Protein finding can pave the way for improved treatment of malignant melanoma
2015-04-15
Today it is not possible to predict spreading from malignant melanomas. Melanoma metastases are furthermore extremely difficult to eliminate as traditional treatment such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy is mostly ineffective. Only ten per cent of the patients survive once they reach an advanced stage with distant metastases.
New research now demonstrates that the presence of the protein megalin in a malignant melanoma is an indicator of cancer cells that are particularly aggressive. The protein improves the ability of the cancer cells to divide and to survive. Accordingly, ...
Optimal substrate moisture content determined for high-quality bedding plants
2015-04-15
COLLEGE STATION, TX - The bedding plants sold in retail outlets are typically grown in greenhouse production environments where professionals can monitor irrigation, light, and temperature. When the greenhouse-grown plants reach the retail market, however, they are often subjected to a range of less-than-ideal light levels, temperatures, and irrigation schedules that can be detrimental to plant quality and vigor. Researchers are looking for ways to increase bedding plants' shelf life to offset the negative impacts of postharvest handling.
A new research study of the popular ...
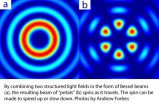
Light in a spin
2015-04-15
Light must travel in a straight line and at a constant speed, or so the laws of nature suggest. Now, researchers at the University of the Witwatersrand in Johannesburg have demonstrated that laser light traveling along a helical path through space, can accelerate and decelerate as it spins into the distance.
This is the first time that angular acceleration has been observed with light, and is therefore likely to lead to new applications using these structured light fields.
The results are contained in a research paper by Professor Andrew Forbes from the Wits School of ...
E-cigarette use is not risk-free
2015-04-15
E-cigarettes are not without health risks for people who vape or for bystanders. This is one of the conclusions from a new risk assessment report from the Norwegian Institute of Public Health (NIPH).
The report has only considered e-cigarettes with nicotine since there has been very little research about e-cigarettes without nicotine.
In summary
Since e-cigarettes supply nicotine in the same quantities as cigarette smoking, the same harmful effects from nicotine can be expected.
The vapour from e-cigarettes contains so much nicotine that bystanders can ingest ...
Surveys miss majority of poisonings, underestimate cost by billions
2015-04-15
Health surveys may underestimate the number of poisonings in the United States by 60 percent to 90 percent, according to a report in the journal Clinical Toxicology by University of Illinois at Chicago researchers.
As of 2009, poisonings became the leading cause of fatal injury in the U.S., surpassing transportation-related deaths and gun-related deaths.
The researchers analyzed hospital billing records, patient demographics, exposure information, and outcomes for Illinois hospital visits related to poisonings in 2010. They also looked at poisoning incidence data from ...
Iowa State anthropologist finds female chimps more likely to use tools when hunting
2015-04-15
AMES, Iowa - It was a discovery that changed what researchers knew about the hunting techniques of chimpanzees. In 2007, Jill Pruetz first reported savanna chimps at her research site in Fongoli, Senegal, were using tools to hunt prey. That alone was significant, but what also stood out to Pruetz was the fact that female chimps were the ones predominantly hunting with tools.
It was a point some dismissed or criticized because of the small sample size, but the finding motivated the Iowa State University anthropology professor to learn more. In the years following, Pruetz ...
Scientists develop mesh that captures oil--but lets water through
2015-04-15
COLUMBUS, Ohio--The unassuming piece of stainless steel mesh in a lab at The Ohio State University doesn't look like a very big deal, but it could make a big difference for future environmental cleanups.
Water passes through the mesh but oil doesn't, thanks to a nearly invisible oil-repelling coating on its surface.
In tests, researchers mixed water with oil and poured the mixture onto the mesh. The water filtered through the mesh to land in a beaker below. The oil collected on top of the mesh, and rolled off easily into a separate beaker when the mesh was tilted.
The ...
Study reveals an absence of consistent standards in children's hospital environments
2015-04-15
The sound, light and temperature levels in paediatric hospital wards often vary, highlighting the lack of consistent environmental standards, according to a new study.
The research is being presented today at the 2015 Sleep and Breathing Conference (16 April, 2015).
Children and parents often suffer sleep deprivation when the environment on a ward is disruptive, which can affect disease recovery and quality of life in hospitalised children. There are no general consistent recommendations covering sound, light and temperature levels to help guide hospitals across ...
Disruption of sleep in children could hamper memory processes
2015-04-15
Sleep disordered breathing can hamper memory processes in children, according to a new study.
