The mechanics of tissue growth
2014-09-23
PITTSBURGH – When the body forms new tissues during the healing process, cells must be able to communicate with each other. For years, scientists believed this communication happened primarily through chemical signaling. Now researchers at Carnegie Mellon University and the University of Pittsburgh have found that another dimension – mechanical communication – is equally if not more crucial. The findings, published in this week's issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, could lead to advancements in treatments for birth defects and therapies for cancer ...
Insects' fear limits boost from climate change, Dartmouth study shows
2014-09-23
Scientists often measure the effects of temperature on insects to predict how climate change will affect their distribution and abundance, but a Dartmouth study shows for the first time that insects' fear of their predators, in addition to temperature, ultimately limits how fast they grow.
"In other words, it's less about temperature and more about the overall environmental conditions that shape the growth, survival and distribution of insects." says the study's lead author Lauren Culler, an Arctic postdoctoral researcher at Dartmouth.
The study appears in the journal ...
Kessler Foundation researchers find foot drop stimulator beneficial in stroke rehab
2014-09-23
West Orange, NJ. September 23, 2014. Kessler Foundation scientists have published a study showing that use of a foot drop stimulator during a task-specific movement for 4 weeks can retrain the neuromuscular system. This finding indicates that applying the foot drop stimulator as rehabilitation intervention may facilitate recovery from this common complication of stroke. "EMG of the tibialis anterior demonstrates a training effect after utilization of a foot drop stimulator," was published online ahead of print on July 2 by NeuroRehabilitation (doi:10.3233/NRE-141126). The ...
'Brain Breaks' increase activity, educational performance in elementary schools
2014-09-23
CORVALLIS, Ore. – A recent Oregon survey about an exercise DVD that adds short breaks of physical activity into the daily routine of elementary school students found it had a high level of popularity with both students and teachers, and offered clear advantages for overly sedentary educational programs.
Called "Brain Breaks," the DVD was developed and produced by the Healthy Youth Program of the Linus Pauling Institute at Oregon State University, and is available nationally.
Brain Breaks leads children in 5-7 minute segments of physical activity, demonstrated by OSU ...
Surveys may assess language more than attitudes, says study involving CU-Boulder
2014-09-23
Scientists who study patterns in survey results might be dealing with data on language rather than what they're really after -- attitudes -- according to an international study involving the University of Colorado Boulder.
The study, published in the journal PLOS ONE, found that people naturally responded to surveys by selecting answer options that were similar in language to each other as they navigated from one question to another, even when the similarities were subtle.
For the study, researchers looked specifically at surveys on organizational behavior, such as ...
Researchers reveal new rock formation in Colorado
2014-09-23
Boulder, Colo., USA - An astonishing new rock formation has been revealed in the Colorado Rockies, and it exists in a deeply perplexing relationship with older rocks. Named the Tava sandstone, this sedimentary rock forms intrusions within the ancient granites and gneisses that form the backbone of the Front Range. The relationship is fascinating because it is backward: ordinarily, it is igneous rocks such as granite that would that intrude into sedimentary rocks.
According to authors Christine Smith Siddoway and George E. Gehrels, to find sandstone injected into granite ...
Note to young men: Fat doesn't pay
2014-09-23
Men who are already obese as teenagers could grow up to earn up to 18 percent less than their peers of normal weight. So says Petter Lundborg of Lund University, Paul Nystedt of Jönköping University and Dan-olof Rooth of Linneas University and Lund University, all in Sweden. The team compared extensive information from Sweden, the United Kingdom and the United States, and the results are published in Springer's journal Demography.
The researchers analyzed large-scale data of 145,193 Swedish-born brothers who enlisted in the Swedish National Service for mandatory military ...
Immune system is key ally in cyberwar against cancer
2014-09-23
Research by Rice University scientists who are fighting a cyberwar against cancer finds that the immune system may be a clinician's most powerful ally.
"Recent research has found that cancer is already adept at using cyberwarfare against the immune system, and we studied the interplay between cancer and the immune system to see how we might turn the tables on cancer," said Rice University's Eshel Ben-Jacob, co-author of a new study this week in the Early Edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Ben-Jacob and colleagues at Rice's Center for Theoretical ...
UTSA microbiologists discover regulatory thermometer that controls cholera
2014-09-23
Karl Klose, professor of biology and a researcher in UTSA's South Texas Center for Emerging Infectious Diseases, has teamed up with researchers at Ruhr University in Bochum, Germany to understand how humans get infected with cholera, Their findings were released this week in an article published by the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Cholera is an acute infection caused by ingestion of food or water that is contaminated with the bacterium Vibrio cholerae. An estimated three to five million cases are reported annually and 100,000-120,000 people die from ...
