Being social: Learning from the behavior of birds
2014-09-17
VIDEO:
In this Science Minute from NIMBioS, Dr. Elizabeth Hobson explains what monk parakeets can teach us about complex sociality.
Click here for more information.
KNOXVILLE—Science has learned a great deal about complex social behavior by studying nonhuman mammals and primates, but parrots might have something to teach too.
With their unusually large brains relative to their body size and advanced cognition, parrots live in a complex social environment---not merely in ...
Malaysia's 'Smart Villages' and 9 other proven ideas for sustainable development
2014-09-17
As nations zero in on the UN's post-2015 global Sustainable Development Goals, innovations being successfully pioneered and demonstrated in Malaysia offer several proven tactical ideas for improving the world, says an influential international sustainable development networking organization.
The UN's Sustainable Development Solutions Network (SDSN), through its Malaysian chapter, cites ways in which the country is "rising to the challenge," including the construction of ingenious, self-sustaining "smart" villages -- each lifting about 100 families out of poverty and ...
New study examines the impact of socioeconomic position and maternal morbidity in Australia
2014-09-17
The risk of severe maternal morbidity amongst women in Australia is increased by lower socioeconomic position, suggests a new study published today (17 September) in BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology.
Australians generally enjoy high standards of living; however, existing research has concluded that health disparities exist, in particular between indigenous and non indigenous Australians.
This case-control study aimed to explore the independent impact of socioeconomic position on severe maternal morbidities associated with direct maternal ...
Global change: Trees continue to grow at a faster rate
2014-09-17
Trees have been growing significantly faster since the 1960s. The typical development phases of trees and stands have barely changed, but they have accelerated -- by as much as 70 percent. This was the outcome of a study carried out by scientists from Technische Universität München based on long-term data from experimental forest plots that have been continuously observed since 1870. Their findings were published recently in Nature Communications.
Three decades ago, "forest dieback" was a hot topic, with the very survival of large forest ecosystems seemingly in doubt. ...
Nanoscience makes your wine better
2014-09-17
One sip of a perfectly poured glass of wine leads to an explosion of flavours in your mouth. Researchers at Aarhus University, Denmark, have now developed a nanosensor that can mimic what happens in your mouth when you drink wine. The sensor measures how you experience the sensation of dryness in the wine.
When wine growers turn their grapes into wine, they need to control a number of processes to bring out the desired flavour in the product that ends up in the wine bottle. An important part of the taste is known in wine terminology as astringency, and it is characteristic ...
The mobility model is closely linked to the city's characteristics
2014-09-17
This news release is available in Spanish and Spanish.
As far as the conclusions of the study are concerned, the following aspects, among others, are worth highlighting: the more compact the town or city is, the more concentrated is its population; the more jobs there are in the municipality itself, etc., the less private vehicles are used; the better the offer of public transport, the lower the number of people who use private cars; the higher the per capita income is (in small localities), the greater is the tendency to use the private car. According to Mendiola, ...
Magnetic resonance helps to detect and quantify fat in liver
2014-09-17
This news release is available in Spanish.
Obesity and overweight affect more than half of the population in our Community. Excess weight causes important alterations in the organism, one of which affects liver function. Fat accumulates in the liver producing hepatic steatosis which, in certain circumstances, causes inflammation, fibrosis and finally, cirrhosis. To date, the most reliable method for determining hepatic fat has been hepatic biopsy. Imaging techniques such as abdominal ecography detect it but are less precise for determining the quantity of fat.
But ...
Car hacking: The security threat facing our vehicles
2014-09-17
The car of the future will be safer, smarter and offer greater high-tech gadgets, but be warned without improved security the risk of car hacking is real, according to a QUT road safety expert.
Professor Andry Rakotonirainy will speak at the Occupational Safety in Transport Conference (OSIT) on the Gold Coast on September 18-19 on the security threat facing drivers as vehicles become computers on wheels.
Professor Rakotonirainy, from QUT's Centre for Accident Research & Road Safety - Queensland (CARRS), has researched the security systems of existing fleet, future ...
Survey finds benefits, risks of yoga for bipolar disorder
2014-09-17
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Right now no one can say whether yoga provides clinical benefits to people with bipolar disorder, but in a new article in the Journal of Psychiatric Practice, researchers report survey responses they gathered from scores of people with the condition who practice yoga. What the collective testimony suggests is that yoga can be a substantial help, but it sometimes carries risks, too.
"There is no scientific literature on hatha yoga for bipolar disorder," said lead author Lisa Uebelacker, associate professor (research) of psychiatry ...