The research, which will be presented today at the Sleep and Breathing Conference (16 April 2015), found that disrupted sleep had an impact on different memory processes and how children learn.
Eszter Csabi led a team of researchers from the University of Szeged and Eötvös Loránd University in Hungary. They analysed 17 children with sleep disordered breathing aged between 6 and 12 years. They looked at different memory processes compared to a control group ...
Quantum cryptography at the speed of light: Researchers design first all-photonic repeaters
2015-04-15
Imagine having your MRI results sent directly to your phone, with no concern over the security of your private health data. Or knowing your financial information was safe on a server halfway around the world. Or sending highly sensitive business correspondence, without worrying that it would fall into the wrong hands.
Thanks to new research from engineers at the University of Toronto, these types of perfectly secure information exchanges are one step closer to reality. Published this week in Nature Communications, researchers have designed the first all-photonic quantum ...
Children with disabilities can make competent witnesses
2015-04-15
Children with intellectual disabilities--significantly low cognitive functioning coupled with significant deficits in adaptive or everyday functioning--make up 2 to 3 percent of the population, and it's estimated that 1 in 3 children with disabilities experiences some form of maltreatment. However, in many cases, the disclosures of children with intellectual disabilities aren't investigated or taken to court, in part because of concern over whether these children can describe their experiences sufficiently and be believed by juries. A new study has found that children with ...
Infants born prematurely: 2 studies identify routes to better outcomes
2015-04-15
Eleven percent of all births worldwide are preterm, or occurring before 37 weeks of pregnancy, and preterm-related causes of death account for a significant number of infant deaths, as well as long-term neurological disabilities. Efforts are under way, including an initiative by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, to reduce elective deliveries before 39 weeks of pregnancy. Now two new longitudinal studies that appear in the journal Child Development offer insights on how to decrease the problems associated with premature ...
Children who understand others' perspectives found to be more popular among peers
2015-04-15
Preschoolers and school-age children who are good at identifying what others want, think, and feel are more popular in school than their peers who aren't as socially adept. That's the conclusion of a new meta-analysis--a type of study that looks at the results of many different studies--out of Australia.
The study was done at the University of Queensland, Australia, and appears in the journal Child Development.
"Our study suggests that understanding others' mental perspectives may facilitate the kind of interactions that help children become or remain popular," notes ...
Mentally stepping back from problems helps youth deal with negative emotions
2015-04-15
Adolescence is a time of frequent and intense emotional experiences, but some youth handle their emotions better than others. Why do some young people react adaptively while others ruminate? A new study of adolescents shows that youth who mentally take a step back from their own point of view when thinking about something troubling can deal with negative emotions more effectively and become less upset by them.
The study, conducted by researchers at the University of Pennsylvania and the University of Michigan, appears in the journal Child Development.
The researchers ...
Paternal sperm may hold clues to autism
2015-04-15
In a small study, Johns Hopkins researchers found that DNA from the sperm of men whose children had early signs of autism shows distinct patterns of regulatory tags that could contribute to the condition. A detailed report of their findings will be published online in the International Journal of Epidemiology on April 15.
Autism spectrum disorder (autism) affects one in 68 children in the U.S. Although studies have identified some culprit genes, most cases remain unexplained. But most experts agree that autism is usually inherited, since the condition tends to run in ...
Father (and mother) knows best
2015-04-15
Cincinnati, OH, April 15, 2015 -- Children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) can develop symptoms before 2 years of age and usually can be diagnosed by 3 years of age; early identification of ASD is associated with improved long-term developmental outcomes. In a new study scheduled for publication in The Journal of Pediatrics, researchers assessed how healthcare providers respond to parents' concerns about their child's early development, as well as how that response affected the timeliness of ASD diagnosis.
Katharine Zuckerman, MD, MPH, and colleagues from Doernbecher ...
3-D printing blossoms into powerful new tool for ecologists
2015-04-15
3D printing has been used to make everything from cars to medical implants. Now, ecologists are using the technology to make artificial flowers, which they say could revolutionise our understanding of plant-pollinator interactions. Their study involving hawkmoths - a close relative of the species made famous by the film Silence of the Lambs - is published in the British Ecological Society's journal Functional Ecology.
Since long before Charles Darwin, ecologists have been fascinated by flower shape, and in particular how animal pollinators have shaped the evolution of ...