'Space bubbles' may have aided enemy in fatal Afghan battle
2014-09-23
WASHINGTON, DC—In the early morning hours of March 4, 2002, military officers in Bagram, Afghanistan desperately radioed a Chinook helicopter headed for the snowcapped peak of Takur Ghar. On board were 21 men, deployed to rescue a team of Navy SEALS pinned down on the ridge dividing the Upper and Lower Shahikot valley. The message was urgent: Do not land on the peak. The mountaintop was under enemy control.
The rescue team never got the message. Just after daybreak, the Chinook crash-landed on the peak under heavy enemy fire and three men were killed in the ensuing firefight.
A ...
This week from AGU: New geologic map of Mars, storm surge in Florida
2014-09-23
From this week's Eos: The New Geologic Map of Mars: Guiding Research and Education
Currently, five spacecraft are investigating Mars, and a swarm of new missions to the Red Planet either have been launched or are in development. They are designed to probe the surface, subsurface, and atmosphere with a host of scientific instruments. Where will they make new discoveries? Clues to where they should focus investigations can be gleaned from the planet's new geologic map.
From AGU's journals: History of storm surge in Florida strongly underestimated
The observational ...
Water-quality trading can reduce river pollution
2014-09-23
DURHAM, N.C. -- Allowing polluters to buy, sell or trade water-quality credits could significantly reduce pollution in river basins and estuaries faster and at lower cost than requiring the facilities to meet compliance costs on their own, a new Duke University-led study finds.
The scale and type of the trading programs, though critical, may matter less than just getting them started.
"Our analysis shows that water-quality trading of any kind can significantly lower the costs of achieving Clean Water Act goals," said Martin W. Doyle, professor of river science and policy ...
State policies are effective in reducing power plant emissions, CU-led study finds
2014-09-23
A new study led by the University of Colorado Boulder found that different strategies used by states to reduce power plant emissions -- direct ones such as emission caps and indirect ones like encouraging renewable energy -- are both effective. The study is the first analysis of its kind.
The findings are important because the success of the Environmental Protection Agency's proposed Clean Power Plan depends on the effectiveness of states' policies in reducing power plants' carbon dioxide emissions. The plan would require each state to cut CO2 pollution from power plants ...
Big changes in the Sargasso Sea
2014-09-23
Over one thousand miles wide and three thousand miles long, the Sargasso Sea occupies almost two thirds of the North Atlantic Ocean. Within the sea, circling ocean currents accumulate mats of Sargassum seaweed that shelter a surprising variety of fishes, snails, crabs, and other small animals. A recent paper by MBARI researcher Crissy Huffard and others shows that in 2011 and 2012 this animal community was much less diverse than it was in the early 1970s, when the last detailed studies were completed in this region.
This study was based on field research led by MBARI ...
Study finds gallbladder surgery can wait
2014-09-23
LOS ANGELES – (September 23, 2014) –Laparoscopic cholecystectomy, a minimally invasive procedure to remove the gallbladder, is one of the most common abdominal surgeries in the U.S. Yet medical centers around the country vary in their approaches to the procedure with some moving patients quickly into surgery while others wait.
In a study published online Monday in the American Journal of Surgery, researchers found gallbladder removal surgery can wait until regular working hours rather than rushing the patients into the operating room at night.
"The urgency of removing ...
'Bendy' LEDs
2014-09-23
VIDEO:
This is an animation of the micro-rod growth process.
Click here for more information.
WASHINGTON D.C., Sept. 23, 2014 -- "Bendy" light-emitting diode (LED) displays and solar cells crafted with inorganic compound semiconductor micro-rods are moving one step closer to reality, thanks to graphene and the work of a team of researchers in Korea.
Currently, most flexible electronics and optoelectronics devices are fabricated using organic materials. But inorganic compound ...
Diabetes: Complexity lost
2014-09-23
WASHINGTON, D.C., September 23, 2014 -- For millions of people in the United States living with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, measuring the daily rise and fall of blood glucose (sugar) is a way of life.
Our body's energy is primarily governed by glucose in the blood, and blood sugar itself is exquisitely controlled by a complicated set of network interactions involving cells, tissues, organs and hormones that have evolved to keep the glucose on a relatively even keel, pumping it up when it falls too low or knocking it down when it goes too high. This natural dynamical balance ...
