Changes in coastal upwelling linked to temporary declines in marine ecosystem
2014-09-19
In findings of relevance to both conservationists and the fishing industry, new research links short-term reductions in growth and reproduction of marine animals off the California Coast to increasing variability in the strength of coastal upwelling currents — currents which historically supply nutrients to the region's diverse ecosystem.
Along the west coast of North America, winds lift deep, nutrient-rich water into sunlit surface layers, fueling vast phytoplankton blooms that ultimately support fish, seabirds and marine mammals.
The new study, led by Bryan Black ...
World population to keep growing this century, hit 11 billion by 2100
2014-09-19
Using modern statistical tools, a new study led by the University of Washington and the United Nations finds that world population is likely to keep growing throughout the 21st century. The number of people on Earth is likely to reach 11 billion by 2100, the study concludes, about 2 billion higher than some previous estimates.
The paper published online Sept. 18 in the journal Science includes the most up-to-date estimates for future world population, as well as a new method for creating such estimates.
"The consensus over the past 20 years or so was that world population, ...
Scientists discover 'dimmer switch' for mood disorders
2014-09-19
Researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have identified a control mechanism for an area of the brain that processes sensory and emotive information that humans experience as "disappointment."
The discovery of what may effectively be a neurochemical antidote for feeling let-down is reported Sept. 18 in the online edition of Science.
"The idea that some people see the world as a glass half empty has a chemical basis in the brain," said senior author Roberto Malinow, MD, PhD, professor in the Department of Neurosciences and neurobiology section ...
Study shows how epigenetic memory is passed across generations
2014-09-19
A growing body of evidence suggests that environmental stresses can cause changes in gene expression that are transmitted from parents to their offspring, making "epigenetics" a hot topic. Epigenetic modifications do not affect the DNA sequence of genes, but change how the DNA is packaged and how genes are expressed. Now, a study by scientists at the University of California, Santa Cruz, shows how epigenetic memory can be passed across generations and from cell to cell during development.
The study, published September 19 in Science, focused on one well studied epigenetic ...
New insights into the world of quantum materials
2014-09-19
This news release is available in German.
How a system behaves is determined by its interaction properties. An important concept in condensed matter physics for describing the energy distribution of electrons in solids is the Fermi surface, named for Italian physicist Enrico Fermi. The existence of the Fermi surface is a direct consequence of the Pauli exclusion principle, which forbids two identical fermions from occupying the same quantum state simultaneously. Energetically, the Fermi surface divides filled energy levels from the empty ones. For electrons and other ...
A more efficient, lightweight and low-cost organic solar cell
2014-09-19
AMHERST, Mass. – For decades, polymer scientists and synthetic chemists working to improve the power conversion efficiency of organic solar cells were hampered by the inherent drawbacks of commonly used metal electrodes, including their instability and susceptibility to oxidation. Now for the first time, researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst have developed a more efficient, easily processable and lightweight solar cell that can use virtually any metal for the electrode, effectively breaking the "electrode barrier."
This barrier has been a big problem ...
Pupil size shows reliability of decisions
2014-09-19
The precision with which people make decisions can be predicted by measuring pupil size before they are presented with any information about the decision, according to a new study published in PLOS Computational Biology this week.
The study, conducted by Peter Murphy and colleagues at Leiden University, showed that spontaneous, moment-to-moment fluctuations in pupil size predicted how a selection of participants varied in their successful decision making. A larger pupil size indicated poorer upcoming task performance, due to more variability in the decisions made once ...
World breakthrough: A new molecule allows for an increase in stem cell transplants
2014-09-19
This news release is available in French. Investigators from the Institute for Research in Immunology and Cancer (IRIC) at the Université de Montréal have just published, in the prestigious magazine Science, the announcement of the discovery of a new molecule, the first of its kind, which allows for the multiplication of stem cells in a unit of cord blood. Umbilical cord stem cells are used for transplants aimed at curing a number of blood-related diseases, including leukemia, myeloma and lymphoma. For many patients this therapy comprises a treatment of last resort.
Directed ...
Toward optical chips
2014-09-19
Chips that use light, rather than electricity, to move data would consume much less power — and energy efficiency is a growing concern as chips' transistor counts rise.
Of the three chief components of optical circuits — light emitters, modulators, and detectors — emitters are the toughest to build. One promising light source for optical chips is molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), which has excellent optical properties when deposited as a single, atom-thick layer. Other experimental on-chip light emitters have more-complex three-dimensional geometries and use rarer materials, ...
