Smallest known galaxy with a supermassive black hole
2014-09-17
SALT LAKE CITY, Sept. 17, 2014 – A University of Utah astronomer and his colleagues discovered that an ultracompact dwarf galaxy harbors a supermassive black hole – the smallest galaxy known to contain such a massive light-sucking object. The finding suggests huge black holes may be more common than previously believed.
"It is the smallest and lightest object that we know of that has a supermassive black hole," says Anil Seth, lead author of an international study of the dwarf galaxy published in Thursday's issue of the journal Nature. "It's also one of the most black ...
Gut bacteria, artificial sweeteners and glucose intolerance
2014-09-17
Artificial sweeteners, promoted as aids to weight loss and diabetes prevention, could actually hasten the development of glucose intolerance and metabolic disease; and they do it in a surprising way: by changing the composition and function of the gut microbiota – the substantial population of bacteria residing in our intestines. These findings, the results of experiments in mice and humans, were published today in Nature. Among other things, says Dr. Eran Elinav of the Weizmann Institute's Immunology Department, who led this research together with Prof. Eran Segal of Computer ...
New branch added to European family tree
2014-09-17
The setting: Europe, about 7,500 years ago.
Agriculture was sweeping in from the Near East, bringing early farmers into contact with hunter-gatherers who had already been living in Europe for tens of thousands of years.
Genetic and archaeological research in the last 10 years has revealed that almost all present-day Europeans descend from the mixing of these two ancient populations. But it turns out that's not the full story.
Researchers at Harvard Medical School and the University of Tübingen in Germany have now documented a genetic contribution from a third ancestor: ...
Natural born killers: Chimpanzee violence is an evolutionary strategy
2014-09-17
ANN ARBOR—Man's nearest relatives kill each other in order to eliminate rivals and gain better access to territory, mates, food or other resources—not because human activities have made them more aggressive.
That is the conclusion of an international analysis of lethal aggression among different groups of chimpanzees in Africa studied over five decades. The research appears in the current issue of Nature.
"Observations that chimpanzees kill members of their own species have influenced efforts to understand the evolution of human violence," said University of Michigan ...
What set the Earth's plates in motion?
2014-09-17
The mystery of what kick-started the motion of our earth's massive tectonic plates across its surface has been explained by researchers at the University of Sydney.
"Earth is the only planet in our solar system where the process of plate tectonics occurs," said Professor Patrice Rey, from the University of Sydney's School of Geosciences.
"The geological record suggests that until three billion years ago the earth's crust was immobile so what sparked this unique phenomenon has fascinated geoscientists for decades. We suggest it was triggered by the spreading of early ...
Nature of war: Chimpanzees inherently violent according to study
2014-09-17
(Chicago) -- Of all of the world's species, humans and chimpanzees are some of the only to engage in coordinated attacks on other members of their same species. Jane Goodall was among the first to introduce the occurrence of lethal inter-community killings and since then primatologists and anthropologists have long debated the concept of warfare in this genus. Research theories have pointed to increased gains and benefits of killing off competitors and opening up increased access to key resources such as food or mates. In contrast, others have argued that warfare is a result ...
Modern Europeans descended from three groups of ancestors
2014-09-17
New studies of ancient DNA are shifting scientists' ideas of how groups of people migrated across the globe and interacted with one another thousands of years ago. By comparing nine ancient genomes to those of modern humans, Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) scientists have shown that previously unrecognized groups contributed to the genetic mix now present in most modern-day Europeans.
"There are at least three major, highly differentiated populations that have contributed substantial amounts of ancestry to almost everybody that has European ancestry today," says ...
Chimpanzee lethal aggression a result of adaptation rather than human impacts
2014-09-17
In the 1970s, Jane Goodall's reports of chimpanzee violence caught the attention of a global audience. Since then, many people have compared chimpanzee intergroup aggression to primitive warfare and have argued that chimpanzee violence is an adaptive strategy that gives the perpetrators an edge. Others have argued that lethal aggression is the consequence of human activities such as provisioning (artificial feeding) by researchers or habitat destruction. A new study of the pattern of intergroup aggression in chimpanzees and their close relatives, bonobos (also called pygmy ...
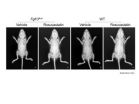
Researchers use iPS cells to show statin effects on diseased bone
2014-09-17
Skeletal dysplasia is a group of rare diseases that afflict skeletal growth through abnormalities in bone and cartilage. Its onset hits at the fetal stage and is caused by genetic mutations. A mutation in the gene encoding fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) has been associated with two types of skeletal dysplasia, thanatophoric dysplasia (TD), a skeletal dysplasia that cause serious respiratory problems at birth and is often lethal, and achondroplasia (ACH), which causes stunted growth and other complications throughout life. Several experimental treatments have ...
