Closer to cure: New imaging method tracks cancer treatment efficacy in preclinical studies
2021-07-02
Several cancer tumors grow through immunosuppression; that is, they manipulate biological systems in their microenvironments and signal to a specific set of immune cells--those that clear out aberrant cells--to stop acting. It is no wonder that immunotherapy designed to re-establish anti-tumor immunity is rapidly becoming the treatment of choice for these cancers.
One natural immunosuppressive molecule that falls prey to helping cancer tumors is indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase 1 (henceforth, IDO1). Because it is found in a broad range of cancer tumors, including those of the skin, breast, colon, lung, and blood, scientists have begun to see it as a promising therapeutic target: Suppress its activity and anti-tumor immunity should be back. But all endeavors so far have ...
Large-scale drug analysis reveals potential new COVID-19 antivirals
2021-07-02
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and University of Dundee have screened thousands of drug and chemical molecules and identified a range of potential antivirals that could be developed into new treatments for COVID-19 or in preparation for future coronavirus outbreaks.
While COVID-19 vaccines are being rolled out, there are still few drug options that can be used to treat patients with the virus, to reduce symptoms and speed up recovery time. These treatments are especially important for groups where the vaccines are less effective, such as some patients with blood cancers.
In a series of seven papers, published today (2 July) in the Biochemical Journal, the scientists ...
Diversity in leadership essential to engage minority-ethnic medical students with academia
2021-07-02
Minority-ethnic medical students must have more role-models in senior leadership positions if they are to engage with academia. This is one of the conclusions drawn by a group of medical students writing in the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine about the drivers and barriers to engaging with academia.
Barriers currently hampering the chances of minority-ethnic medical students accessing formal pathways into academia, they write, include differential attainment and unconscious bias, difficulties forming meaningful mentor-mentee relationships, as well as the ...
Autistic individuals more likely to use recreational drugs to self-medicate
2021-07-02
While autistic individuals are less likely to use substances, those who do so are more likely to self-medicate for their mental health symptoms, according to new research from the University of Cambridge and published today in The Lancet Psychiatry.
There is significant debate about substance use of autistic adolescents and adults. Some studies indicate that autistic individuals are less likely to use substances, whereas others suggest that autistic individuals are at greater risk of substance misuse or abuse. The team at the Autism Research Centre in Cambridge used a 'mixed methods' design to consider ...
UCLA scientists say COVID-19 test offers solution for population-wide testing
2021-07-02
In an article appearing in Nature Biomedical Engineering, a team of scientists from the UCLA David Geffen School of Medicine and UCLA School of Engineering report real-world results on SwabSeq, a high-throughput testing platform that uses sequencing to test thousands of samples at a time to detect COVID-19. They were able to perform more than 80,000 tests in less than two months, with the test showing extremely high sensitivity and specificity.
SwabSeq uses sample-specific molecular barcodes to simultaneously analyze thousands of samples for the presence or absence of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. SwabSeq was granted FDA Emergency Use Authorization in October ...
Don't worry, the kids are cool if you cash in on their inheritance
2021-07-01
Cash in on the kids' inheritance and spend up big on the retirement plans - that's the message coming from the University of South Australia as new research reveals that older people are keen to spend their well-earned savings, rather than passing them on to their kids.
And while it may seem like bad news for the younger generation, the research also confirms that the kids are just fine with this scenario, claiming that no one owes anyone anything.
The surprising findings are part of a new study that explores contemporary attitudes towards wealth ...
Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines prime T cells to fight SARS-CoV-2 variants
2021-07-01
LA JOLLA, CA--Researchers at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) have found that T cells from people who have recovered from COVID-19 or received the Moderna or Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines are still able to recognize several concerning SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Their new study, published online on July 1, 2021 in Cell Reports Medicine, shows that both CD4+ "helper" T cells and CD8+ "killer" T cells can still recognize mutated forms of the virus. This reactivity is key to the body's complex immune response to the virus, which allows the body to kill infected cells and stop severe infections.
"This study suggests that the impact of mutations ...
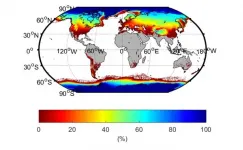
Earth's cryosphere shrinking by 87,000 square kilometers per year
2021-07-01
WASHINGTON--The global cryosphere--all of the areas with frozen water on Earth--shrank by about 87,000 square kilometers (about 33,000 square miles), a area about the size of Lake Superior, per year on average, between 1979 and 2016 as a result of climate change, according to a new study. This research is the first to make a global estimate of the surface area of the Earth covered by sea ice, snow cover and frozen ground.
The extent of land covered by frozen water is just as important as its mass because the bright white surface reflects sunlight so effectively, cooling the planet. Changes in the size or location of ice and snow can alter air temperatures, change the sea level and even affect ocean currents worldwide.
The new study is published in Earth's ...
Rethinking plastics
2021-07-01
People lived without plastic until the last century or so, but most of us would find it hard to imagine how.
