Peacock's train is not such a drag
2014-09-18
The magnificent plumage of the peacock may not be quite the sacrifice to love that it appears to be, University of Leeds researchers have discovered.
Dr Graham Askew, from the University's School of Biomedical Sciences, filmed five Indian peacocks taking off using two high-speed video cameras to try to work out what price male birds pay for carrying the spectacular iridescent feathers they use in displays to attract females.
"These feathers weigh about 300g and can exceed 1.5m, so it's expected that the male birds would be making a significant sacrifice in their flight ...
'Office life' of bacteria may be their weak spot
2014-09-18
Scientists at the University of Leeds think we may be able to drown deadly bacteria in their own paperwork.
A research team in the University's Astbury Centre for Structural Molecular Biology has identified for the first time how the "paper shredder" that keeps the bacteria E. coli on top of its day job works.
Now the group are looking for ways to jam the mechanism and leave E. coli and similar bacteria in filing hell.
Dr Kenneth McDowall, Associate Professor in Molecular Microbiology, who led the research, said: "If we block the 'shredder' using genetics in the ...
Space: The final frontier ... open to the public
2014-09-18
Historically, spaceflight has been reserved for the very healthy. Astronauts are selected for their ability to meet the highest physical and psychological standards to prepare them for any unknown challenges. However, with the advent of commercial spaceflight, average people can now fly for enjoyment. The aerospace medicine community has had very little information about what medical conditions or diseases should be considered particularly risky in the spaceflight environment, as most medical conditions have never been studied for risk in space — until now.
The aerospace ...
Nile River monitoring influences northeast Africa's future
2014-09-18
Curtin University research that monitors the volume of water in the Nile River Basin will help to level the playing field for more than 200 million North-East Africans who rely on the river's water supply.
Despite being arguably the longest river in the world, winding through nine different countries, the Nile River is shallow and has a low volume, making its water precious, particularly to those countries located downstream.
Curtin Associate Professor Joseph Awange, Department of Spatial Sciences, has been monitoring extractions or additions of water to the Nile River, ...
Kids eat better if their parents went to college
2014-09-18
Children of college-educated parents eat more vegetables and drink less sugar, according to a new study from the University of British Columbia. But it's still not enough, the study goes on to say, as all kids are falling short when it comes to eating healthier at school
The research suggests a parent's educational attainment, an indicator of socioeconomic status, may inform a child's diet.
The study found Vancouver school children whose parents completed some post-secondary education were 85 per cent more likely to eat vegetables during the school week than those with ...
Dogs can be pessimists too
2014-09-18
Dogs generally seem to be cheerful, happy-go-lucky characters, so you might expect that most would have an optimistic outlook on life.
In fact some dogs are distinctly more pessimistic than others, research from the University of Sydney shows.
"This research is exciting because it measures positive and negative emotional states in dogs objectively and non-invasively. It offers researchers and dog owners an insight into the outlook of dogs and how that changes," said Dr Melissa Starling, from the Faculty of Veterinary Science. Her PhD research findings are published ...
The viability of premature babies is minimal at 22 weeks' gestation
2014-09-18
A new study analyses the survival rates in Spain of newborns with a gestational age under 26 weeks. The results show that survival under 23 weeks is 'exceptional', although other factors such as birth weight and sex also have an influence.
Experts from the Spanish Society of Neonatology have studied the survival rates in Spain of newborns with a gestational age under 26 weeks, taking into account that a newborn carried to term is between 37 and 42 weeks.
The data have been drawn from the national database that gathers information on all babies born weighing less than ...
A second look at glaucoma surgery
2014-09-18
New research led by Queen's University professor Robert Campbell (Ophthalmology) has revealed using anti-inflammatory medications after glaucoma laser surgery is not helpful or necessary.
Glaucoma is the most common cause of irreversible blindness in the world and about 400,000 Canadians are afflicted with the disease, which is mainly caused by pressure within the eye being high enough to damage the optic nerve. The optic nerve is responsible for sending messages from the eye to the brain and is a vital part of vision.
"The use of strong anti-inflammatory therapies after ...
Tropical fish a threat to Mediterranean Sea ecosystems
2014-09-18
The tropical rabbitfish which have devastated algal forests in the eastern Mediterranean Sea pose a major threat to the entire Mediterranean basin if their distribution continues to expand as the climate warms, a new study warns.
The study, by an international team of researchers led by Dr Adriana Vergés of UNSW Australia and Dr Fiona Tomas of the Mediterranean Institute for Advanced Studies in Spain, is published in the Journal of Ecology.