Math model designed to replace invasive kidney biopsy for lupus patients
2014-09-17
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Mathematics might be able to reduce the need for invasive biopsies in patients suffering kidney damage related to the autoimmune disease lupus.
In a new study, researchers developed a math model that can predict the progression from nephritis – kidney inflammation – to interstitial fibrosis, scarring in the kidney that current treatments cannot reverse. A kidney biopsy is the only existing way to reach a definitive diagnosis of the damage and its extent.
The model could also be used to monitor the effectiveness of experimental treatments for inflammation ...
Large study reveals new genetic variants that raise risk for prostate cancer
2014-09-17
In an analysis of genetic information among more than 87,000 men, a global team of scientists says it has found 23 new genetic variants – common differences in the genetic code -- that increase a man's risk for prostate cancer. The so-called "meta-analysis," believed to be the largest of its kind, has revealed once hidden mutations among men in a broad array of ethnic groups comprising men of European, African, Japanese and Latino ancestry.
The meta-analysis combined information from smaller studies, according to William B. Isaacs, Ph.D., a genetic scientist at the Brady ...
Babies learn words differently as they age, researcher finds
2014-09-17
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Research has shown that most 18-month-olds learn an average of two to five new words a day; however, little is known about how children process information to learn new words as they move through the preschool years. In a new study, a University of Missouri researcher has found that toddlers learn words differently as they age, and a limit exists as to how many words they can learn each day. These findings could help parents enhance their children's vocabularies and assist speech-language professionals in developing and refining interventions to help children ...
Contributions on Fauna Europaea: Data papers as innovative model on expert involvement
2014-09-17
Fauna Europaea started in 2000 as an EC-FP5 four-year project, delivering its first release in 2004. After 14 years of steady progress and successful participations in several EC projects, as a part of the EC-FP7 European Biodiversity Observation Network project (EU BON), to increase the general awareness of the work done by the contributors and to extend the general dissemination of the Fauna Europaea results, the Biodiversity Data Journal has applied its novel e-Publishing tools to prepare data papers for all 56 major taxonomic groups.
Fauna Europaea provides a public ...
Big surprises can come in small packages
2014-09-17
Astronomers using the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope have found a monster lurking in a very unlikely place. New observations of the ultracompact dwarf galaxy M60-UCD1 have revealed a supermassive black hole at its heart, making this tiny galaxy the smallest ever found to host a supermassive black hole. This suggests that there may be many more supermassive black holes that we have missed, and tells us more about the formation of these incredibly dense galaxies. The results will be published in the journal Nature on 18 September 2014.
Lying about 50 million light-years ...
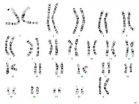
A link between Jacobsen syndrome and autism
2014-09-17
SAN DIEGO, Calif. (Sept. 17, 2014)— A rare genetic disorder known as Jacobsen syndrome has been linked with autism, according to a recent joint investigation by researchers at San Diego State University and the University of California, San Diego. In addition to suggesting better treatment options for people with Jacobsen syndrome, the finding also offers more clues into the genetic underpinnings of autism.
Jacobsen syndrome affects approximately 1 in 100,000 people, according to the National Institutes of Health. It occurs in a person when there is a deletion at the end ...
Lack of facial expression leads to perceptions of unhappiness, new OSU research shows
2014-09-17
CORVALLIS, Ore. – People with facial paralysis are perceived as being less happy simply because they can't communicate in the universal language of facial expression, a new study from an Oregon State University psychology professor shows.
The findings highlight the important role the face plays in everyday communication and indicates people may hold a prejudice against those with facial paralysis because of their disability, said Kathleen Bogart, an assistant professor of psychology in the College of Liberal Arts at Oregon State University.
"People are more wary and ...
Entrepreneurs aren't overconfident gamblers
2014-09-17
Leaving one's job to become an entrepreneur is inarguably risky. But it may not be the fear of risk that makes entrepreneurs more determined to succeed. A new study finds entrepreneurs are also concerned about what they might lose in the transition from steady employment to startup.
In Entrepreneurship and Loss-Aversion in a Winner-Take-All Society, Professor John Morgan at UC Berkeley's Haas School of Business and co-author Dana Sisak, assistant professor at the Erasmus University Rotterdam, focused on the powerful impact of loss aversion.
Loss aversion, or the fear ...