Plastics now are everywhere in our lives, providing low-cost convenience and other benefits in countless applications. They can be shaped to almost any task, from wispy films to squishy children's toys and hard-core components. They have shown themselves vital in medicine and have been pivotal in the global effort to slow the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic over the past 16 months.
Plastics seem indispensable these days.
Unfortunately for the long-term, they are also nearly indestructible. Our planet now bears the weight of more than seven billion tons ...
Skin in the game: Transformative approach uses the human body to recharge smartwatches
2021-07-01
As smart watches are increasingly able to monitor the vital signs of health, including what's going on when we sleep, a problem has emerged: those wearable, wireless devices are often disconnected from our body overnight, being charged at the bedside.
"Quality of sleep and its patterns contain a lot of important information about patients' health conditions," says Sunghoon Ivan Lee, assistant professor in the University of Massachusetts Amherst College of Information and Computer Sciences and director of the Advanced Human Health Analytics Laboratory.
But that information can't be tracked on smartwatches if the wearable devices are ...
Vaccines grown in eggs induce antibody response against an egg-associated glycan
2021-07-01
Over years of studying antibody responses against the flu in the Wilson lab at the University of Chicago, researchers kept coming up with a strange finding: antibodies that seemed to bind not only to the flu virus, but to every virus the lab could throw at them. Since antibodies are usually highly specific to individual pathogens, in order to maximize their targeted protective response, this pattern was extremely unusual.
Until finally, they realized: The antibodies weren't responding to the viruses, but rather to something in the biological material in which the viruses had been grown. ...
The key role of astrocytes in cognitive development
2021-07-01
Astrocytes are cells in the brain which have long been considered only as mere support cells for neurons. In recent years, the study of astrocytes has grown, gradually revealing their importance in brain function. Researchers from Inserm, CNRS and Collège de France at the Center for Interdisciplinary Research in Biology have now uncovered their crucial role in closing the period of brain plasticity that follows birth, finding them to be key to the development of sensory and cognitive faculties. Over the longer term, these findings will make it possible to envisage new strategies for reintroducing brain plasticity in adults, thereby promoting rehabilitation following brain lesions or neurodevelopmental disorders. This research has been published in Science.
Brain plasticity is ...
How information beyond the genetic sequence is encoded in plant sperm
2021-07-01
Hereditary information is passed from parent to offspring in the genetic code, DNA, and epigenetically through chemically induced modifications around the DNA.
New research from the John Innes Centre has uncovered a mechanism which adjusts these modifications, altering the way information beyond the genetic code is passed down the generations.
DNA methylation, one example of these epigenetic modifications, happens when a methyl group or chemical cap is added to the DNA, switching a gene, or genes, on or off.
As germline (eggs and sperm) cells develop some of the methyl markers are reset, affecting the information passed onto the next generation.
How this process ...
Special issue: Our plastics dilemma
2021-07-01
Although plastics have become an essential material, permeating almost all aspects of modern living, many of the inherent properties that make them useful in such a wide variety of applications also make them a serious environmental threat. In a special issue of Science, "Our Plastics Dilemma," four Reviews, two Perspectives, a Policy Forum, an associated Report and two News features examine a wide range of topics related to plastics and the problems they present. "As for much new technology, their development and proliferation occurred with little consideration for their impacts, but now it's impossible to deny their dark side as we confront a rapidly ...
Massive exome-wide association study in humans identifies rare variants that protect against obesity
2021-07-01
Through the sequencing of more than 640,000 human exomes, researchers identify rare gene coding variants strongly associated with body mass index (BMI) - including the variant GPR75, which conferred protection from obesity in mouse models. Not only do the findings provide potential therapeutic targets for treating obesity, but they also demonstrate the power and versatility of massive-scale exome sequencing in discovering rare coding variants that could offer new and potentially translatable biological functions. Body fat is a highly heritable trait and the obesity to which body ...
In full-shell semiconductor-superconductor nanowires, zero-bias peaks induced by Andreev states, not Majorana modes
2021-07-01
Researchers could not confirm that a feature that supposedly signals the presence of Majorana bound states - the unusual quasiparticles that may become the cornerstone of topological quantum computing - was in fact due to elusive Majorana particles, in full-shell semiconductor/superconductor nanowires. Rather, this feature, known as zero bias conductance peak, can arise from another quantum phenomenon in these hybrid nanowire structures, the authors say. In recent years, intense research has been conducted on nanowire-based semiconductor-superconductor hybrid systems because predictions suggest that a topological superconductor state with Majorana zero modes (MZMs) can be engineered from them. Even though several experiments in such platforms have reported ...
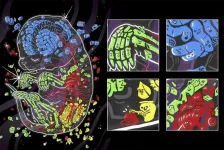
Introducing 'sci-Space,' a new method for embryo-scale, single-cell spatial transcriptomics
2021-07-01
Researchers introduce "sci-Space," a new approach to spatial transcriptomics that can retain single-cell resolution and spatial heterogeneity at scales much larger than previous methods. They used their approach to build single-cell atlases of whole sections of mouse embryos at 14 days of development. Single-cell RNA sequencing methods have led to great advances in understanding how organisms and complex tissues develop. Although cells' spatial organization is central to normal development, homeostasis, and pathophysiology, many single-cell RNA sequencing methods lose valuable contextual spatial information. Those that preserve spatial context between cells can be limited to a specific set of genes and/or ...