Cape Cod saltmarsh recovery looks good, falls short
2014-09-17
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — After decades of decline, grasses have returned to some once-denuded patches of Cape Cod's saltmarshes. To the eye, the marsh in those places seems healthy again, but a new study makes clear that a key service of the marsh – coastal protection – remains diminished.
"We've got the aesthetics back but the ecosystem function hasn't come back," said ecologist Mark Bertness, professor of biology at Brown and senior author of the study in the journal Biological Conservation. "The metric of a recovered habitat should not be 'Does it look ...
Recruiting bacteria to be technology innovation partners
2014-09-17
For most people biofilms conjure up images of slippery stones in a streambed and dirty drains. While there are plenty of "bad" biofilms around – they even cause pesky dental plaque and a host of other more serious medical problems – a team at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University sees biofilms as a robust new platform for designer nanomaterials that could clean up polluted rivers, manufacture pharmaceutical products, fabricate new textiles, and more.
In short, they want to give biofilms a facelift, and have developed a novel protein ...
Phthalates heighten risk for childhood asthma
2014-09-17
Researchers at the Columbia Center for Children's Environmental Health at the Mailman School of Public Health are the first to demonstrate an association between childhood asthma and prenatal exposure to two phthalates used in a diverse array of household products. Results appear online in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives.
Children born to mothers exposed during pregnancy to higher levels of the chemicals, butylbenzyl phthalate (BBzP) and di-n-butyl phthalate (DnBP) had a 72 percent and 78 percent increase in risk of developing asthma between age 5 and 11, ...
New study examines the impact of socioeconomic position & maternal morbidity in Australia
2014-09-17
The risk of severe maternal morbidity amongst women in Australia is increased by lower socioeconomic position, suggests a new study published today (17 September) in BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology.
Australians generally enjoy high standards of living; however, existing research has concluded that health disparities exist, in particular between indigenous and non indigenous Australians.
This case-control study aimed to explore the independent impact of socioeconomic position on severe maternal morbidities associated with direct maternal ...
A greater focus on socially disadvantaged women is needed to improve maternity care in England
2014-09-17
Women from lower socioeconomic groups in the UK report a poorer experience of care during pregnancy and there needs to be a greater focus on their care, suggests a new study published today (17 September) in BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology (BJOG).
Differences in health outcomes amongst different socioeconomic groups have been demonstrated in many areas and have provided the focus for national initiatives in the UK to reduce the observed inequalities.
The Oxford University study, funded by the National Institute for Health Research, explores ...
NAMS issues first comprehensive recommendations on care of women at menopause and beyond
2014-09-17
CLEVELAND, Ohio (September 17, 2014)—The North American Menopause Society (NAMS) has published its key, evidence-based recommendations for the comprehensive care of midlife women—on everything from hot flashes to heart disease. The special feature, "The North American Menopause Society Recommendations for Clinical Care of Midlife Women," was published online today in the Society's journal Menopause. This is the first, comprehensive set of evidence-based recommendations for the care of midlife women freely available to all clinicians who care for women at this stage of life. ...
Sharks' skin has teeth in the fight against hospital superbugs
2014-09-17
Transmission of bacterial infections, including MRSA and MSSA could be curbed by coating hospital surfaces with microscopic bumps that mimic the scaly surface of shark skin, according to research published in the open access journal Antimicrobial Resistance and Infection Control.
The study modelled how well different materials prevented the spread of human disease bacteria through touching, sneezes or spillages. The micropattern, named Sharklet™, is an arrangement of ridges formulated to resemble shark skin. The study showed that Sharklet harboured 94% less MRSA bacteria ...
Violent origins of disc galaxies probed by ALMA
2014-09-17
An international research group led by Junko Ueda, a Japan Society for the Promotion of Science postdoctoral fellow, has made surprising observations that most galaxy collisions in the nearby Universe — within 40 million light-years from Earth — result in so-called disc galaxies. Disc galaxies — including spiral galaxies like the Milky Way and lenticular galaxies — are defined by pancake-shaped regions of dust and gas, and are distinct from the category of elliptical galaxies.
It has, for some time, been widely accepted that merging disc galaxies would eventually form ...
Global shift away from cars saves US$100 trillion, eliminates 1,700 MT of CO2 pollution
2014-09-17
NEW YORK (17 September, 2014)—More than $100 trillion in cumulative public and private spending, and 1,700 megatons of annual carbon dioxide (CO2)—a 40 percent reduction of urban passenger transport emissions—could be eliminated by 2050 if the world expands public transportation, walking and cycling in cities, according to a new report released by the University of California, Davis, and the Institute for Transportation and Development Policy (ITDP).