Bone eating worms dined on marine reptile carcasses
2015-04-15
A species of bone-eating worm that was believed to have evolved in conjunction with whales has been dated back to prehistoric times when it fed on the carcasses of giant marine reptiles.
Scientists at Plymouth University found that Osedax - popularised as the 'zombie worm' - originated at least 100 million years ago, and subsisted on the bones of prehistoric reptiles such as plesiosaurs and sea turtles.
Reporting in the Royal Society journal Biology Letters this month, the research team at Plymouth reveal how they found tell-tale traces of Osedax on plesiosaur fossils ...
First signs of self-interacting dark matter?
2015-04-15
Using the MUSE instrument on ESO's VLT in Chile, along with images from Hubble in orbit, a team of astronomers studied the simultaneous collision of four galaxies in the galaxy cluster Abell 3827. The team could trace out where the mass lies within the system and compare the distribution of the dark matter with the positions of the luminous galaxies.
Although dark matter cannot be seen, the team could deduce its location using a technique called gravitational lensing. The collision happened to take place directly in front of a much more distant, unrelated source. The ...
Disabled girls vulnerable to abuse by carers and partners due to isolation and incapacity
2015-04-15
Disabled girls and women are vulnerable to abuse by carers and partners because of their isolation and physical incapacity, new research says.
In some cases the abuse took place in special education institutions, the British Sociological Association's annual conference in Glasgow was told today [Wednesday 15 April 2015].
Dr Sarah Woodin, of the University of Leeds, and Dr Sonali Shah, of the University of Glasgow, carried out research with 45 physically disabled or deaf women in the UK who had been abused. The project was part of a large EU-funded international study. ...
Facebook use can worsen as well as improve mental health conditions
2015-04-15
Facebook can help people recover from mental health problems but it needs to be used cautiously and strategically as it can also make symptoms worse, new research shows.
Dr Keelin Howard told the British Sociological Association's annual conference in Glasgow today [Wednesday 15 April] that users she interviewed found their paranoid, manic and depressive symptoms could worsen as well as improve.
Dr Howard, of Buckinghamshire New University, carried out research with 20 people aged 23-68 who had experienced conditions such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, depression ...
The Lancet Respiratory Medicine: Sleep apnea media alert
2015-04-15
The Lancet Respiratory Medicine journal is pleased to announce that the following Review papers will be published to coincide with the European Respiratory Society's Sleep and Breathing Conference 2015:
Sleep apnoea and the brain: a complex relationship [Embargo: 6:30pm [New York time] Tuesday 14 April, 2015]
On the cutting edge of obstructive sleep apnoea: where next? [Embargo: 6:30pm [New York time] Tuesday 14 April, 2015]
Sleep apnoea and the brain: a complex relationship - by Dr Ivana Rosenzweig et al
Obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) is a common disease that ...
Are health apps beneficial for healthy people?
2015-04-15
Health apps have the potential to make a broad impact on the health of the general population, argues one expert in The BMJ this week. But another explains that there is not enough evidence to support such claims and suggests that health apps may even be harmful.
Widely available on smartphones, health apps aim to encourage people to adopt healthy behaviours ranging from weight loss to physical activity, and to help patients to manage conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure.
Health apps have been around for more than 10 years and tens of thousands are available ...
Benefits of heroin treatment for drug users
2015-04-15
Drug users who do not benefit from conventional treatments for heroin addiction should be able to access the drug through the health system, urges a Canadian expert in The BMJ today.
Standard treatments for heroin drug addiction include detoxification, abstinence programmes and methadone maintenance, but there is a subgroup of patients for whom these do not work.
As doctors can provide no effective treatments for these patients, many will remain "outside the healthcare system" and there is "overwhelming" evidence that they will relapse into using illicit heroin and ...
Most comprehensive study to date reveals evolutionary history of citrus
2015-04-15
Citrus fruits -- delectable oranges, lemons, limes, kumquats and grapefruits -- are among the most important commercially cultivated fruit trees in the world, yet little is known of the origin of the citrus species and the history of its domestication.
Now, Joaquin Dopazo et al, in a new publication in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution, have performed the largest and most detailed genomic analysis on 30 species of Citrus, representing 34 citrus genotypes, and used chloroplast genomic data to reconstruct its evolutionary history.
Overall, the results confirm ...
[1] ... [3032]
[3033]
[3034]
[3035]
[3036]
[3037]
[3038]
[3039]
3040
[3041]
[3042]
[3043]
[3044]
[3045]
[3046]
[3047]
[3048]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.