Future flexible electronics based on carbon nanotubes
2014-09-23
WASHINGTON, D.C., September 23, 2014—Researchers from the University of Texas at Austin and Northwestern University have demonstrated a new method to improve the reliability and performance of transistors and circuits based on carbon nanotubes (CNT), a semiconductor material that has long been considered by scientists as one of the most promising successors to silicon for smaller, faster and cheaper electronic devices. The result appears in a new paper published in the journal Applied Physics Letters, from AIP Publishing.
In the paper, researchers examined the effect ...
Lack of sleep increases risk of failure in school
2014-09-23
A new Swedish study shows that adolescents who suffer from sleep disturbance or habitual short sleep duration are less likely to succeed academically compared to those who enjoy a good night's sleep. The results have recently been published in the journal Sleep Medicine.
In a new study involving more than 20,000 adolescents aged between 12 and 19 from Uppsala County, researchers from Uppsala University demonstrate that reports of sleep disturbance and habitual short sleep duration (less than 7 hours per day) increased the risk of failure in school.
The study was led ...
Moving to the 'burbs is bad for business
2014-09-23
This news release is available in French. Montreal, September 23, 2014 — It's rare to see a Wal-Mart downtown. Big box stores usually set up shop in the suburbs, where rent is cheap and the consumer base is growing. So should smaller stores follow suit?
Not so fast, says Concordia University professor Tieshan Li. His recent study, published in the Canadian Journal of Administrative Sciences, shows that higher profits are had by retailers located furthest from where the market is expanding.
"Those results may seem counterintuitive but the decreased profits are ...
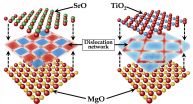
Los Alamos researchers uncover properties in nanocomposite oxide ceramics for reactor fuel
2014-09-23
Nanocomposite oxide ceramics have potential uses as ferroelectrics, fast ion conductors, and nuclear fuels and for storing nuclear waste, generating a great deal of scientific interest on the structure, properties, and applications of these blended materials.
"The interfaces separating the different crystalline regions determine the transport, electrical, and radiation properties of the material as a whole," said Pratik Dholabhai, principal Los Alamos National Laboratory researcher on the project. "It is in the chemical makeup of these interfaces where we can improve ...
Beating stress outdoors? Nature group walks may improve mental health
2014-09-23
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — They are common suggestions to remedy stress: You just need a breath of fresh air. Walk it off. Get out and see people.
Turns out all those things combined may in fact make you feel better – a lot better – a new large scale study suggests.
Group nature walks are linked with significantly lower depression, less perceived stress and enhanced mental health and well-being, according to the study conducted by the University of Michigan, with partners from De Montfort University, James Hutton Institute, and Edge Hill University in the United Kingdom. The ...
Paraffins to cut energy consumption in homes
2014-09-23
Thermal energy storage is a common strategy in energy production systems in which the period of production does not coincide with that of consumption. This happens with the production of hot water by means of solar thermal panels, for example; here, hot water is produced during sunlight hours when demand is lower. It is also the case in residential cogeneration, where heat and electrical power are simultaneously generated but not so demand. In both cases, storing the heat allows production to be decoupled from demand, thus making the integration of these technologies into ...
Advancing the understanding of an understudied food allergy disorder
2014-09-23
Investigators at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center have published the first study to extensively characterize eosinophilic gastritis (EG). The study, published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, found that EG is a systemic disorder that has high levels of eosinophils in the blood and gastrointestinal tract, involves a series of allergy-associated-immune mechanisms and has a gene expression pattern (transcriptome) that is distinct from that of a related disorder, eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE).
Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders are chronic ...
Gene mutation discovered in blood disorder
2014-09-23
An international team of scientists has identified a gene mutation that causes aplastic anemia, a serious blood disorder in which the bone marrow fails to produce normal amounts of blood cells. Studying a family in which three generations had blood disorders, the researchers discovered a defect in a gene that regulates telomeres, chromosomal structures with crucial roles in normal cell function.
"Identifying this causal defect may help suggest future molecular-based treatments that bypass the gene defect and restore blood cell production," said study co-leader Hakon Hakonarson, ...
[1] ... [3320]
[3321]
[3322]
[3323]
[3324]
[3325]
[3326]
[3327]
3328
[3329]
[3330]
[3331]
[3332]
[3333]
[3334]
[3335]
[3336]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.