Members of the team surveyed more than 1000 kilometres of coastline in Turkey and Greece, where two species of rabbitfish have become ...
University of Kentucky research explores STXBP5 gene and its role in blood clotting
2014-09-18
LEXINGTON, Ky (Sept. 17, 2014) -- Two independent groups of researchers led by Sidney (Wally) Whiteheart, PhD, of the University of Kentucky, and Charles Lowenstein, MD, of the University of Rochester, have published important studies exploring the role that a gene called STXBP5 plays in the development of cardiovascular disease.
According to Whiteheart, previous genome-wide association studies (GWAS) identified a gene called STXBP5 as a factor that regulates a protein called Von Willebrand factor (VWF).
VWF is an important contributor to normal blood clotting. When ...
UT Dallas study uncovers factors in students' reporting of weapons at school
2014-09-18
As a result of outbreaks of violence in the nation's schools, concerns have grown about school safety and the overall well-being of students.
In a new study, UT Dallas criminology researchers have found that certain factors affect students' willingness to report weapons at school.
"A big part of adolescent development is figuring out your identity, and that does not always mean talking to grown-ups about what is going on," said Dr. Nadine Connell, assistant professor of criminology in the School of Economic, Political and Policy Sciences. "We can't stop students from ...
Improving medicines for children in Canada
2014-09-18
Ottawa (September 18, 2014) – A new expert panel report, Improving Medicines for Children in Canada, released today by the Council of Canadian Academies, addresses the importance of developing safe and effective medicines for children. Each year about half of Canada's seven million children use at least one prescription drug. Much of this prescribing is done off-label (i.e. the prescription differs from the authorized use), creating potential health risks.
Children have historically been excluded in drug research and development, including clinical trials. As a result, ...
Rosuvastatin treatments particularly effective among prediabetic patients
2014-09-18
Los Angeles, CA (September 18, 2014) Cardiovascular disease is the leading causes of death worldwide and high cholesterol plays a major role in accelerating its progression. Medical practitioners have turned to statins as a treatment to decrease cholesterol-carrying lipoproteins such as small dense lipoproteins (sdLDL), considered to be especially harmful. A new study, out today in the Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology and Therapeutics finds that rosuvastatin may be more effective among prediabetic patients than patients with normal glucose levels.
Study author ...
Middle school dilemma: Girls' body image affected by older peers
2014-09-18
Los Angeles, CA (September 18, 2014) The media is highly criticized for contributing to body image issues in adolescents. However, a study out today in Psychology of Women Quarterly finds a different source for body dissatisfaction among young girls: older girls at school.
A research team led by Jaine Strauss, Professor of Psychology at Macalester College, surveyed 1,536 5th through 8th-grade female students attending schools with different grade groupings. Some 5th and 6th graders attended school with older students (i.e. in districts that follow the "middle school" ...
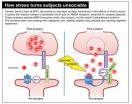
How stress tears us apart
2014-09-18
Why is it that when people are too stressed they are often grouchy, grumpy, nasty, distracted or forgetful? Researchers from the Brain Mind Institute (BMI) at EPFL have just highlighted a fundamental synaptic mechanism that explains the relationship between chronic stress and the loss of social skills and cognitive impairment. When triggered by stress, an enzyme attacks a synaptic regulatory molecule in the brain. This was revealed by a work published in Nature Communications.
Carmen Sandi's team went to look for answers in a region of the hippocampus known for its involvement ...
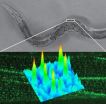
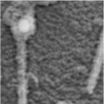
Scientists pioneer microscopy technique that yields fresh data on muscular dystrophy
2014-09-18
Scientists at USC have developed a new microscopy technology that allows them to view single molecules in living animals at higher-than-ever resolution.
Dubbed "Complementation Activated Light Microscopy" (CALM), the new technology allows imaging resolutions that are an order of magnitude finer than conventional optical microscopy, providing new insights into the behavior of biomolecules at the nanometer scale.
In a paper published on Sept. 18 by Nature Communications, the researchers behind CALM used it to study dystrophin – a key structural protein of muscle cells ...
In mice, vaccine stops urinary tract infections linked to catheters
2014-09-18
The most common type of hospital-associated infection may be preventable with a vaccine, new research in mice suggests.
The experimental vaccine, developed by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, prevented urinary tract infections associated with catheters, the tubes used in hospitals and other care facilities to drain urine from a patient's bladder.
Each day a catheter is present in the urethra and the bladder, the risk of urinary tract infection increases. Nearly every patient who has a catheter for more than 30 days acquires a urinary ...