Spatial patterns of gene transcripts captured across single cells of mouse embryo
2021-07-01
A new technique called sci-Space, combined with data from other technologies, could lead to four-dimensional atlases of gene expression across diverse cells during embryonic development of mammals.
Such atlases would map how the gene transcripts in individual cells reflect the passage of time, cell lineages, cell migration, and location on the developing embryo. They would also help illuminate the spatial regulation of gene expression.
Mammalian embryonic development is a remarkable phenomenon: a fertilized egg divides repeatedly and turns, in a matter of weeks or months, into a complex organism capable of a myriad of physiological processes and composed of a variety ...
Unfinding a split electron
2021-07-01
Quantum computers promise great advances in many fields - from cryptography to the simulation of protein folding. Yet, which physical system works best to build the underlying quantum bits is still an open question. Unlike regular bits in your computer, these so-called qubits cannot only take the values 0 and 1, but also mixtures of the two. While this potentially makes them very useful, they also become very unstable.
One approach to solve this problem bets on topological qubits that encode the information in their spatial arrangement. That could provide a more stable ...
Is global plastic pollution nearing an irreversible tipping point?
2021-07-01
Current rates of plastic emissions globally may trigger effects that we will not be able to reverse, argues a new study by researchers from Sweden, Norway and Germany published on July 2nd in Science. According to the authors, plastic pollution is a global threat, and actions to drastically reduce emissions of plastic to the environment are "the rational policy response".
Plastic is found everywhere on the planet: from deserts and mountaintops to deep oceans and Arctic snow. As of 2016, estimates of global emissions of plastic to the world's lakes, rivers and ...
Scientists discover a new class of memory cells in the brain
2021-07-01
Scientists have long searched in vain for a class of brain cells that could explain the visceral flash of recognition that we feel when we see a very familiar face, like that of our grandmothers. But the proposed "grandmother neuron"--a single cell at the crossroads of sensory perception and memory, capable of prioritizing an important face over the rabble--remained elusive.
Now, new research reveals a class of neurons in the brain's temporal pole region that links face perception to long-term memory. It's not quite the apocryphal grandmother neuron--rather than a single ...
COVID-19 aggravates antibiotic misuse in India
2021-07-01
The COVID-19 catastrophe in India has resulted in more than 30 million people infected with the virus and nearly 400,000 deaths, though experts are concerned that the figures most likely are much higher. Meanwhile, another public health crisis has emerged along with COVID-19: the widespread misuse of antibiotics.
During India's first surge of COVID-19, antibiotic sales soared, suggesting the drugs were used to treat mild and moderate cases of COVID-19, according to research led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. Such use is considered inappropriate because antibiotics are only effective against bacterial infections, not viral infections such as COVID-19, and overuse increases the risk ...
The first commercially scalable integrated laser and microcomb on a single chip
2021-07-01
Fifteen years ago, UC Santa Barbara electrical and materials professor John Bowers pioneered a method for integrating a laser onto a silicon wafer. The technology has since been widely deployed in combination with other silicon photonics devices to replace the copper-wire interconnects that formerly linked servers at data centers, dramatically increasing energy efficiency -- an important endeavor at a time when data traffic is growing by roughly 25% per year.
For several years, the Bowers group has collaborated with the group of Tobias J. Kippenberg at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (EPFL), within the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) Direct On-Chip Digital Optical ...
Scalable manufacturing of integrated optical frequency combs
2021-07-01
Optical frequency combs consist of light frequencies made of equidistant laser lines. They have already revolutionized the fields of frequency metrology, timing and spectroscopy. The discovery of ''soliton microcombs'' by Professor Tobias Kippenberg's lab at EPFL in the past decade has enabled frequency combs to be generated on chip. In this scheme, a single-frequency laser is converted into ultra-short pulses called dissipative Kerr solitons.
Soliton microcombs are chip-scale frequency combs that are compact, consume low power, and exhibit broad bandwidth. Combined with large spacing of comb "teeth", microcombs are uniquely ...
Using computation to improve words: Novel tool could improve serious illness conversations
2021-07-01
Conversations between seriously ill people, their families and palliative care specialists lead to better quality-of-life. Understanding what happens during these conversations - and particularly how they vary by cultural, clinical, and situational contexts - is essential to guide healthcare communication improvement efforts. To gain true understanding, new methods to study conversations in large, inclusive, and multi-site epidemiological studies are required. A new computer model offers an automated and valid tool for such large-scale scientific analyses.
Research results on this model were published today in PLOS ONE.
Developed by a team of computer scientists, clinicians and engineers at the University of Vermont, the approach - called CODYM ...
[1] ... [2168]
[2169]
[2170]
[2171]
[2172]
[2173]
[2174]
[2175]
2176
[2177]
[2178]
[2179]
[2180]
[2181]
[2182]
[2183]
[2184]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.