Mouse model sheds light on role of mitochondria in neurodegenerative diseases
2014-09-19
(SALT LAKE CITY)—A new study by researchers at the University of Utah School of Medicine sheds light on a longstanding question about the role of mitochondria in debilitating and fatal motor neuron diseases and resulted in a new mouse model to study such illnesses.
Researchers led by Janet Shaw, Ph.D., professor of biochemistry, found that when healthy, functioning mitochondria was prevented from moving along axons – nerve fibers that conduct electricity away from neurons – mice developed symptoms of neurodegenerative diseases. In a study in the Proceedings of the ...
Penn research helps uncover mechanism behind solid-solid phase transitions
2014-09-19
Two solids made of the same elements but with different geometric arrangements of the atoms, or crystal phases, can produce materials with different properties. Coal and diamond offer a spectacular example of this effect.
While it is well known that one crystal phase can transform into another under the right circumstances, the mechanisms that facilitate solid-to-solid transitions are still not well understood. Atoms can rearrange themselves to transform from a "parent" phase into a "daughter" phase by two major routes, but it is difficult to predict which route a material ...
Evolution of responses to (un)fairness
2014-09-19
The sense of fairness did not evolve for the sake of fairness per se but in order to reap the benefits of continued cooperation, so say Frans de Waal, PhD, and Sarah Brosnan, PhD, co-authors of a review article about inequity aversion (IA), which is defined as a negative reaction to unequal outcomes. The review is published in Science.
Their conclusion comes after the co-authors reviewed more than 35 IA-related studies to address their hypothesis that it is the evolution of forestalling partner dissatisfaction with obtained outcomes and its negative impact on future ...
Even without kids, couples eat frequent family meals
2014-09-19
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Couples and other adult family members living without minors in the house are just as likely as adults living with young children or adolescents to eat family meals at home on most days of the week, new research suggests.
The study is the first large-scale look at family-meal eating patterns in American adults. While a substantial amount of research has focused on health benefits for children who regularly eat family meals, such eating patterns have not been widely studied in adult-only households.
Researchers analyzed data on more than 14,000 Ohio ...
For legume plants, a new route from shoot to root
2014-09-19
A new study shows that legume plants regulate their symbiotic relationship with soil bacteria by using cytokinins—signaling molecules— that are transmitted through the plant structure from leaves into the roots to control the number of bacteria-holding nodules in the roots. This collaborative study was conducted by researchers from the National Institute for Basic Biology, the Graduate University for Advanced Studies (SOKENDAI), and the RIKEN Center for Sustainable Resource Science in Japan.
Legumes, an important plant family which includes lentils, soybeans, and peanuts, ...
Monster galaxies gain weight by eating smaller neighbors
2014-09-19
VIDEO:
In about five billion years time, nearby massive galaxy Andromeda will merge with our own galaxy, the Milky Way, in an act of galactic cannibalism (technically Andromeda will be eating...
Click here for more information.
Massive galaxies in the Universe have stopped making their own stars and are instead snacking on nearby galaxies, according to research by Australian scientists.
Astronomers looked at more than 22,000 galaxies and found that while smaller galaxies ...
The 'Angelina Effect' was not only immediate, but also long-lasting
2014-09-19
Referrals for genetic counselling and testing for breast cancer risk more than doubled across the UK after actress Angelina Jolie announced in May last year that she tested positive for a BRCA1 gene mutation and underwent a double mastectomy. The rise in referrals continued through to October long after the announcement was made. This is according to research published in the journal Breast Cancer Research.
New research based on data from 21 centers shows that many more women approached their GPs with concerns. Far from these being women with unfounded concerns, it ...
Experts issue plea for better research and education for advanced breast cancer
2014-09-19
Breast cancer experts around the world have issued a plea to researchers, academics, drug companies, funders and advocates to carry out high quality research and clinical trials for advanced breast cancer, a disease which is almost always fatal and for which there are many unanswered questions.
In the latest international consensus guidelines for the management of advanced breast cancer, published simultaneously in the leading cancer journals The Breast and Annals of Oncology [1] today (Friday), the experts say that further research and clinical trials are "urgently needed" ...
Gun deaths twice as high among African-Americans as white citizens in US
2014-09-19
The researchers looked at all recorded gun deaths across the USA between 2000 and 2010, to include murders, suicides, and unintentional shooting, using data from the Injury Statistics Query and Reporting System.
