Link between social anxiety and drug use offers opportunities for more effective treatment
2015-04-15
A team led by Case Western Reserve researchers has identified a potentially powerful approach to lowering relapse rates among the ranks of those addicted to illegal drugs or alcohol.
In a study of nearly 200 teenagers admitted to a residential treatment center in the northeastern United States, psychiatry professor Maria Pagano, PhD, confirmed both the prevalence of social anxiety issues among them as well as the benefits of measures designed to alleviate social distress. These findings were posted online this month in the journal Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental ...
Relativistic heavy ion collider smashes record for polarized proton luminosity
2015-04-15
UPTON, NY - The Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC, http://www.bnl.gov/rhic/), a powerful particle accelerator for nuclear physics research at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory, just shattered its own record for producing polarized proton collisions at 200-giga-electron-volt (GeV) collision energy. In the experimental run currently underway at this two-ringed, 2.4-mile-circumference particle collider, accelerator physicists are now delivering 1200 billion of these subatomic smashups per week-more than double the number routinely achieved ...
Paternal alcohol problems, death from liver disease, signal offspring risk for cirrhosis
2015-04-14
While the risk of alcohol-related liver cirrhosis is known to increase with heavy drinking, a number of people who drink large quantities of alcohol seem to escape developing the disease. This variation in susceptibility may be due to several factors beyond quantity such as genetics, gender, and obesity. A preliminary clinical analysis of hundreds of drinkers with and without alcoholic cirrhosis has found that affected individuals often report a father with alcohol problems who had died from liver disease, which underscores the heritability of this disease.
Results will ...
Alcohol may elevate the expression of two enzymes called CYP2E1 and CYP2U1
2015-04-14
The prefrontal cortex (PFC) and amygdala (AMG) are brain regions that not only referee cognitive functions and emotional states, but also contribute to the reinforcing effects of alcohol and tobacco. Researchers already knew that alcohol and tobacco use can modulate cytochrome P450 expression in the liver and other tissues, but little is known about the effects of alcohol and tobacco on P450s in the human AMG. A new study focusing on two CYP2 enzymes that metabolize drugs and endogenous compounds has found that chronic drinking is associated with higher CYP2E1 and CYP2U1 ...
Socially anxious youth in treatment can enhance recovery through simple service tasks
2015-04-14
This century's increase in addiction issues among U.S. youth may be related to their developmental need to fit in, particularly youth with social anxiety disorder (SAD), which could exacerbate the drink/trouble cycle. In addition, socially anxious youths may avoid participating in therapeutic activities during treatment for fear of negative peer appraisal. A study of the influence of SAD on clinical severity at intake, peer helping in Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) during treatment, and subsequent outcomes has found that almost half of the patients entering treatment had a persistent ...
Simultaneous drinking and smoking marijuana increases odds of drunk driving and other
2015-04-14
Cannabis is the most commonly used drug among adults who drink, besides tobacco, yet no study has directly compared those who use cannabis and alcohol simultaneously, or at the exact same time, versus those who use both separately and on a regular basis. A new study looks at the relationship between marijuana and alcohol use, finding that simultaneous users had double the odds of drunk driving, social consequences, and harms to self.
Results will be published in the May 2015 online-only issue of Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research and are currently available ...
Experimental drug that may repair nerve damage in MS moves forward
2015-04-14
WASHINGTON, DC - A new study suggests that an investigational drug for multiple sclerosis (MS) may repair myelin, the fatty material that protects nerves and is damaged in MS, according to a study released today that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology's 67th Annual Meeting in Washington, DC, April 18 to 25, 2015.
"This study, for the first time, provides biological evidence of repair of damaged myelin in the human brain, and advances the field of neuro-reparative therapies," said study lead author Diego Cadavid, MD, with Biogen in Cambridge, Mass., ...
Heart attack risk high in divorced women, even after remarrying
2015-04-14
Divorced women suffer heart attacks at higher rates than women who are continuously married, a new study from Duke Medicine has found. A woman who has been through two or more divorces is nearly twice as likely to have a heart attack when compared to their stably-married female peers, according to the findings.
Even among women who remarry after the stress of divorce, their heart attack risk remains elevated according to the study published in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes, a journal of the American Heart Association.
"Divorce is a major stressor, ...
Opioid relapse rates fall after jail release, according to pilot study
2015-04-14
New York, NY -- It has been called a pioneering strategy for treating opioid addiction, and has already been adopted in a small yet growing number of jails and prisons in the United States. Now, a clinical trial published in the journal Addiction by researchers at NYU Langone Medical Center finds that the extended-release medication naltrexone (XR-NTX) is associated with a significant decline in relapse rates for a group of mostly heroin-dependent men after their release from New York City jails.