Oxides discovered by CCNY team could advance memory devices
2014-09-17
The quest for the ultimate memory device for computing may have just taken an encouraging step forward. Researchers at The City College of New York led by chemist Stephen O'Brien have discovered new complex oxides that exhibit both magnetic and ferroelectric properties.
Combining both properties is very exciting scientifically for the coupling that can occur between them and for the devices that might ultimately be designed, in logic circuits or spintronics. Combining these two properties in a single material, however, has proved difficult until now.
Using an innovative ...
Engineers develop algorithms to switch out and recharge battery modules in electric cars
2014-09-17
Imagine being able to switch out the batteries in electric cars just like you switch out batteries in a photo camera or flashlight. A team of engineers at the University of California, San Diego, are trying to accomplish just that, in partnership with a local San Diego engineering company.
They have developed smaller units within the battery, called modules, and a battery management system that will allow them to swap out and recharge the modules, rather than swapping out the whole battery, which is cumbersome and requires large, heavy equipment. They recently presented ...
US health system not properly designed to meet needs of patients nearing end of life, says IOM
2014-09-17
WASHINGTON -- The U.S. health care system is not properly designed to meet the needs of patients nearing the end of life and those of their families, and major changes to the system are necessary, says a new report from the Institute of Medicine. The 21-member committee that wrote the report envisioned an approach to end-of-life care that integrates traditional medical care and social services and that is high-quality, affordable, and sustainable. The committee called for more "advance care planning" for end-of-life by individuals, for improved training and credentialing ...
First blood test to diagnose depression in adults
2014-09-17
CHICAGO --- The first blood test to diagnose major depression in adults has been developed by Northwestern Medicine® scientists, a breakthrough approach that provides the first objective, scientific diagnosis for depression. The test identifies depression by measuring the levels of nine RNA blood markers. RNA molecules are the messengers that interpret the DNA genetic code and carry out its instructions.
The blood test also predicts who will benefit from cognitive behavioral therapy based on the behavior of some of the markers. This will provide the opportunity for more ...
Many throat cancer patients can skip neck surgery
2014-09-17
A new study shows that patients with human papillomavirus (HPV) – the same virus associated with both cervical and head and neck cancer – positive oropharyngeal cancer see significantly higher rates of complete response on a post-radiation neck dissection than those with HPV-negative oropharyngeal cancer. Fox Chase Cancer Center researchers presented the findings at the American Society for Radiation Oncology's 56th Annual Meeting on Wednesday, September 17.
"For patients that achieve a complete response, neck surgery is probably unnecessary," says Thomas J. Galloway, ...
Five genes to predict colorectal cancer relapses
2014-09-17
Researchers at the Catalan Institute of Oncology-Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (ICO-IDIBELL), led by David Garcia-Molleví have identified 5 genes differentially expressed in normal accompanying cells in colorectal tumors. Analysis of these genes could be used to classify colorectal tumors, predict the evolution of the patient and thus take appropriate clinical decisions to prevent relapses.
Biomarkers
Colorectal cancer is the most common in our population considering both sexes. About 30,000 new cases are diagnosed each year. Of these, approximately 70% are ...
Abnormal properties of cancer protein revealed in fly eyes
2014-09-17
EAST LANSING, Mich. – Mutations in the human retinoblastoma protein gene are a leading cause of eye cancer. Now, Michigan State University scientists have turned to fruit fly eyes to unlock the secrets of this important cancer gene.
In a paper featured on the cover of the current issue of the Journal of Biological Chemistry, Michigan State University researchers provide the first detailed examination of a set of mutations similar to those present in the human cancer gene, said Irina Pushel, MSU undergraduate and co-author.
"By systematically evaluating mutations of ...
Moffitt researchers help lead efforts to find new genetic links to prostate cancer
2014-09-17
Researchers at Moffitt Cancer Center, including Center Director Thomas A. Sellers, Ph.D., M.P.H., Jong Park, Ph.D. and Hui-Yi Lin, Ph.D., have discovered 23 new regions of the genome that influence the risk for developing prostate cancer, according to a study published Sept. 14 in Nature Genetics.
Prostate cancer is the most common non-skin cancer in American men. About 1 in 6 men will be diagnosed with the disease in his lifetime. Family history is the strongest risk factor. A man with one close relative, a brother or father with prostate cancer is twice as likely to ...
[1] ... [3333]
[3334]
[3335]
[3336]
[3337]
[3338]
[3339]
[3340]
3341
[3342]
[3343]
[3344]
[3345]
[3346]
[3347]
[3348]
[3349]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.