Hawaii recorded the lowest rate of gun deaths at 3.02 per 100 000 citizens, while the District of Columbia topped the league table at 21.71 per 100 000. Rates rose in Florida and Massachusetts, largely owing to more gun deaths among people of white and non-Hispanic ethnicities, and an increase in the gun related murder rate.
Firearm deaths fell in Arizona, California, ...
Cooling of dialysis fluids protects against brain damage
2014-09-19
Washington, DC (September 18, 2014) — While dialysis can cause blood pressure changes that damage the brain, cooling dialysis fluids can protect against such effects. The findings come from a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (JASN). The cooling intervention can be delivered without additional cost and is simple to perform.
While dialysis is an essential treatment for many patients with kidney disease, it can cause damage to multiple organs, including the brain and heart, due to the sudden removal of bodily fluids. ...
Vitamin E, selenium supplements unlikely to effect age-related cataracts in men
2014-09-18
Taking daily supplements of selenium and/or vitamin E appears to have no significant effect on the development of age-related cataracts in men, writes Author William G. Christen, Sc.D., of Brigham & Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
Some research, including animal studies, has suggested that dietary nutrients can have an effect on the onset and progression of cataracts. Vitamin E and selenium are of particular interest.
The authors report the findings for cataracts from the Selenium and Vitamin E Cancer Prevention Trial (SELECT) Eye ...
Exercise boosts tumor-fighting ability of chemotherapy, Penn team finds
2014-09-18
Study after study has proven it true: exercise is good for you. But new research from University of Pennsylvania scientists suggests that exercise may have an added benefit for cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy.
Their work, performed in a mouse model of melanoma, found that combining exercise with chemotherapy shrunk tumors more than chemotherapy alone.
Joseph Libonati, an associate professor in the School of Nursing and director of the Laboratory of Innovative and Translational Nursing Research, was the senior author on the study, which appears in the American ...
Researchers study vital 'on/off switches' that control when bacteria turn deadly
2014-09-18
MADISON, Wis. — No matter how many times it's demonstrated, it's still hard to envision bacteria as social, communicating creatures.
But by using a signaling system called "quorum sensing," these single-celled organisms radically alter their behavior to suit their population. In short, some bacteria "know" how many of them are present, and act accordingly.
Once the population of quorum-sensing bacteria reaches the millions, it may change from innocuous to pathogenic, or from unhelpful to helpful. The quorum-sensing messages are carried in small molecules that the bacteria ...
Researchers develop unique waste cleanup for rural areas
2014-09-18
PULLMAN, Wash. - Washington State University researchers have developed a unique method to use microbes buried in pond sediment to power waste cleanup in rural areas.
The first microbe-powered, self-sustaining wastewater treatment system could lead to an inexpensive and quick way to clean up waste from large farming operations and rural sewage treatment plants while reducing pollution.
Professor Haluk Beyenal and graduate student Timothy Ewing in the Voiland College of Engineering and Architecture discuss the system in the online edition of Journal of Power Sources ...
Video games could dramatically streamline educational research
2014-09-18
PULLMAN, Wash. – "Seeking educational curriculum researchers. Humans need not apply."
A Washington State University professor has figured out a dramatically easier and more cost-effective way to do research on science curriculum in the classroom – and it could include playing video games.
Called "computational modeling," it involves a computer "learning" student behavior and then "thinking" as students would. Rich Lamb, who teaches science education at WSU's College of Education, said the process could revolutionize the way educational research is done.
Lamb's research ...
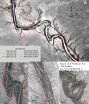
Tree rings and arroyos
2014-09-18
Boulder, Colo., USA – A new GSA Bulletin study uses tree rings to document arroyo evolution along the lower Rio Puerco and Chaco Wash in northern New Mexico, USA. By determining burial dates in tree rings from salt cedar and willow, investigators were able to precisely date arroyo sedimentary beds 30 cm thick or greater. They then combined this data with aerial imagery, LiDAR, longitudinal profiles, and repeat surveys to reconstruct the history of these arroyos.
Arroyos are deep, oversized channels that have vertical or steeply cut walls made up of silt, clay, or sand. ...
[1] ... [3328]
[3329]
[3330]
[3331]
[3332]
[3333]
[3334]
[3335]
3336
[3337]
[3338]
[3339]
[3340]
[3341]
[3342]
[3343]
[3344]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.