The NYU Langone researchers say that their study is the only randomized ...
Selecting the right tool for the job
2015-04-14
New York, April 14, 2015 - Randomized clinical trials of new drugs have long been considered the "gold standard" in determining safety and efficacy before drugs, biologics, vaccines or devices are introduced to the general public. However, in the case of a deadly, rapidly spreading, infectious disease with no known cure, such as Ebola, ethical considerations demand that reliance only on RCTs be reexamined, according to a new Target Article now online and in print in the American Journal of Bioethics.
Authors Arthur Caplan, PhD and Carolyn Plunkett of the Division of ...
Nanoparticles at specific temperature stimulate antitumor response
2015-04-14
Seeking a way to stimulate antitumor responses via the immune system, Steven Fiering, PhD, of Norris Cotton Cancer Center at Dartmouth, has identified the precise temperature that results in a distinct body-wide antitumor immune response that resists metastatic disease. Fiering's team published the research in the paper "Local Hyperthermia Treatment of Tumors Induces CD8+ T Cell-Mediated Resistance Against Distal and Secondary Tumors," which appeared in Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine.
"Mild hyperthermia treatment of an identified tumor, prior to surgery ...
Rare, deadly lymphoma demystified
2015-04-14
NEW YORK, NY (April 14, 2015) -- The first-ever systematic study of the genomes of patients with ALK-negative anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL), a particularly aggressive form of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, shows that many cases of the disease are driven by alterations in the JAK/STAT3 cell signaling pathway. The study also demonstrates, in mice implanted with human-derived ALCL tumors, that the disease can be inhibited by compounds that target this pathway, raising hopes that more effective treatments might soon be developed. The study, led by researchers at Columbia University ...
How Salmonella survives the macrophage's acid attack
2015-04-14
Macrophages destroy bacteria by engulfing them in intracellular compartments, which they then acidify to kill or neutralize the bacteria. However, some pathogenic bacteria, such as Salmonella enterica, have evolved to exist and even grow while within these acidified compartments. Yet, how Salmonella responds to the acidic environment and how that environment affects the virulence of this pathogen are unclear. New research reveals that Salmonella fights acid with acid, by lowering the pH of its own interior in response to the acidification of the Salmonella-containing compartment ...
How best to test Ebola treatment
2015-04-14
An unconventional clinical trial design might have advantages over classical trials for testing treatments for Ebola virus disease (EVD), suggests a study published this week in PLOS Medicine. The work of an international team led by John Whitehead of Lancaster University, UK and Ben Cooper of Oxford University, UK, provides much-needed data to inform a debate on the scientific and ethical justification for non-randomized EVD trials that has taken place in the editorial pages of a number of medical journals in past months.
The researchers compared three different scenarios ...
New research sheds light on how popular probiotic benefits the gut
2015-04-14
In recent years, research into the benefits of gut bacteria has exploded. Scientists across the globe are examining how these microbes can help improve health and prevent disease.
One of the most well-known of these is Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG). This strain of bacteria, which is part of many popular probiotic products, has a reputation as a helpful microbe. Researchers have found evidence that it can help with intestinal problems, respiratory infections and some skin disorders. Some research suggests that it may even help with weight loss.
But a key question ...
Typhoon Haiyan's storm surge may contaminate aquifer for years
2015-04-14
In research of significance to the world's expanding coastal populations, scientists have found that geology and infrastructure play key roles in determining whether aquifers that provide drinking water are inundated with seawater during a typhoon or hurricane and how long the contamination lasts.
In 2013, Typhoon Haiyan devastated the Philippines, killing more than 6,000 people and destroying nearly $3 billion worth of property. While the country is still recovering from the storm, researchers with The University of Texas at Austin have found that an aquifer on the island ...
Study puts a price on help nature provides agriculture
2015-04-14
PULLMAN, Wash. - A team of international scientists has shown that assigning a dollar value to the benefits nature provides agriculture improves the bottom line for farmers while protecting the environment. The study confirms that organic farming systems do a better job of capitalizing on nature's services.
Scientists from Australia, Denmark, New Zealand, the United Kingdom and the United States describe the research they conducted on organic and conventional farms to arrive at dollar values for natural processes that aid farming and that can substitute for costly fossil ...