Migraine in middle age linked to increased risk of Parkinson's, movement disorders later
2014-09-17
MINNEAPOLIS – A new study suggests that people who experience migraine in middle age may be more likely to develop Parkinson's disease, or other movement disorders later in life. Those who have migraine with aura may be at double the risk of developing Parkinson's, according to the study published in the September 17, 2014, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
"Migraine is the most common brain disorder in both men and women," said study author Ann I. Scher, PhD, with Uniformed Services University in Bethesda, MD, and ...
For some lung cancer patients, surgery may yield better long-term results
2014-09-17
(September 17, 2014, San Francisco) – Patients with early stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who are otherwise healthy fare better over time if they undergo conventional surgery versus less-invasive radiosurgery to remove their cancer, according to a Yale study. The findings are scheduled to be presented at the 56th annual conference of the American Society for Radiation Oncology in San Francisco. (Abstract # 302; Comparative Effectiveness of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy versus Surgery for Stage I Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.)
The study used Medicare billing records ...
Brain imaging research pinpoints neurobiological basis for key symptoms associated with post-traumatic stress disorder like listlessness and emotional detachment in trauma victims
2014-09-17
NEW YORK, NY, September 17, 2014 - In a novel brain-imaging study among trauma victims, researchers at NYU Langone Medical Center have linked an opioid receptor in the brain -- associated with emotions -- to a narrow cluster of trauma symptoms, including sadness, emotional detachment and listlessness. The study, published online today in the journal JAMA Psychiatry, holds important implications for targeted, personalized treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder, or PTSD, a psychiatric condition affecting more than 8 million Americans that can cause a wide range of debilitating ...
PTSD symptoms associated with increased food addiction
2014-09-17
Bottom Line: Symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) were associated with increased food addiction, especially when individuals had more symptoms or the symptoms occurred earlier in life.
Authors: Susan M. Mason, Ph.D., of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and colleagues.
Background: PTSD is a potentially severe psychiatric condition. A growing body of evidence suggests that PTSD is a risk factor for obesity and obesity-related diseases. Food addiction is not established as a psychiatric diagnosis but may indicate use of food to cope with psychological ...
Vitiligo treatment holds promise for restoring skin pigmentation
2014-09-17
VIDEO:
Henry Lim, M.D., chair of Dermatology, Henry Ford Hospital, highlights the study.
Click here for more information.
DETROIT – A treatment regimen is safe and effective for restoring skin pigmentation in vitiligo patients, according to a Henry Ford Hospital study.
"Our findings offer patients with vitiligo worldwide a renewed hope for a bright future in the treatment of this disfiguring disease," says Henry Lim, M.D., chair of Dermatology at Henry Ford and the study's ...
Combo of phototherapy, drug results in faster repigmentation in vitiligo
2014-09-17
Bottom Line: Patients with the skin depigmentation disease known as vitiligo had faster and better repigmentation after a combination therapy of the implantable drug afamelanotide and narrowband UV-B (NB-UV-B) phototherapy as part of a clinical trial.
Author: Henry W. Lim, M.D., of Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, Mich., and colleagues.
Background: Vitiligo is characterized by white patches of skin and affects 1 percent to 2 percent of the population. The authors report the results of a multicenter randomized clinical trial comparing the safety and effectiveness of the ...
Chromosome buffers hold key to better melanoma understanding
2014-09-17
Buffers that guard against damage to the ends of chromosomes could hold the key to a better understanding of malignant melanoma – the deadliest form of skin cancer – according to new research from the University of Leeds.
The study has uncovered an important new genetic risk factor for melanoma.
It is well known that pigmentation and mole count are the strongest indicators of those most at risk of developing melanoma. For example, paler people should take more care in the sun, as they burn more easily.
It now appears that another risk factor is the length of telomeres, ...
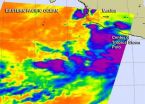
NASA sees Tropical Storm Polo intensifying
2014-09-17
Tropical storm warnings now issued for a portion of the Southwestern coast of Mexico as Polo continues to strengthen. Infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite showed powerful thunderstorms around the center of the storm.
A Tropical Storm Warning is in force for the southwest coast of Mexico from Punta San Telmo to Playa Perula. A Tropical Storm Watch is in force from Punta San Telmo to Zihuatanejo and from Playa Perula to Cabo Corrientes. Rainfall totals of 5 to 10, locally up to 15 inches, can be expected over coastal areas of Michoacan, Colima and Jalisco states ...
[1] ... [3331]
[3332]
[3333]
[3334]
[3335]
[3336]
[3337]
[3338]
3339
[3340]
[3341]
[3342]
[3343]
[3344]
[3345]
[3346]
[3347]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.