Further, an estimated 1.4 million early deaths could be avoided annually by 2050 if governments require the strongest ...
'Smart material' chin strap harvests energy from chewing
2014-09-17
A chin strap that can harvest energy from jaw movements has been created by a group of researchers in Canada.
It is hoped that the device can generate electricity from eating, chewing and talking, and power a number of small-scale implantable or wearable electronic devices, such as hearing aids, cochlear implants, electronic hearing protectors and communication devices.
The first results of the device's performance have been published today, 17 September, in IOP Publishing's journal Smart Materials and Structures.
Jaw movements have proved to be one of the most promising ...
World Alzheimer Report 2014 reveals persuasive evidence for dementia risk reduction
2014-09-17
The World Alzheimer Report 2014 'Dementia and Risk Reduction: An analysis of protective and modifiable factors', released today, calls for dementia to be integrated into both global and national public health programmes alongside other major non communicable diseases (NCDs).
Alzheimer's Disease International (ADI) commissioned a team of researchers, led by Professor Martin Prince from King's College London, to produce the report. ADI is publishing this report, in conjunction with World Alzheimer's Day™ (21 September) and as a part of World Alzheimer's Month, an international ...
Diabetes complications make patients more likely to fall down stairs
2014-09-17
New research presented at this year's annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Vienna, Austria, shows that people suffering from diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN)—a complication of diabetes that affects the nerves in the limbs—are likely to sway more during stair climbing, and thus are more likely to fall. Steven Brown, Manchester Metropolitan University, UK, is the lead author on this research, which has been conducted by researchers at Manchester Metropolitan University and the University of Manchester, UK.
Patients with DPN ...
Study shows users of insulin pumps are at 29 percent lower risk of death compared with patients on insulin injections
2014-09-17
A study of more than 18,000 patients with type 1 diabetes has shown that use of insulin pumps to administer insulin rather than treatment with multiple daily insulin injections results in a 29% reduction in all-cause mortality and 43% reduction in the risk of fatal cardiovascular disease (CVD, i.e. coronary heart disease or stroke). The study is presented at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes in Vienna, Austria, and was prepared by Dr Soffia Gudbjörnsdottir, University of Gothenburg, Sweden and colleagues.
Insulin pump treatment (CSII ...
The Lancet: Scientists use modern forensic techniques to identify most likely cause of King Richard III's death
2014-09-17
New research led by the University of Leicester in the UK gives a blow-by-blow account of the injuries inflicted on King Richard III's body at the Battle of Bosworth Field on Aug 22, 1485. Modern forensic analysis of the King's skeletal remains reveals that three of his injuries had the potential to cause death quickly—two to the skull (page 4, figure 4) and one to the pelvis (page 5, figure 6).
The remains of King Richard III—the last English monarch to die in battle—were found under a car park in Leicester by archaeologists from the University of Leicester, and subsequently ...
Urine HPV test could offer non-invasive alternative to conventional smear, improve screening uptake
2014-09-17
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections. Up to 80% of sexually active women are infected at some point in their lives and infection with specific "high risk" strains of HPV has an established link to cervical cancer.
Current screening by cervical cytology (smear test) is invasive and time-consuming - and in recent years, cervical screening in the UK has fallen below 80%, particularly amongst women aged 25-30. Several studies have suggested that detecting HPV in urine may be a feasible alternative to cervical sampling, but the ...
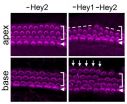
Hey1 and Hey2 ensure inner ear 'hair cells' are made at the right time, in the right place
2014-09-17
Two Johns Hopkins neuroscientists have discovered the "molecular brakes" that time the generation of important cells in the inner ear cochleas of mice. These "hair cells" translate sound waves into electrical signals that are carried to the brain and are interpreted as sounds. If the arrangement of the cells is disordered, hearing is impaired.
A summary of the research will be published in The Journal of Neuroscience on Sept. 16.
"The proteins Hey1 and Hey2 act as brakes to prevent hair cell generation until the time is right," says Angelika Doetzlhofer, Ph.D., an ...
[1] ... [3335]
[3336]
[3337]
[3338]
[3339]
[3340]
[3341]
[3342]
3343
[3344]
[3345]
[3346]
[3347]
[3348]
[3349]
[3350]
[3351]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.