songbird plumage and testosterone
2021-06-30
PULLMAN, Wash. - Fire can put a tropical songbird's sex life on ice.
Following habitat-destroying wildfires in Australia, researchers found that many male red-backed fairywrens failed to molt into their red-and-black ornamental plumage, making them less attractive to potential mates. They also had lowered circulating testosterone, which has been associated with their showy feathers.
For the study published in the Journal of Avian Biology, the researchers also measured the birds' fat stores and the stress hormone corticosterone but found those remained at normal levels.
"Really, it ended up all coming down to testosterone," said ...
Jackdaws don't console traumatized mates
2021-06-30
Male jackdaws don't stick around to console their mate after a traumatic experience, new research shows.
Jackdaws usually mate for life and, when breeding, females stay at the nest with eggs while males gather food.
Rival males sometimes visit the nest and attack the lone female, attempting to mate by force.
In the new study, University of Exeter researchers expected males to console their partner after these incidents by staying close and engaging in social behaviours like preening their partner's feathers.
However, males focussed on their own safety - they still brought food to the nest, but they visited less often and spent less time with the female.
"Humans often console friends or family in distress, but it's unclear whether animals do this in the wild," said Beki ...
COVID-19 review: Analysis of 58 studies finds male sex and obesity are not associated with ICU mortality, but many factors are
2021-06-30
A new analysis of 58 studies and 44305 patients published in Anaesthesia (a journal of the Association of Anaesthetists) shows that, contrary to some previous research, being male and increasing body mass index (BMI) are not associated with increased mortality in COVID-19 in patients admitted into intensive care (ICU).
However, the study, by Dr Bruce Biccard (Groote Schuur Hospital and University of Cape Town, South Africa) and colleagues finds that a wide range of factors are associated with death from COVID-19 in ICU.
Patients with COVID-19 in ICU were 40% more likely to die with a history of smoking, 54% more likely with high blood pressure, 41% more likely with diabetes, ...
A promising new pathway to treating type 2 diabetes
2021-06-30
This year marks the 100th anniversary of the discovery of insulin, a scientific breakthrough that transformed Type 1 diabetes, once known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, from a terminal disease into a manageable condition.
Today, Type 2 diabetes is 24 times more prevalent than Type 1. The rise in rates of obesity and incidence of Type 2 diabetes are related and require new approaches, according to University of Arizona researchers, who believe the liver may hold the key to innovative new treatments.
"All current therapeutics for ...
ACTG announces publication of REPRIEVE sub-study in JAMA Network Open, providing insights into cardiovascular disease risk among people living with HIV
2021-06-30
Los Angeles, Calif. - The AIDS Clinical Trials Group (ACTG), the largest global HIV research network, today announced that findings from a sub-study of REPRIEVE (A5332/A5332s, an international clinical trial studying heart disease prevention in people living with HIV) have been published in the Journal of the American Medical Association Network Open (JAMA Network Open). The study found that approximately half of study participants, who were considered by traditional measures to be at low-to-moderate risk of future heart disease, had atherosclerotic plaque in their coronary arteries.
While it is well-known that people living with HIV are at ...
Dedicated journal edition on largest ever study on First Nations Food Security & Environment
2021-06-29
(OTTAWA, ON) The University of Ottawa, the University of Montreal and the Assembly of First Nations are pleased to announce the newly published First Nations Food, Nutrition and Environment Study (FNFNES) in the Canadian Journal of Public Health. Mandated by First Nations leadership across Canada through Assembly of First Nations Resolution 30 / 2007 and realized through a unique collaboration with researchers and communities, the First Nations Food, Nutrition and Environment Study is the first national study of its kind. It was led by principal investigators Dr. Laurie Chan, a professor ...
Novel heat-management material keeps computers running cool
2021-06-29
UCLA engineers have demonstrated successful integration of a novel semiconductor material into high-power computer chips to reduce heat on processors and improve their performance. The advance greatly increases energy efficiency in computers and enables heat removal beyond the best thermal-management devices currently available.
The research was led by Yongjie Hu, an associate professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering. Nature Electronics recently published the finding in this article.
Computer processors have shrunk down to nanometer scales over the years, with billions of transistors sitting on a single computer chip. While the increased number of transistors helps make computers faster and more powerful, it also generates ...
Gene therapy breakthrough offers hope to children with rare and fatal brain disease
2021-06-29
Scientists and doctors at University College London Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health (UCL GOS ICH) and Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH) have given hope of a gene therapy cure to children with a rare degenerative brain disorder called Dopamine Transporter Deficiency Syndrome (DTDS).
The team have recreated and cured the disease using state-of-the-art laboratory and mouse models of the disease and will soon apply for a clinical trial of the therapy. Their breakthrough comes just a decade after the faulty gene causing the disease was first discovered by the lead scientist of this work.
The results, published in Science Translational Medicine, are so promising that the UK regulatory agency MHRA has advised ...
New Geology articles published online ahead of print in June
2021-06-29
Boulder, Colo., USA: Article topics include the Great Unconformity of the
Rocky Mountain region; new Ediacara-type fossils; the southern Cascade arc
(California, USA); the European Alps and the Late Pleistocene glacial
maximum; Permian-Triassic ammonoid mass extinction; permafrost thaw; the
southern Rocky Mountains of Colorado (USA); "gargle dynamics"; invisible
gold; and alluvial fan deposits in Valles Marineris, Mars. These Geology articles are online at
https://geology.geoscienceworld.org/content/early/recent
.
A new kind of invisible gold in pyrite hosted in deformation-related
dislocations
Denis Fougerouse; Steven M. Reddy; Mark ...
[1] ... [2162]
[2163]
[2164]
[2165]
[2166]
[2167]
[2168]
[2169]
2170
[2171]
[2172]
[2173]
[2174]
[2175]
[2176]
[2177]
[2178]
... [8821]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.