Six questions about HIV/AIDS that deserve more attention
2015-04-14
As HIV investigators work to control and eradicate the virus worldwide, certain myths or misconceptions about the disease have been embraced, whereas other concepts with merit have been left relatively unexplored, argues American HIV/AIDS researcher Jay Levy, MD, in a commentary publishing April 14 in the journal Trends in Molecular Medicine. He calls on fellow researchers to continue questioning and not to lose sight of alternative strategies that could ultimately lead to a sustainable, long-term solution to HIV infection.
"This paper may be controversial, but people ...
Five days of eating fatty foods can alter how your body's muscle processes food
2015-04-14
You might think that you can get away with eating fatty foods for a few days without it making any significant changes to your body.
Think again.
After just five days of eating a high-fat diet, the way in which the body's muscle processes nutrients changes, which could lead to long-term problems such as weight gain, obesity, and other health issues, a new study has found.
"Most people think they can indulge in high-fat foods for a few days and get away with it," said Matt Hulver, an associate professor of human nutrition, foods, and exercise in the Virginia Tech College ...
Infectious ants become antisocial
2015-04-14
This news release is available in German. Looking after yourself, and trying not to infect others, is a good strategy to prevent disease from spreading - not only if you are a considerate co-worker, but also if you are an ant, meerkat or other social animal, as revealed by an epidemiological model developed by the groups of Professor Fabian Theis from the Helmholtz Center Munich and Professor Sylvia Cremer from the Institute of Science and Technology (IST) Austria. In a Theme Issue of the Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B on "The Society-Health-Fitness ...
PharmaMar to present data on anticancer candidates PM1183 and plitidepsin at the AACR 2015
2015-04-14
This news release is available in Spanish and Spanish.
Combination of the anticancer drug PM1183 with PARP inhibitors and doxorubicin results in a synergistic effect against breast cancer cell lines and a SCLC mouse tumor model, respectively.
The anticancer candidate plitidepsin binds to eEF1A2, a novel therapeutic target in multiple myeloma, and shows activity in patient-derived tumor mouse models from a wide range of solid tumors and hematological cancers.
The new antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), MI130004, shows in vivo potent and long-lasting anticancer effects ...
New treatment for common digestive condition Barrett's Oesophagus
2015-04-14
New research from the University of Warwick and University Hospitals Coventry and Warwickshire (UHCW) NHS Trust could transform treatments and diagnosis for a common digestive condition which affects thousands of patients.
The oesophagus or food pipe (gullet) is part of the digestive system. It is the tube that carries food from your mouth to your stomach. Barrett's Oesophagus (also known as BE) and low-grade dysplasia affects approximately 2% of the adult population, particularly those with heartburn, as acid reflux from the stomach can, over time, damage the lining ...
Making carboxyl(ate) friends
2015-04-14
When it comes to supramolecular chemistry, the carboxylic acid group (and its conjugate carboxylate base) is one of the chemist's most flexible friends. In pairs, they act as supramolecular synthons from which more complicated structures might be built but also offer up complex hydrogen bond connectivity. Luigi D'Ascenzo and Pascal Auffinger of the University of Strasbourg, France [D'Ascenzo, L. & Auffinger, P. (2015), Acta Cryst. B71, 164-175; doi: 10.1107/S205252061500270X], point out that until now there has been no exhaustive classification of these carboxyl(ate) motifs ...
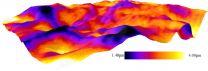
The microscopic topography of ink on paper
2015-04-14
WASHINGTON, D.C., April 14, 2015 - A team of Finnish scientists has found a new way to examine the ancient art of putting ink to paper in unprecedented 3-D detail. The technique could improve scientists' understanding of how ink sticks to paper and ultimately lead to higher quality, less expensive and more environmentally-friendly printed products.
Using modern X-ray and laser-based technologies, the researchers created a nano-scale map of the varying thickness of toner ink on paper. They discovered that wood fibers protruding from the paper received relatively thin coatings ...
Intrauterine exposure to maternal gestational diabetes linked with risk of autism
2015-04-14
Among a group of more than 320,000 children, intrauterine exposure to gestational diabetes mellitus diagnosed by 26 weeks' gestation was associated with risk of autism spectrum disorders (ASDs), according to a study in the April 14 issue of JAMA. Maternal pre-existing type 2 diabetes was not significantly associated with risk of ASD in offspring.
Exposure of fetuses to maternal hyperglycemia may have long-lasting effects on organ development and function. Previous studies have revealed long-term risks of obesity and related metabolic disorders in offspring of women who ...
[1] ... [3033]
[3034]
[3035]
[3036]
[3037]
[3038]
[3039]
[3040]
3041
[3042]
[3043]
[3044]
[3045]
[3046]
[3047]
[3048]
[3049]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.